Abstract
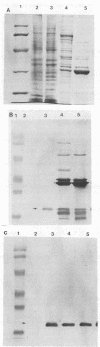
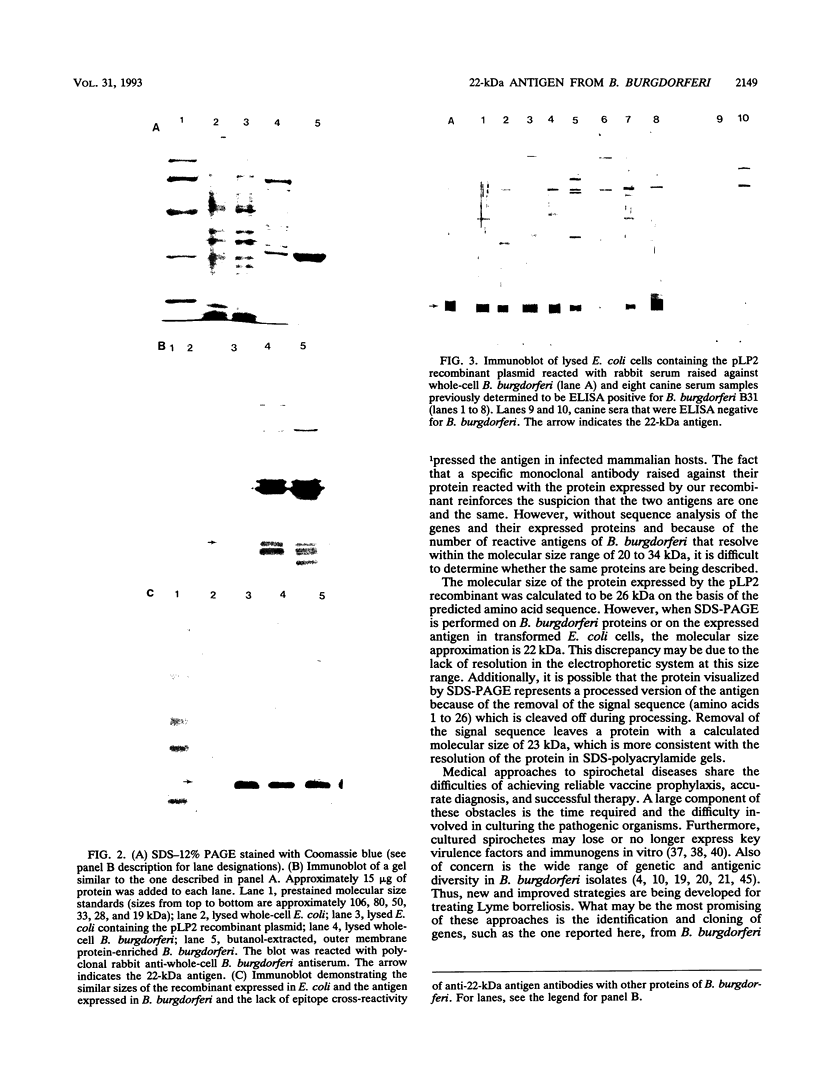
The sequence and characterization of a chromosomal gene from the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi and the antigen it encodes are described. The gene was cloned and expressed in transformed Escherichia coli cells. The gene is composed of 597 bases and expresses a predicted protein of 199 amino acids. Antibodies specific for the recombinant antigen reacted with a single B. burgdorferi protein with a molecular mass of approximately 22 kDa. The protein was not susceptible to proteinase digestion but was extracted by n-butanol phase partitioning, suggesting a periplasmic location of the antigen. Sera from humans and canines seropositive for B. burgdorferi reacted with the recombinant antigen. The antigen characterized in this report appears to be immunologically significant in naturally infected hosts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Stoenner H. G. Variable major proteins of Borrellia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1312–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L., Hill W. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi strains isolated from Ixodes pacificus ticks in California. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2296–2301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2296-2301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Characterization of antigenic determinants of Borrelia burgdorferi shared by other bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;165(4):658–666. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.4.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Seamans C., Lomedico P., McAndrew S. Versatile expression vectors for high-level synthesis of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Jauris S., Lottspeich F., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Soutschek E. Molecular analysis and expression of a Borrelia burgdorferi gene encoding a 22 kDa protein (pC) in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gondolf K. B., Batsford S. R., Vogt A. Isolation of an outer membrane protein complex from Borrelia burgdorferi by n-butanol extraction and high-performance ion-exchange chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1990 Nov 23;521(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(90)85056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., LaQuier F. W., Barbour A. G. Organization of genes encoding two outer membrane proteins of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi within a single transcriptional unit. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Mayer L. W., Barbour A. G. A single recombinant plasmid expressing two major outer surface proteins of the Lyme disease spirochete. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):645–646. doi: 10.1126/science.3969554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W., Luft B. J., Munoz P., Dattwyler R. J., Gorevic P. D. Cross-antigenicity between the major surface proteins (ospA and ospB) and other proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Pascocello J. A. Antigenic characteristics of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates from ixodid ticks in California. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2344–2349. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2344-2349.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Lane R. S., Perng G. C., Brown J. A., Johnson R. C. DNA and protein analyses of tick-derived isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi from California. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.700-707.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):636–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.636-639.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. The 83-kilodalton antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi which stimulates immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG responses in infected hosts is expressed by a chromosomal gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1673–1675. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1673-1675.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Jiang W., Munoz P., Dattwyler R. J., Gorevic P. D. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3637–3645. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3637-3645.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Borrelia: a comparison of North American and European isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):241–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.241-244.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Lubke L., Hauglum W., Garon C. F. Species-specific identification of and distinction between Borrelia burgdorferi genomic groups by using 16S rRNA-directed oligonucleotide probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.628-632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perng G. C., LeFebvre R. B. Expression of antigens from chromosomal and linear plasmid DNA of Borrelia coriaceae. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1744–1748. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1744-1748.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perng G. C., LeFebvre R. B., Johnson R. C. Further characterization of a potent immunogen and the chromosomal gene encoding it in the Lyme disease agent, Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2070–2074. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2070-2074.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic D., Edlinger C., Richaud C., Grimont F., Dufresne Y., Perolat P., Baranton G., Grimont P. A. Two genomic species in Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1990 May;141(4):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Hogan D., Schwan T. G. Polymerase chain reaction analyses identify two distinct classes of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):524–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.524-532.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T. G. A specific and sensitive assay for the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Burgdorfer W., Schrumpf M. E., Karstens R. H., Schwan T. G. Antibody to a 39-kilodalton Borrelia burgdorferi antigen (P39) as a marker for infection in experimentally and naturally inoculated animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):236–243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.236-243.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Garon C. F., Schwan T. G. Analysis of supercoiled circular plasmids in infectious and non-infectious Borrelia burgdorferi. Microb Pathog. 1990 Feb;8(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., Schrumpf M. E., Hayes S. F., Schwan T. G. Molecular and immunological analysis of a polymorphic periplasmic protein of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1940–1948. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1940-1948.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]