Abstract
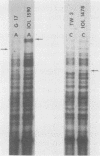
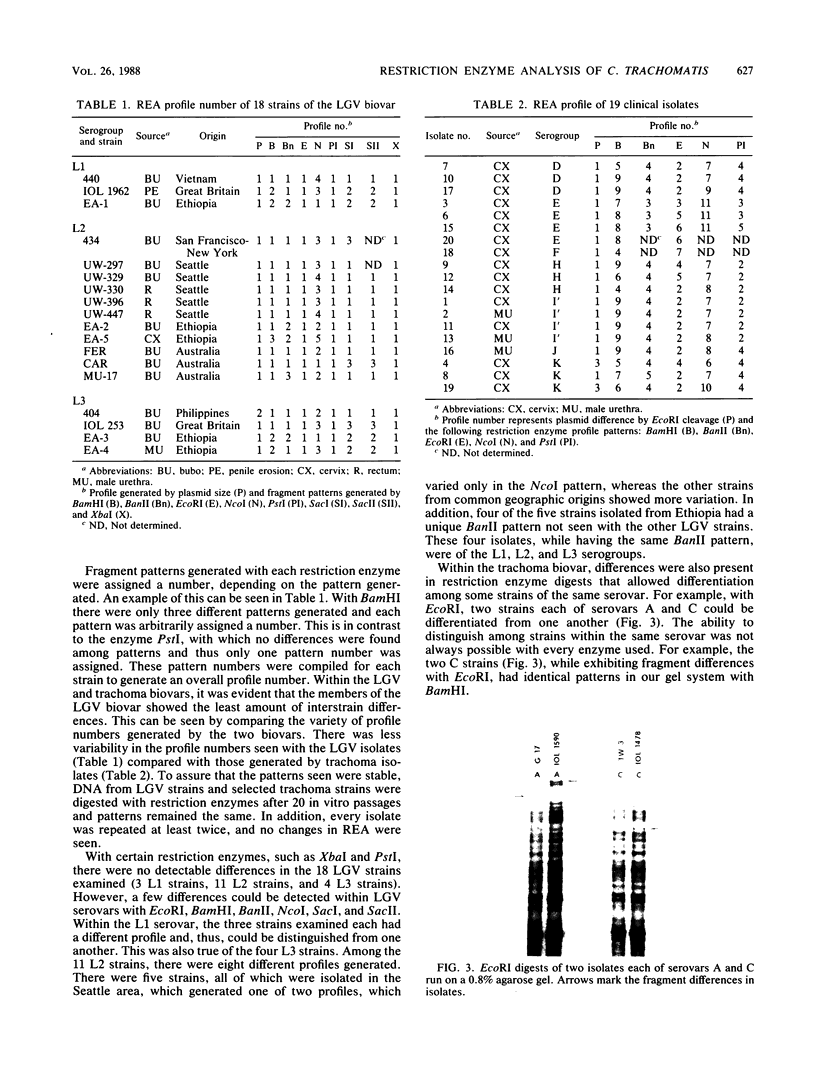
DNA from a total of 60 Chlamydia trachomatis isolates was examined by restriction endonuclease analysis. Strains from all established biovars and serovars were tested. There was great diversity between the mouse biovar and the lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) and trachoma biovars. The LGV and trachoma biovar isolates generated similar fragment patterns; however, distinct fragments appeared to be unique to both biovars, thus allowing differentiation of these two major groups. In most cases, strains of the same serovar could be differentiated from one another when a battery of restriction enzymes was used. In addition, in some cases, certain restriction fragments appeared to be characteristic of strains from a particular geographical location. The DNA patterns generated by all C. trachomatis isolates differed greatly from the DNA patterns generated from the Chlamydia psittaci isolates tested, including TWAR, a human C. psittaci strain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan I., Pearce J. H. Differential amino acid utilization by Chlamydia psittaci (strain guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis) and its regulatory effect on chlamydial growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):1991–2000. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-1991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B. E., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. Differences in outer membrane proteins of the lymphogranuloma venereum and trachoma biovars of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):488–494. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.488-494.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. A., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Characterization of the new Chlamydia agent, TWAR, as a unique organism by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA-DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1911–1916. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1911-1916.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Altman J. A new Chlamydia psittaci strain, TWAR, isolated in acute respiratory tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 17;315(3):161–168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607173150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland J., Brown S. M. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2 (strain HG52). J Gen Virol. 1985 Jun;66(Pt 6):1305–1321. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-6-1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Frenkel N., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: strain differences and heterogeneity in the locations of restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1768–1772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph T., Nano F. E., Garon C. F., Caldwell H. D. Molecular characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis and Chlamydia psittaci plasmids. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):699–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.699-703.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Weiss E. Lack of deoxyribonucleic acid homology between species of the genus Chlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1421–1423. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1421-1423.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClenaghan M., Herring A. J., Aitken I. D. Comparison of Chlamydia psittaci isolates by DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.384-389.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., de la Maza L. M. Characterization of Chlamydia DNA by restriction endonuclease cleavage. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):604–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.604-608.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripa K. T., Mårdh P. A. Cultivation of Chlamydia trachomatis in cycloheximide-treated mccoy cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.328-331.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S., Troup N., Labigne-Roussel A., Cohen M. L. Cloned, random chromosomal sequences as probes to identify Salmonella species. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):156–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Immunologic relationship between genital TRIC, lymphogranuloma venereum, and related organisms in a new microtiter indirect immunofluorescence test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Barnes R. C., Stephens R. S., Grayston J. T. Immunotyping of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):791–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Schramek S., Wilson N. N., Newman L. W. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Heterogeneity Between Human and Murine Strains of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.24-28.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]