Abstract
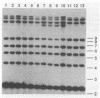
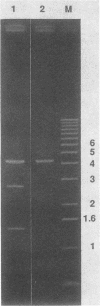
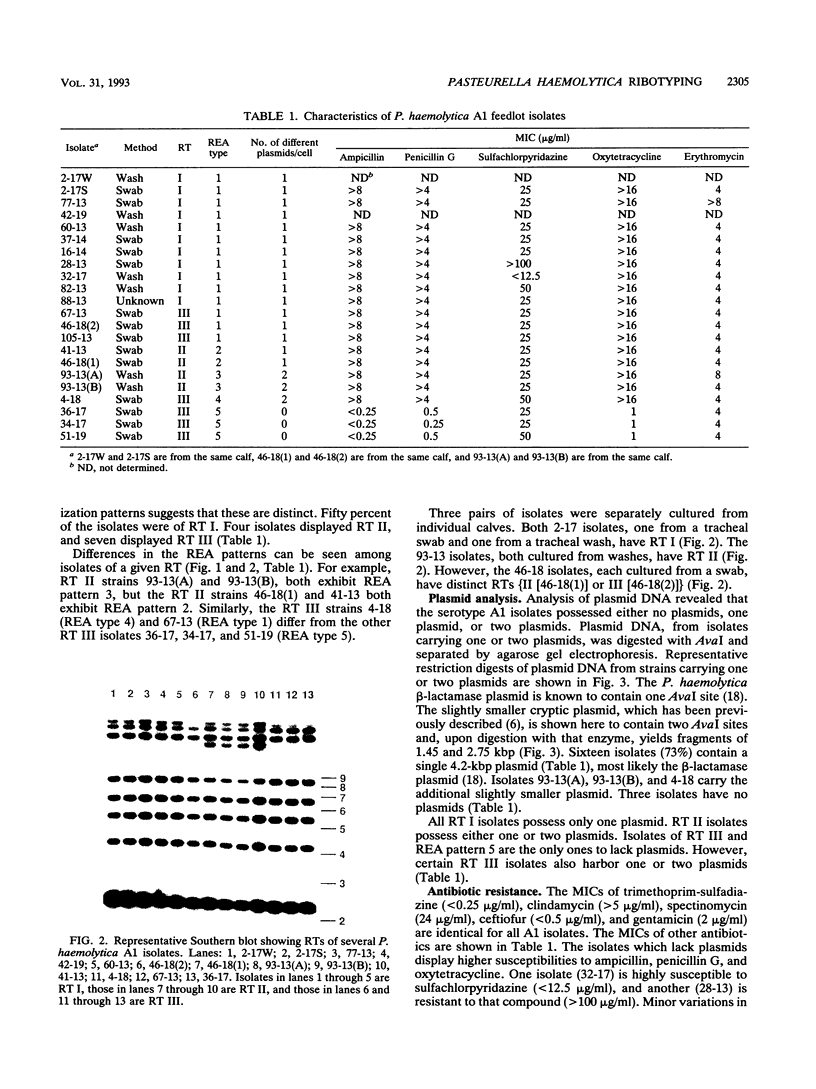
Pasteurella haemolytica serotype A1 isolates were collected from cattle within a feedlot during an outbreak of bovine respiratory disease. Genetic heterogeneity among the isolates was examined by restriction endonuclease analysis (REA), ribotyping, and analysis of plasmid content. The susceptibilities of isolates to several antibiotics were also examined. Five different REA patterns and three different ribotypes were observed among the isolates. Fifty percent of the isolates had an identical REA type, ribotype, and plasmid profile. Examination of the plasmid content of the isolates revealed that most (73%) carry a single plasmid which encodes beta-lactamase, 13.5% carry two plasmids, and 13.5% carry no plasmid. The data reveal the presence of genetic differences among isolates of P. haemolytica A1, associated with shipping fever pneumonia within a closed feedlot, and suggest that a combination of REA, ribotyping, plasmid analysis, and antibiotic susceptibility determination will be useful in analyzing the molecular epidemiology of this disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar N., Eley A. Restriction endonuclease analysis and ribotyping differentiate genital and nongenital strains of Bacteroides ureolyticus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2408–2414. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2408-2414.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altwegg M., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns provide increased sensitivity for typing Salmonella typhi strains. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):145–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H. M., Stephens D. S., Licitra C., Pigott N., Facklam R., Swaminathan B., Wachsmuth I. K. Molecular epidemiology of group B streptococcal infections: use of restriction endonuclease analysis of chromosomal DNA and DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms of ribosomal RNA genes (ribotyping). J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):574–579. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. R., Morter R. L. Plasmid profile analysis of bovine isolates of Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jun;47(6):1204–1206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson D. G. Calf pneumonia. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1985 Jul;1(2):237–257. doi: 10.1016/S0749-0720(15)31326-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. H., Carter G. R. Multiple drug resistance in Pasteurella multocida and Pasteurella haemolytica from cattle and swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Oct 1;169(7):710–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Renshaw H. W., Young R. Pneumonic pasteurellosis: examination of typable and untypable Pasteurella haemolytica strains for leukotoxin production, plasmid content, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst F. E., Paster B. J., Olsen I., Fraser G. J. Phylogeny of 54 representative strains of species in the family Pasteurellaceae as determined by comparison of 16S rRNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):2002–2013. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.2002-2013.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I. New molecular techniques for microbial epidemiology and the diagnosis of infectious diseases. