Abstract
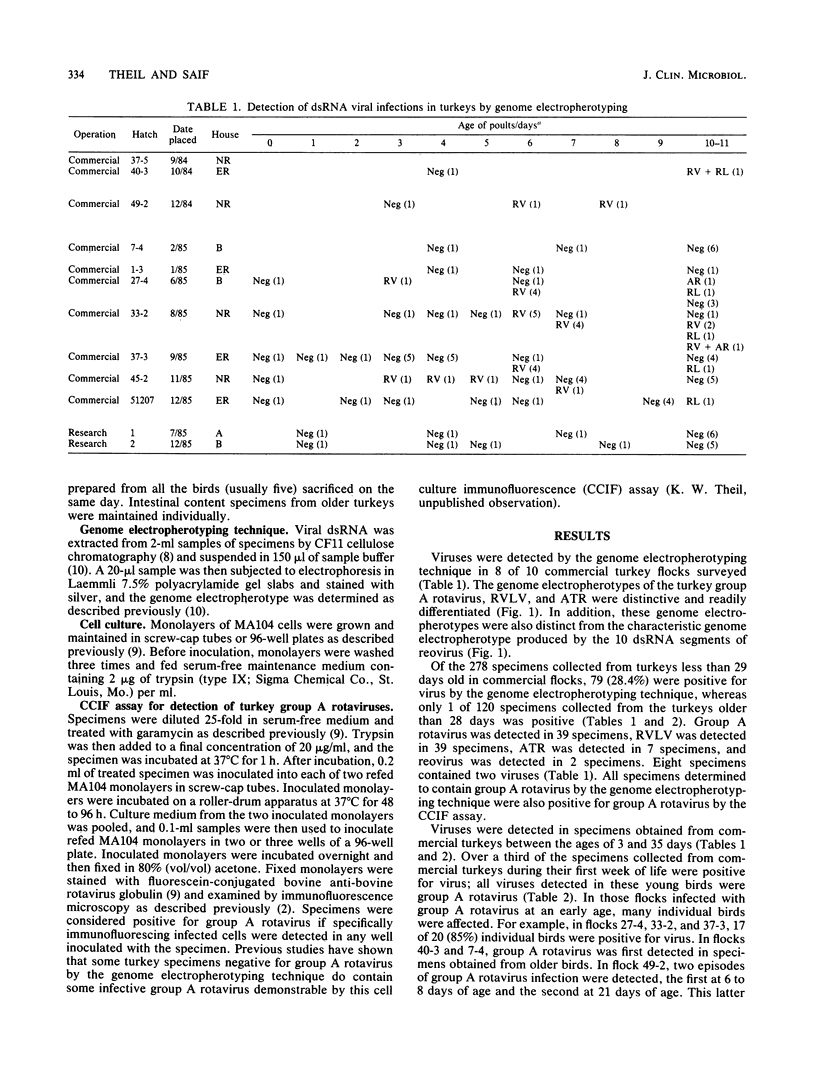
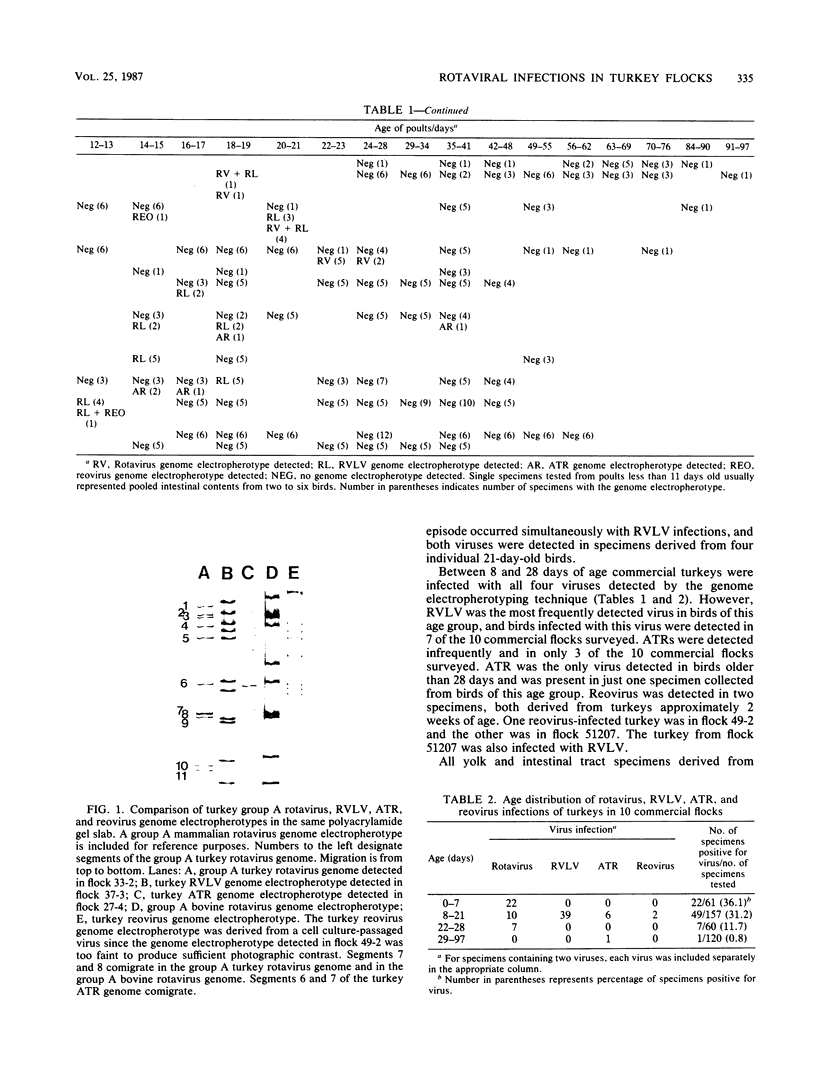
The genome electropherotyping technique was used in longitudinal surveys to detect group A rotavirus, rotaviruslike virus (RVLV), atypical rotavirus (ATR), and reovirus in intestinal contents or fecal specimens collected from turkeys in 10 commercial and 2 research station flocks. These viruses were detected in turkeys from 8 to 10 commercial flocks surveyed. Of 278 specimens collected from turkeys less then 29 days old in commercial flocks, 79 (28.4%) contained one or more viruses, whereas only 1 of 120 specimens collected from turkeys older than 28 days had virus. Viruses were detected in commercial turkeys between 3 and 35 days old, and over a third of the specimens collected from birds during their first week of life were positive for group A rotavirus. Between 8 and 28 days of age, commercial turkeys were infected with group A rotavirus, RVLV, ATR, and reovirus. ATR was the only virus detected in birds older than 28 days. Overall, group A rotavirus and RVLV were each detected in 39 specimens, and ATR was detected in 7 specimens; reovirus was detected in 2 specimens. Eight of the positive specimens contained two viruses. All 102 specimens collected from turkeys 1 to 56 days old in the two research station flocks were negative for virus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Stuart J. C. Rotavirus infection in avian species. Vet Rec. 1978 Sep 30;103(14):319–320. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.14.319-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B. Isolation and cell culture propagation of rotaviruses from turkeys and chickens. Arch Virol. 1979;61(1-2):13–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01320587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Todd D., Allan G. M., McFerran J. B., Greene J. A. Epidemiology of rotavirus infection in broiler chickens: recognition of four serogroups. Arch Virol. 1984;81(1-2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF01309301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Saif Y. M., Theil K. W. Enteric viruses in diarrheic turkey poults. Avian Dis. 1985 Jul-Sep;29(3):798–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M., Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Bohl E. H., Hancock D. D., Kohler E. M., Moorhead P. D. Rapid, simple method of preparing rotaviral double-stranded ribonucleic acid for analysis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.273-280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Reynolds D. L., Saif Y. M. Comparison of immune electron microscopy and genome electropherotyping techniques for detection of turkey rotaviruses and rotaviruslike viruses in intestinal contents. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):695–699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.695-699.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Reynolds D. L., Saif Y. M. Isolation and serial propagation of turkey rotaviruses in a fetal rhesus monkey kidney (MA104) cell line. Avian Dis. 1986 Jan-Mar;30(1):93–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yason C. V., Schat K. A. Isolation and characterization of avian rotaviruses. Avian Dis. 1985 Apr-Jun;29(2):499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]