Abstract
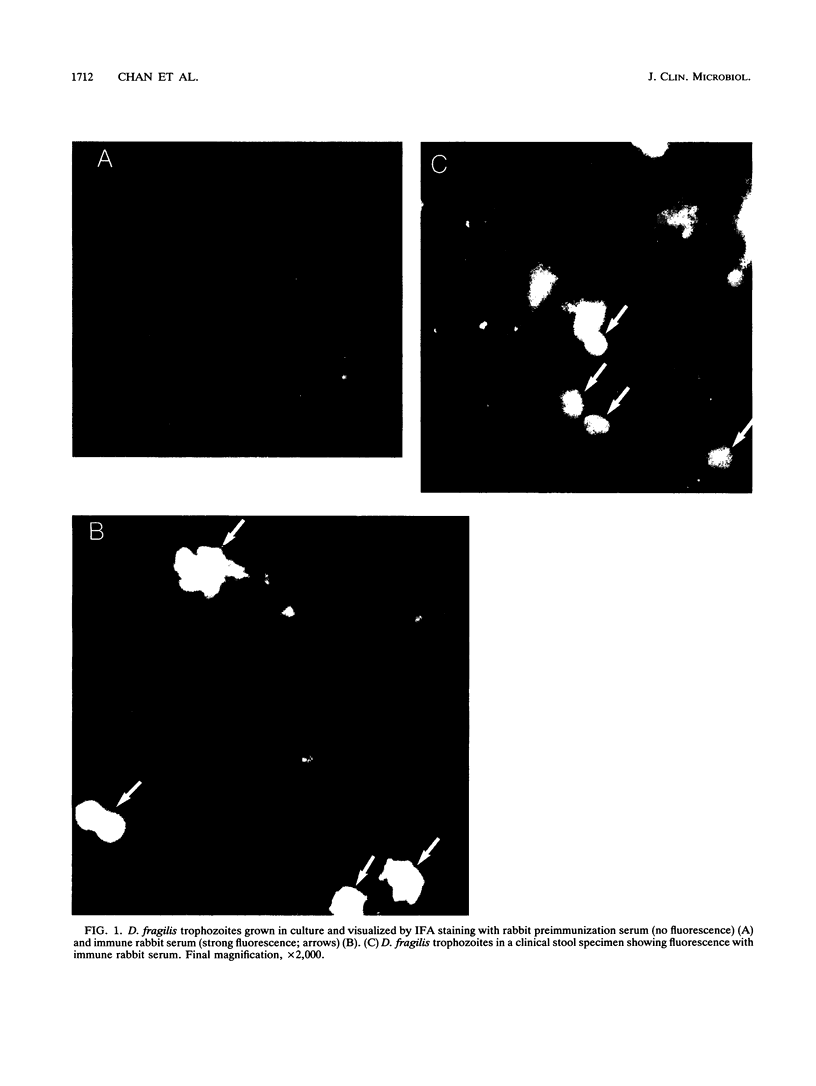
An indirect fluorescent-antibody (IFA) assay was carried out to examine for the presence of Dientamoeba fragilis trophozoites in preserved fecal specimens. Antiserum to D. fragilis trophozoites was raised in a rabbit with a dixenic culture of D. fragilis (ATCC 30948) from the American Type Culture Collection. After absorption with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Bacteroides vulgatus, the immune rabbit serum was used for examination by the IFA assay. A total of 155 clinical samples were tested; 42 with no parasites, 9 with D. fragilis, and 104 with other parasites. The IFA assay identified seven D. fragilis organisms. Two specimens with doubtful IFA assay readings showed very scanty amounts of D. fragilis trophozoites on stained smears. There were no false-positive IFA assay readings. The IFA assay appeared to be a promising method because of its speed in screening. The specificity of the IFA assay indicates that other diagnostic tests such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay could be developed to identify D. fragilis antigens in fecal specimens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURROWS R. B., SWERDLOW M. A. Enterobius vermicularis as a probable vector of Dientamoeba fragilis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Mar;5(2):258–265. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1956.5.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner D. A., Garcia L. S., Voge M. Intestinal parasites in Los Angeles, California. Am J Med Technol. 1979 Dec;45(12):1020–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Improved method for the monoxenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae with trypanosomatids. J Parasitol. 1968 Aug;54(4):715–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. M. Analysis of the antigenic relationships among Trichomonas, Histomonas, Dientamoeba, and Entamoeba. I. Quantitative fluorescent antibody methods. J Protozool. 1972 May;19(2):316–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1972.tb03467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. M. Analysis of the antigenic relationships among Trichomonas, Histomonas, Dientamoeba, and Entamoeba. II. Gel diffusion methods. J Protozool. 1972 May;19(2):326–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1972.tb03468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia L. S., Brewer T. C., Bruckner D. A. Fluorescence detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts in human fecal specimens by using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):119–121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.119-121.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grendon J. H., Digiacomo R. F., Frost F. J. Dientamoeba fragilis detection methods and prevalence: a survey of state public health laboratories. Public Health Rep. 1991 May-Jun;106(3):322–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean B. H., Malloch C. L. The neglected ameba: dientamoeba fragilis. A report of 100 "pure" infections. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Sep;11(9):735–746. doi: 10.1007/BF02239427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine N. D., Corliss J. O., Cox F. E., Deroux G., Grain J., Honigberg B. M., Leedale G. F., Loeblich A. R., 3rd, Lom J., Lynn D. A newly revised classification of the protozoa. J Protozool. 