Abstract
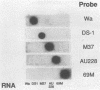
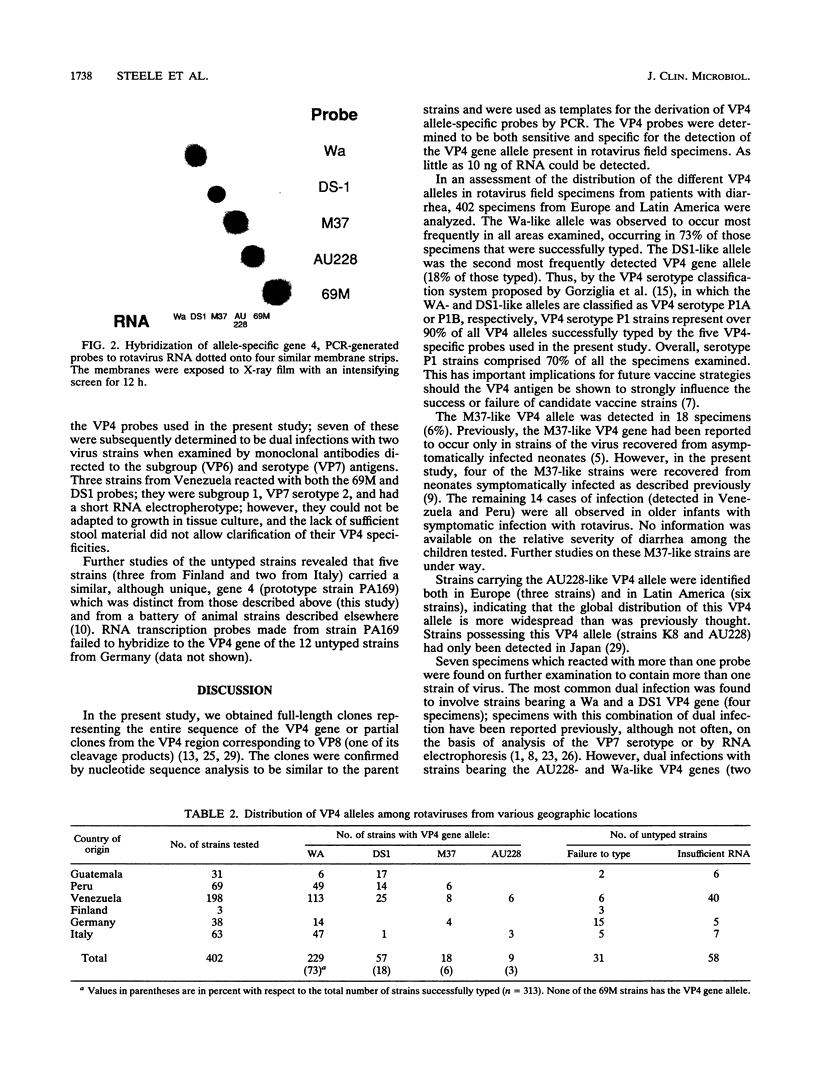
The rotavirus VP4 protein elicits the production of neutralizing antibodies and is known to play a role in inducing resistance to disease. At least five human rotavirus VP4 gene alleles have been described on the basis of antigenic polymorphism and/or nucleotide sequence differences. In the present study, we developed cDNA probes directed at the hyperdivergent region of the VP4 gene of the five described human rotavirus VP4 alleles (Wa, DS1, M37, AU228, and 69M) and used them in hybridization assays with human rotavirus strains from Latin America and Europe to determine the distribution of the VP4 gene alleles in nature. The Wa-like allele was detected most frequently, occurring in 57% of the 402 rotavirus strains tested, and the DS1-like allele was the next most common, occurring in 14% of the strains tested. The M37- and AU228-like alleles were detected in only 4 and 3% of the rotavirus strains tested, respectively, whereas the 69M-like VP4 gene allele was not detected. Several rotavirus strains from Europe did not react with any of the VP4 gene probes, although they did hybridize to a probe generated from a representative strain from the group. These data indicate the global distribution of various VP4 gene alleles and raise the possibility that other, unrecognized human VP4 alleles exist in nature because almost one-fourth of the strains could not be classified into any of the established VP4 groups.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M. U., Taniguchi K., Kobayashi N., Urasawa T., Wakasugi F., Islam M., Shaikh H., Urasawa S. Characterization by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using subgroup- and serotype-specific monoclonal antibodies of human rotavirus obtained from diarrheic patients in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1678–1681. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1678-1681.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Green K. Y., Garcia D., Sears J., Perez-Schael I., Avendaño L. F., Rodriguez W. B., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z. Dot hybridization assay for distinction of rotavirus serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.29-34.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Green K., Gorziglia M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Conservation of the fourth gene among rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic newborn infants and its possible role in attenuation. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):972–979. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.972-979.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Myslinski J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. In vitro transcription of two human rotaviruses. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1032–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1032-1037.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Blanco M., Vilar M., Garcia D., Perez M., Daoud N., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z. Reactions to and antigenicity of two human-rhesus rotavirus reassortant vaccine candidates of serotypes 1 and 2 in Venezuelan infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):512–518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.512-518.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Taniguchi K., Green K., Perez-Schael I., Garcia D., Sears J., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z. Relative frequencies of rotavirus serotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4 in Venezuelan infants with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2092–2095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2092-2095.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Forster J., Parea M., Sarasini A., Di Matteo A., Baldanti F., Langosch B., Schmidt S., Battaglia M. Nosocomial outbreak of neonatal gastroenteritis caused by a new serotype 4, subtype 4B human rotavirus. J Med Virol. 1990 Jul;31(3):175–182. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Di Matteo A., Zentilin L., Miranda P., Parea M., Baldanti F., Arista S., Milanesi G., Battaglia M. Serotype 3 human rotavirus strains with subgroup I specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1342–1347. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1342-1347.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Parea M., Arista S., Miranda P., Brüssow H., Hoshino Y., Flores J. Isolation and characterization of two distinct human rotavirus strains with G6 specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.9-16.