Abstract
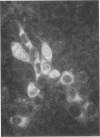
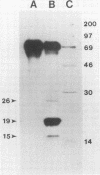
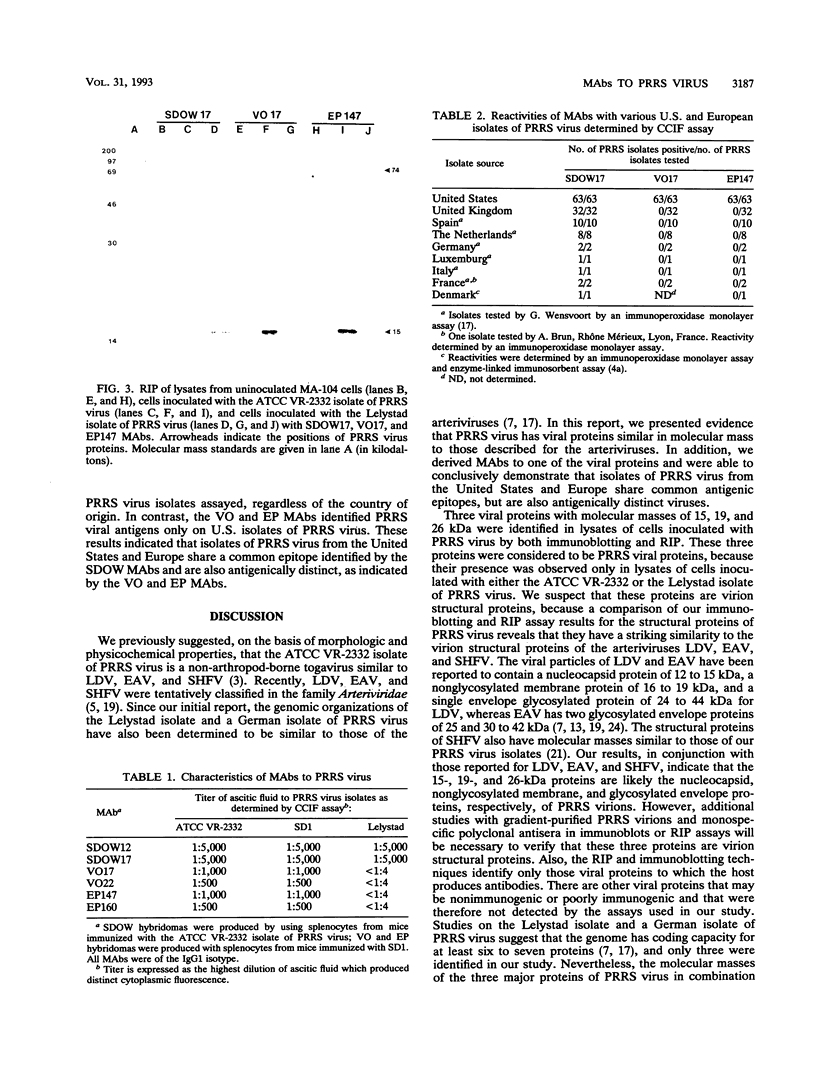
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to two U.S. isolates of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus were prepared. Two MAbs specifically recognized a conserved epitope on the putative 15-kDa nucleocapsid protein of U.S. and European isolates of PRRS virus. Four other MAbs recognized epitopes on the 15-kDa protein of U.S. but not European isolates of PRRS virus. Collectively, this indicates that PRRS viruses contain both conserved and divergent epitopes on the 15-kDa viral protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benfield D. A., Jackwood D. J., Bac I., Saif L. J., Wesley R. D. Detection of transmissible gastroenteritis virus using cDNA probes. Arch Virol. 1991;116(1-4):91–106. doi: 10.1007/BF01319234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfield D. A., Nelson E., Collins J. E., Harris L., Goyal S. M., Robison D., Christianson W. T., Morrison R. B., Gorcyca D., Chladek D. Characterization of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332). J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992 Apr;4(2):127–133. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfield D. A., Stotz I., Moore R., McAdaragh J. P. Shedding of rotavirus in feces of sows before and after farrowing. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):186–190. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.186-190.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Genus Torovirus assigned to the Coronaviridae. Arch Virol. 1993;128(3-4):395–396. doi: 10.1007/BF01309450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. E., Benfield D. A., Christianson W. T., Harris L., Hennings J. C., Shaw D. P., Goyal S. M., McCullough S., Morrison R. B., Joo H. S. Isolation of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332) in North America and experimental reproduction of the disease in gnotobiotic pigs. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992 Apr;4(2):117–126. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann K. K., Visser N., Van Woensel P., Thiel H. J. Molecular characterization of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, a member of the arterivirus group. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):329–339. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harty J. T., Plagemann P. G. Formalin inactivation of the lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus reveals a major neutralizing epitope not recognized during natural infection. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3210–3216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3210-3216.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClurkin A. W., Norman J. O. Studies on transmissible gastroenteritis of swine. II. Selected characteristics of a cytopathogenic virus common to five isolates from transmissible gastroenteritis. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1966 Jul;30(7):190–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulenberg J. J., Hulst M. M., de Meijer E. J., Moonen P. L., den Besten A., de Kluyver E. P., Wensvoort G., Moormann R. J. Lelystad virus, the causative agent of porcine epidemic abortion and respiratory syndrome (PEARS), is related to LDV and EAV. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):62–72. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Moennig V. Lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus, equine arteritis virus, and simian hemorrhagic fever virus: a new group of positive-strand RNA viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1992;41:99–192. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60036-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS or blue-eared pig disease). Vet Rec. 1992 Feb 1;130(5):87–89. doi: 10.1136/vr.130.5.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trousdale M. D., Trent D. W., Shelokov A. Simian hemorrhagic fever virus: a new togavirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Dec;150(3):707–711. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-39111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensvoort G., de Kluyver E. P., Luijtze E. A., den Besten A., Harris L., Collins J. E., Christianson W. T., Chladek D. Antigenic comparison of Lelystad virus and swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992 Apr;4(2):134–138. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G., Brinton M. A., Gaidamovich SYa, Horzinek M. C., Igarashi A., Käriäinen L., Lvov D. K., Porterfield J. S., Russell P. K., Trent D. W. Togaviridae. Intervirology. 1985;24(3):125–139. doi: 10.1159/000149632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries A. A., Chirnside E. D., Horzinek M. C., Rottier P. J. Structural proteins of equine arteritis virus. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6294–6303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6294-6303.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]