Abstract
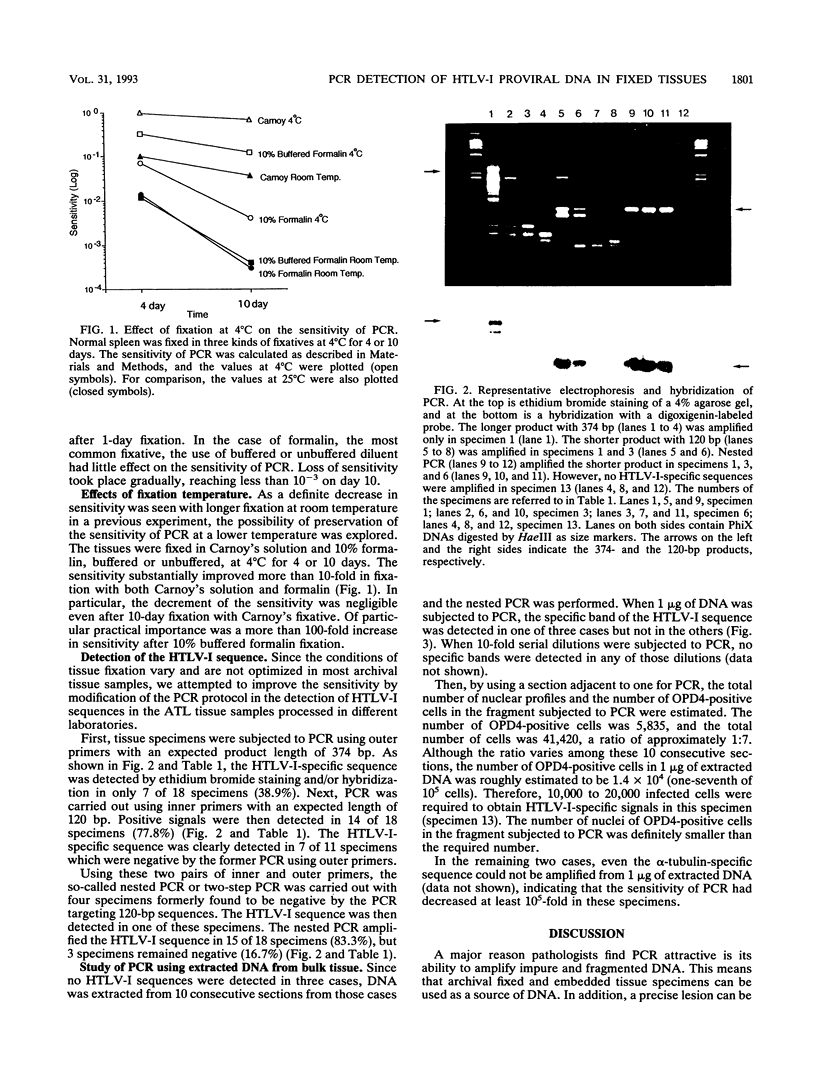
In this study, the fixation condition most suitable for maintaining the sensitivity of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was investigated by using the alpha-tubulin gene sequence, and the PCR procedure most effective for detecting human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) proviral sequences in fixed, embedded tissues of adult T-cell leukemia patients was explored. First, the sensitivity of the PCR targeting a 286-bp alpha-tubulin sequence was studied in tissue sections fixed in several fixatives for various periods at 25 or 4 degrees C. For histological examination, fixation with 10% buffered formalin at a lower temperature for a shorter period was found to be preferable to retain the sensitivity. And the HTLV-I sequence was detected in only 7 of 18 specimens (38.9%) when the 374-bp sequence of the gag region was targeted, but the rate increased to 77.8% (14 of 18 specimens) when the length of the target sequence was reduced to 120 bp within the same region. Therefore, the one-round PCR targeting a shorter sequence is preferable for application of PCR to archival fixed tissue specimens, the fixation condition of which may not be ideal for DNA preservation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J., Fenyö E. M. Simple, sensitive, and specific detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in clinical specimens by polymerase chain reaction with nested primers. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1560–1564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1560-1564.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates P. J., d'Ardenne A. J., Khan G., Kangro H. O., Slavin G. Simplified procedures for applying the polymerase chain reaction to routinely fixed paraffin wax sections. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Feb;44(2):115–118. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.2.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Dobner P. R., Fuchs E. V., Cleveland D. W. Expression of human alpha-tubulin genes: interspecies conservation of 3' untranslated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelz S. E., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B. Purification of DNA from formaldehyde fixed and paraffin embedded human tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 16;130(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Impraim C. C., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Teplitz R. L. Analysis of DNA extracted from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues by enzymatic amplification and hybridization with sequence-specific oligonucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):710–716. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. P., Lewis F. A., Taylor G. R., Boylston A. W., Quirke P. Tissue extraction of DNA and RNA and analysis by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jun;43(6):499–504. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.6.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi I., Kubonishi I., Yoshimoto S., Shiraishi Y. A T-cell line derived from normal human cord leukocytes by co-culturing with human leukemic T-cells. Gan. 1981 Dec;72(6):978–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara Y., Honma M., Iwasaki Y. Sensitivity of the polymerase chain reaction for detecting human T-cell leukemia virus type I sequences in paraffin-embedded tissue. Effect of unbuffered formalin fixation. J Virol Methods. 1992 Apr;37(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. H., Edwards A. J., Cruickshank J. K., Rudge P., Dalgleish A. G. In vivo cellular tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5682–5687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5682-5687.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers B. B., Alpert L. C., Hine E. A., Buffone G. J. Analysis of DNA in fresh and fixed tissue by the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):541–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata D. K., Arnheim N., Martin W. J. Detection of human papilloma virus in paraffin-embedded tissue using the polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):225–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino T., Mukuzono H., Aoki H., Takahashi K., Takeuchi T., Kubonishi I., Ohtsuki Y., Motoi M., Akagi T. A novel monoclonal antibody (OPD4) recognizing a helper/inducer T cell subset. Its application to paraffin-embedded tissues. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1339–1346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Franchis R., Cross N. C., Foulkes N. S., Cox T. M. A potent inhibitor of Taq polymerase copurifies with human genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10355–10355. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]