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Sarasini A., Zentilin L., Di Matteo A., Miranda P., Parea M., Battaglia M., Milanesi G. Isolation in Europe of 69 M-like (serotype 8) human rotavirus strains with either subgroup I or II specificity and a long RNA electropherotype. Arch Virol. 1990;112(1-2):27–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01348983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Green K., Nishikawa K., Taniguchi K., Jones R., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Sequence of the fourth gene of human rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic or symptomatic infections. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2978–2984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2978-2984.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Hoshino Y., Buckler-White A., Blumentals I., Glass R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Conservation of amino acid sequence of VP8 and cleavage region of 84-kDa outer capsid protein among rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic neonatal infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Larralde G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Antigenic relationships among human rotaviruses as determined by outer capsid protein VP4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7155–7159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Taniguchi K., Mackow E. R., Kapikian A. Z. Homotypic and heterotypic epitope-specific antibody responses in adult and infant rotavirus vaccinees: implications for vaccine development. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):667–679. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic characterization of rotaviruses derived from asymptomatic human neonatal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):425–430. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.425-430.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larralde G., Flores J. Identification of gene 4 alleles among human rotaviruses by polymerase chain reaction-derived probes. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):469–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90317-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E. R., Shaw R. D., Matsui S. M., Vo P. T., Dang M. N., Greenberg H. B. The rhesus rotavirus gene encoding protein VP3: location of amino acids involved in homologous and heterologous rotavirus neutralization and identification of a putative fusion region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):645–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Katsushima N., Nakagomi O. Relative frequency of human rotavirus subgroups I and II in relation to "short" and "long" electrophoretypes of viral RNA. Ann Inst Pasteur Virol. 1988 Jul-Sep;139(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2617(88)80043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Shaw R. D., Greenberg H. B. Passive protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea by monoclonal antibodies to surface proteins vp3 and vp7. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.700-703.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y., Green K. Y. Human rotavirus strain 69M has a unique VP4 as determined by amino acid sequence analysis. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90691-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. D., Merson M. H. The magnitude of the global problem of acute diarrhoeal disease: a review of active surveillance data. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(4):605–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Maloy W. L., Nishikawa K., Green K. Y., Hoshino Y., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Gorziglia M. Identification of cross-reactive and serotype 2-specific neutralization epitopes on VP3 of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2421–2426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2421-2426.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Nishikawa K., Urasawa T., Urasawa S., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z., Gorziglia M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding VP4 of a human rotavirus (strain K8) which has unique VP4 neutralization epitopes. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4101–4106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4101-4106.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]