1980 Feb;27(1):37–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.tb04228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millet V., Spencer M. J., Chapin M., Stewart M., Yatabe J. A., Brewer T., Garcia L. S. Dientamoeba fragilis, a protozoan parasite in adult members of a semicommunal group. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Apr;28(4):335–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01324950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff J. D., Sanders C. A., Sonnad S. S., De Lay P. R., Hadley W. K., Vincenzi F. F., Yajko D. M., O'Hanley P. D. Stool diagnosis of giardiasis using a commercially available enzyme immunoassay to detect Giardia-specific antigen 65 (GSA 65). J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):1997–2002. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.1997-2002.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWERDLOW M. A., BURROWS R. B. Dientamoeba fragilis, an intestinal pathogen. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 May 21;158(3):176–178. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02960030026008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholten T. H., Yang J. Evaluation of unpreserved and preserved stools for the detection and identification of intestinal parasites. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Oct;62(4):563–567. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shein R., Gelb A. Colitis due to Dientamoeba fragilis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983 Oct;78(10):634–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. J., Chapin M. R., Garcia L. S. Dientamoeba fragilis: a gastrointestinal protozoan infection in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 1982 Aug;77(8):565–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. J., Garcia L. S., Chapin M. R. Dientamoeba fragilis. An intestinal pathogen in children? Am J Dis Child. 1979 Apr;133(4):390–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz H., Talis B., Stein B. Entamoeba histolytica and Dientamoeba fragilis and the syndrome of chronic recurrent intestinal amoebiasis in Israel. Digestion. 1970;3(3):146–153. doi: 10.1159/000197025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbs H. H. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme immunoassay for Giardia lamblia antigen in human stool. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2582–2588. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2582-2588.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talis B., Stein B., Lengy J. Dientamoeba fragilis in human feces and bile. Isr J Med Sci. 1971 Sep;7(9):1063–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Scholten T. A fixative for intestinal parasites permitting the use of concentration and permanent staining procedures. Am J Clin Pathol. 1977 Mar;67(3):300–304. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/67.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Scholten T. Dientamoeba fragilis: a review with notes on its epidemiology, pathogenicity, mode of transmission, and diagnosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jan;26(1):16–22. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. H., Bullock S. L., Melvin D. M., Spruill C. L. Ethyl acetate as a substitute for diethyl ether in the formalin-ether sedimentation technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):852–853. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.852-853.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H. Blastocystis hominis--past and future. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):61–79. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]