Abstract
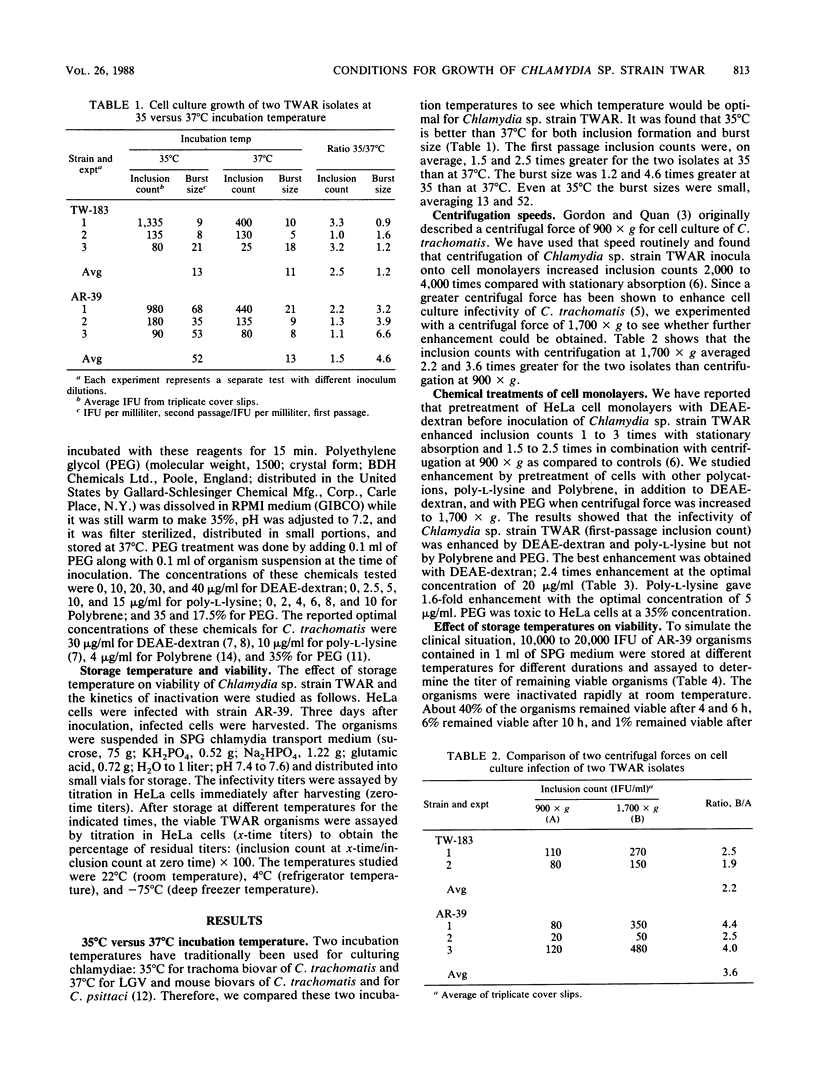
Two prototype isolates (TW-183 and AR-39) of Chlamydia sp. strain TWAR were used to study factors affecting growth of this organism in HeLa 229 cells. The results showed that an incubation temperature of 35 degrees C was better than one of 37 degrees C for growth. The burst size after 3 days of incubation at 35 degrees C was found to be small (13 to 52), which partially explains the difficulty of serial passage in cell culture. Application of a higher centrifugal force (1,700 X g versus 900 X g) at the time of inoculation enhanced growth 2.2 to 3.6 times. Infectivity was enhanced by treatment of cells with DEAE-dextran (2.4 times) or poly-L-lysine (1.6 times), but not with Polybrene or polyethylene glycol. The viability of the TWAR organism in chlamydia transport medium SPG was also studied. It was shown that the organism was rapidly inactivated at room temperature (22 degrees C); only 1% remained viable after storage for 24 h. The viability was preserved at 4 degrees C, and 70% remained viable after storage for 24 h. Freezing at -75 degrees C inactivated 23% of the organisms when the organisms were frozen within 4 h after harvesting and stored at 4 degrees C before freezing.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell L. A., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Characterization of the new Chlamydia agent, TWAR, as a unique organism by restriction endonuclease analysis and DNA-DNA hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1911–1916. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1911-1916.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E. Y., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Unique ultrastructure in the elementary body of Chlamydia sp. strain TWAR. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3757–3763. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3757-3763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON F. B., QUAN A. L. ISOLATION OF THE TRACHOMA AGENT IN CELL CULTURE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Feb;118:354–359. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Altman J. A new Chlamydia psittaci strain, TWAR, isolated in acute respiratory tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 17;315(3):161–168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607173150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. W., Hobson D. Factors affecting the sensitivity of replicating McCoy cells in the isolation and growth of chlamydia A (TRIC agents). J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Jun;76(3):441–451. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400055376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Chen H. H., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Identification of a new group of Chlamydia psittaci strains called TWAR. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):1034–1037. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.1034-1037.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Effect of polycations, polyanions and neuraminidase on the infectivity of trachoma-inclusin conjunctivitis and lymphogranuloma venereum organisms HeLa cells: sialic acid residues as possible receptors for trachoma-inclusion conjunction. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.74-79.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C., Wang S., Wentworth B. B., Grayston J. T. Primary isolation of TRIC organisms in HeLa 229 cells treated with DEAE-dextran. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):665–668. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony J. B., Chernesky M. A. Effect of swab type and storage temperature on the isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):865–867. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.865-867.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Grayston J. T., Wang S. P., Kuo C. C. Pneumonia associated with the TWAR strain of Chlamydia. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):507–511. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed N. R., Hillary I. B. Improved method for isolation and growth of Chlamydia trachomatis in McCoy cells treated with cycloheximide using polyethylene glycol. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Sep;38(9):1052–1054. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.9.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Simmons J., Caldwell H. D. Enhancement of Chlamydia trachomatis infectious progeny by cultivation of HeLa 229 cells treated with DEAE-dextran and cycloheximide. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):217–222. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.217-222.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar-Mistry P., Albota V., Knelsen B. Effect of polybrene on isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):671–673. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.671-673.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjiam K. H., van Heijst B. Y., de Roo J. C., de Beer A., van Joost T., Michel M. F., Stolz E. Survival of Chlamydia trachomatis in different transport media and at different temperatures: diagnostic implications. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):92–94. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


