Abstract
The presence and quantity of the enterobacterial common antigen (ECA) in several species belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae as well as to other gram-negative families were determined by a solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay system and Western blotting by using mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for ECA. Except for Erwinia chrysanthemi, previously known to be an exception, all species known or presumed to belong to Enterobacteriaceae produced ECA (89 of 90 species). Most species not belonging to Enterobacteriaceae did not produce ECA (25 of 28 species), with one already known (Plesiomonas shigelloides) and two hitherto unknown (Actinobacillus equuli and Actinobacillus suis) exceptions. Interestingly, all strains of P. shigelloides produced ECA, regardless of the presence of the Shigella sonnei cross-reacting O antigen. Quantitation of the amount of ECA in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae revealed a remarkable heterogeneity among genera and species as well as within one species. We conclude that the rapid, sensitive, and reliable determination of ECA is a useful aid in taxonomic classification and may help to characterize the relatedness of the family Enterobacteriaceae to other families. However, a quantitative analysis of ECA appears to be without value for these purposes.
Full text
PDF

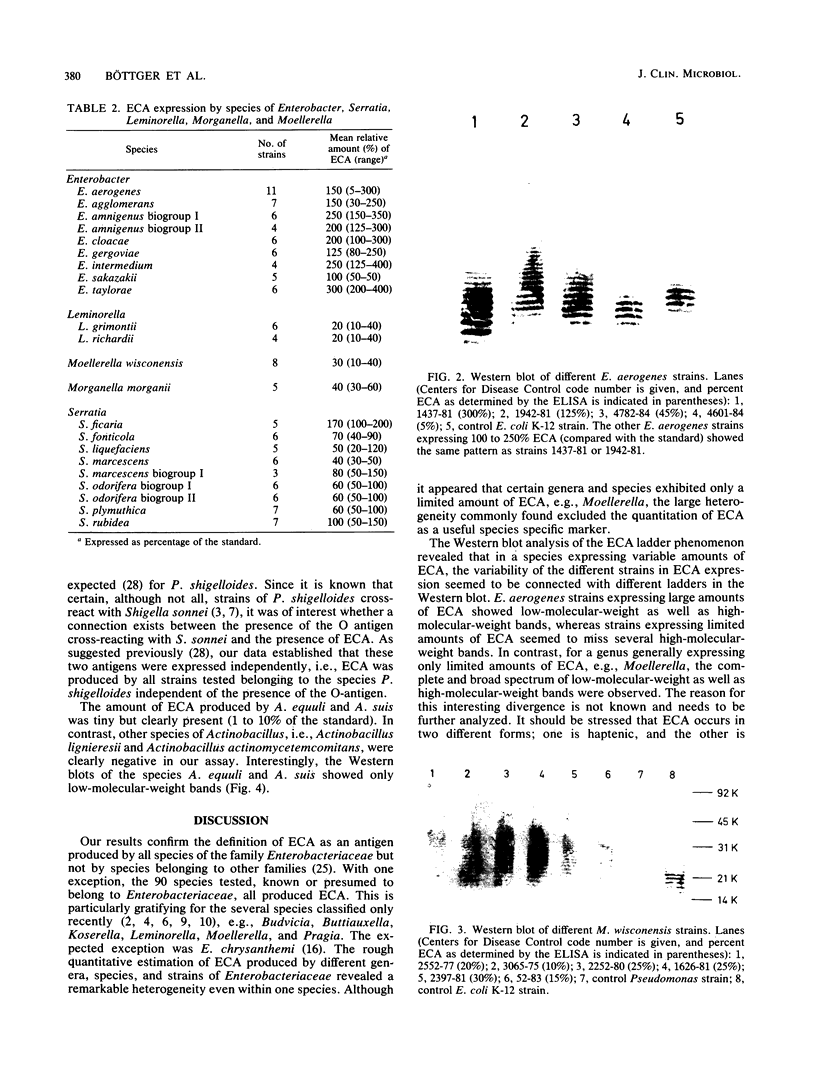
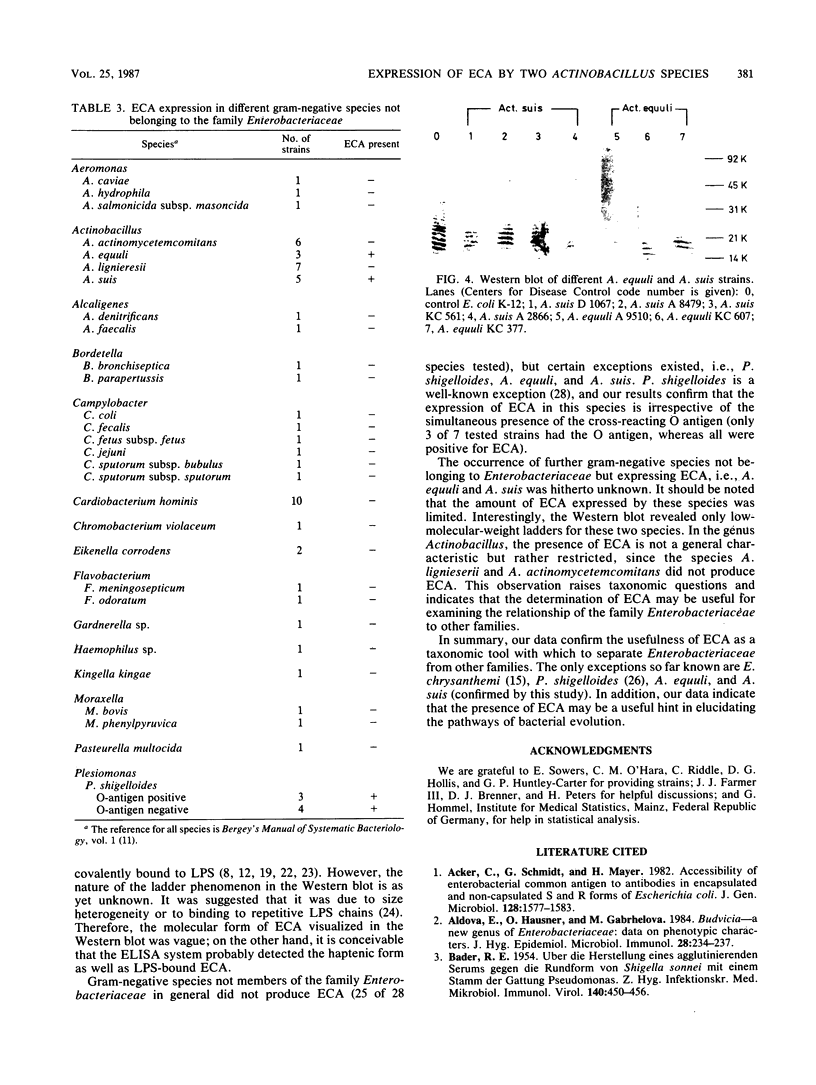

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acker G., Schmidt G., Mayer H. Accessibility of enterobacterial common antigen to antibodies in encapsulated and non-capsulated S and R forms of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jul;128(7):1577–1583. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-7-1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldová E., Hausner O., Gabrhelová M. Budvicia--a new genus of Enterobacteriaceae. Data on phenotypic characters. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(2):234–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADER R. E. Uber die Herstellung eines agglutinierenden Serums gegen die Rundform von Shigella sonnei mit einem Stamm der Gattung Pseudomonas. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1954;140(5):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Davis B. R., Hickman-Brenner F. W., McWhorter A., Huntley-Carter G. P., Asbury M. A., Riddle C., Wathen-Grady H. G., Elias C., Fanning G. R. Biochemical identification of new species and biogroups of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):46–76. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.46-76.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson W. W., Henderson N. D. Description of Strain C27: A Motile Organism with the Major Antigen of Shigella sonnei Phase I. J Bacteriol. 1947 Aug;54(2):179–181. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.2.179-181.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Carlsson H. E., Perlmann P., Svensson S. Immunochemistry of the common antigen of Enterobacteriaceae (Kunin). Relation to lipopolysaccharide core structure. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):565–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Huntley-Carter G. P., Fanning G. R., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Koserella trabulsii, a new genus and species of Enterobacteriaceae formerly known as Enteric Group 45. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.39-42.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Vohra M. P., Huntley-Carter G. P., Fanning G. R., Lowery V. A., 3rd, Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Leminorella, a new genus of Enterobacteriaceae: identification of Leminorella grimontii sp. nov. and Leminorella richardii sp. nov. found in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):234–239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.234-239.