Abstract
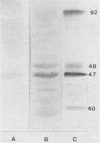
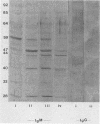
Candidal antigens were isolated by affinity chromatography from the sera of patients with disseminated Candida albicans infections. The immunodominant 47-kilodalton (kDa) antigen appeared to be a heat-stable breakdown product of several larger heat-labile components (84 to 92, 74 to 79, and 66 to 72 kDa). It was undetectable in normal sera and sera from four patients with systemic C. parapsilosis, C. tropicalis, and C. krusei infections. Serum samples from 92 patients with proven systemic C. albicans infections were examined by the immunoblot technique. Seventy-four patients had detectable antibody, and 92% of these produced antibody to the 47-kDa antigen. All survivors had major serological responses to this antigen, whereas patients who died had no, minor, or fading responses. Fifty-five of the patients were neutropenic following cytotoxic chemotherapy for malignancies, usually lymphoproliferative disorders (hematological patients). The remainder were surgical or medical patients (nonhematological). Hematological patients differed from nonhematological patients in the range of antigens that were commonly recognized by their immune systems, although antibodies to the 47- and 60-kDa antigens were frequently present in both groups. They also differed in that they produced mainly an immunoglobulin M (IgM) response, failing to seroconvent to IgG. This did not reduce survival rates, which were similar in both groups. It may be responsible, however, for the lower antigen titers that were observed in hematological patients when measured by reverse passive latex agglutination.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araj G. F., Hopfer R. L., Chesnut S., Fainstein V., Bodey G. P., Sr Diagnostic value of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Candida albicans cytoplasmic antigen in sera of cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.46-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au-Young J. K., Troy F. A., Goldstein E. Serologic analysis of antigen-specific reactivity in patients with systemic candidiasis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;3(5):419–432. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. W., Sada E., Brass C., Bennett J. E. Diagnosis of systemic candidiasis by latex agglutination for serum antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):749–752. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.749-752.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burges G., Holley H. P., Virella G. Circulating immune complexes in patients with Candida albicans infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jul;53(1):165–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Matthews R. C., Fox A., Tabaqchali S. Use of immunoblotting to identify antigenic differences between the yeast and mycelial phases of Candida albicans. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jun;38(6):701–706. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Odds F. C., Lee W., Webster C., Williams J. D. Outbreak of systemic Candida albicans in intensive care unit caused by cross infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Mar 9;290(6470):746–748. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6470.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Williams J. D. Evaluation of the Ramco latex agglutination test in the early diagnosis of systemic candidiasis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):98–101. doi: 10.1007/BF02013571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. A reverse passive latex agglutination test for the diagnosis of systemic candidosis. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Oct 10;82(2):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Wilkinson I. D., Lea A. S., Price M. F. Latex agglutination test for detection of Candida antigen in patients with disseminated disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):122–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02001577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield R. A., Jones J. M. Purification and characterization of a major cytoplasmic antigen of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):469–477. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.469-477.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M. Quantitation of antibody against cell wall mannan and a major cytoplasmic antigen of Candida in rabbits, mice, and humans. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):78–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.78-89.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning-Zweerink M., Maloney C. S., Mitchell T. G., Weston H. Immunoblot analyses of Candida albicans-associated antigens and antibodies in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):46–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.46-52.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Tabaqchali S. Immunoblot analysis of the serological response in systemic candidosis. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1415–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Berg R. A., Pizzo P. A., Bennett J. E. Detection of Candida antigen in sera of patients with candidiasis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-inhibition technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):116–118. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.116-118.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Largen M. T., Buckley H. R. Production and characterization of three monoclonal antibodies to Candida albicans proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1012–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1012-1018.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Largen M. T., Zweibel S. M., Buckley H. R. Identification and molecular weight characterization of antigens from Candida albicans that are recognized by human sera. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):715–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.715-721.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]