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):595–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Wessman G. E. Rapid plate agglutination procedure for serotyping Pasteurella haemolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):142–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.142-145.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izard N. C., Hächler H., Grehn M., Kayser F. H. Ribotyping of coagulase-negative staphylococci with special emphasis on intraspecific typing of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):817–823. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.817-823.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livrelli V., Peduzzi J., Joly B. Sequence and molecular characterization of the ROB-1 beta-lactamase gene from Pasteurella haemolytica. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):242–251. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinetti Lucchini G., Altwegg M. rRNA gene restriction patterns as taxonomic tools for the genus Aeromonas. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):384–389. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. L., Dallas W. S. Analysis of two genes encoding heat-labile toxins and located on a single Ent plasmid from Escherichia coli. Gene. 1991 Jul 15;103(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90388-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy C. W., Scanlan C. M., Loan R. W., Foster G. S. Identification of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 isolates from market-stressed feeder calves by use of enzyme and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles. Am J Vet Res. 1993 Jan;54(1):92–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmanith S. E., Wilt G. R., Wu G. Characterization and comparison of antimicrobial susceptibilities and outer membrane protein and plasmid DNA profiles of Pasteurella haemolytica and certain other members of the genus Pasteurella. Am J Vet Res. 1991 Dec;52(12):2016–2022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian S. K., Woods T. C., Knapp J. S., Swaminathan B., Morse S. A. Molecular characterization of Haemophilus ducreyi by ribosomal DNA fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1949–1954. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1949-1954.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snipes K. P., Hirsh D. C., Kasten R. W., Hansen L. M., Hird D. W., Carpenter T. E., McCapes R. H. Use of an rRNA probe and restriction endonuclease analysis to fingerprint Pasteurella multocida isolated from turkeys and wildlife. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1847–1853. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1847-1853.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snipes K. P., Kasten R. W., Wild M. A., Miller M. W., Jessup D. A., Silflow R. L., Foreyt W. J., Carpenter T. E. Using ribosomal RNA gene restriction patterns in distinguishing isolates of Pasteurella haemolytica from bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis). J Wildl Dis. 1992 Jul;28(3):347–354. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-28.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao G., Pijoan C., Murtaugh M. P., Molitor T. W. Use of restriction endonuclease analysis and ribotyping to study epidemiology of Pasteurella multocida in closed swine herds. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1401–1405. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1401-1405.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M. L., Hirsh D. C. Demonstration of an R plasmid in a strain of Pasteurella haemolytica isolated from feedlot cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Feb;41(2):166–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]