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., BEARD M. V. SEROLOGICAL STUDIES OF O ANTIGENS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI BY MEANS OF THE HEMAGGLUTINATION TEST. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:541–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.541-548.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. SEPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND BIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF A COMMON ANTIGEN IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:565–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Chalon A. M., Véron M. Recherches sur la présence de l'antigène commun des "Enterobacteriaceae" (antigène Kunin) chez les "Yersinia", "Levinea", "Aeromonas" et "Vibrio". Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Dec;123(6):761–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Petcovici M. Immunochemical studies on purified common enterobacterial antigen (KUNIN). Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Dec;233(4):486–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mc Laughlin J. C., Dominque G. J. The immunologic role of the ethanol-soluble enterobacterial common antigen versus experimental renal infection. Immunol Commun. 1974;3(1):51–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Mayer H. Enterobacterial common antigen. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):591–632. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.591-632.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Mayer H., Whang H. Y., Neter E. Participation of lipopolysaccharide genes in the determination of the enterobacterial common antigen: analysis of R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.760-764.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
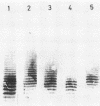
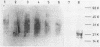
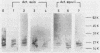
- Männel D., Mayer H. Isolation and chemical characterization of the enterobacterial common antigen. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):361–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H., Jürs M., Jann B., Jann K., Timmis K. N., Bitter-Suermann D. Monoclonal antibodies to enterobacterial common antigen and to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide outer core: demonstration of an antigenic determinant shared by enterobacterial common antigen and E. coli K5 capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):459–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.459-466.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick P. D., Mayer H., Neumeyer B. A., Wolski S., Bitter-Suermann D. Biosynthesis of enterobacterial common antigen. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):494–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.494-503.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinno J., Golecki J. R., Mayer H. Localization of enterobacterial common antigen:immunogenic and nonimmunogenic enterobacterial common antigen-containing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):814–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.814-821.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHANG H. Y., NETER E. Immunological studies of a heterogenetic enterobacterial antigen (Kunin). J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84:1245–1250. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1245-1250.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang H. Y., Heller M. E., Neter E. Production by Aeromonas of common enterobacterial antigen and its possible taxonomic significance. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):161–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.161-164.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]