Abstract
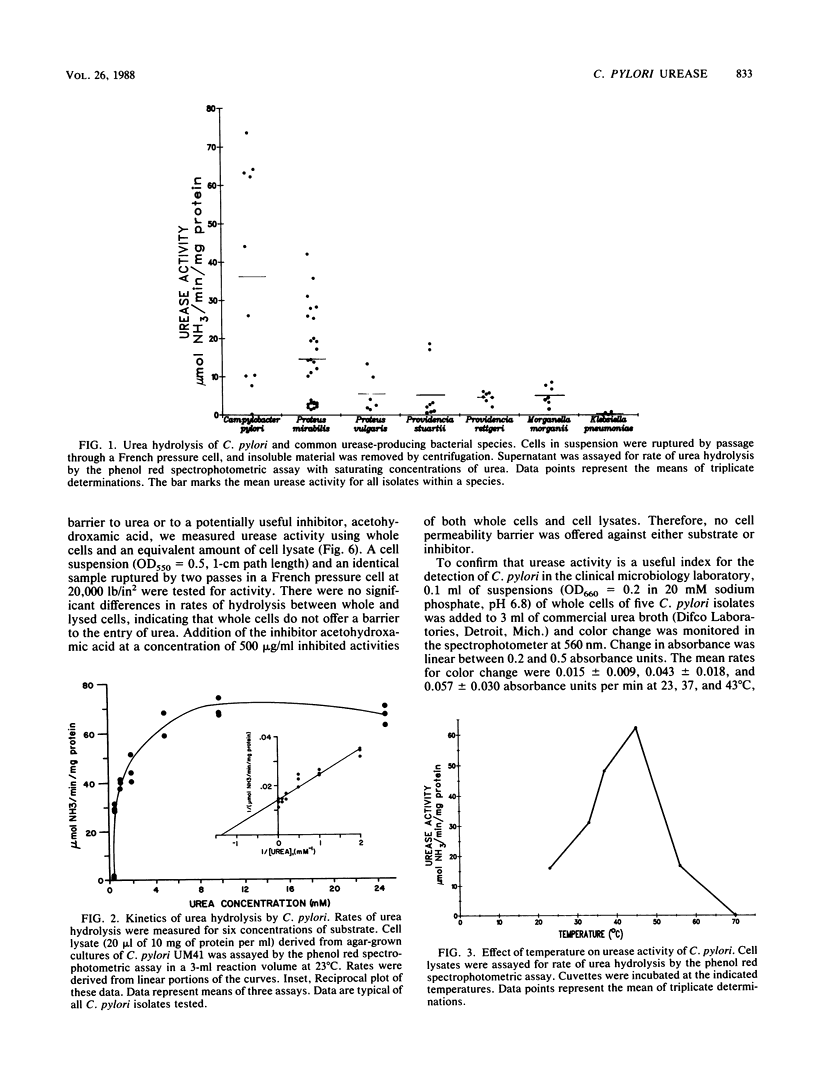
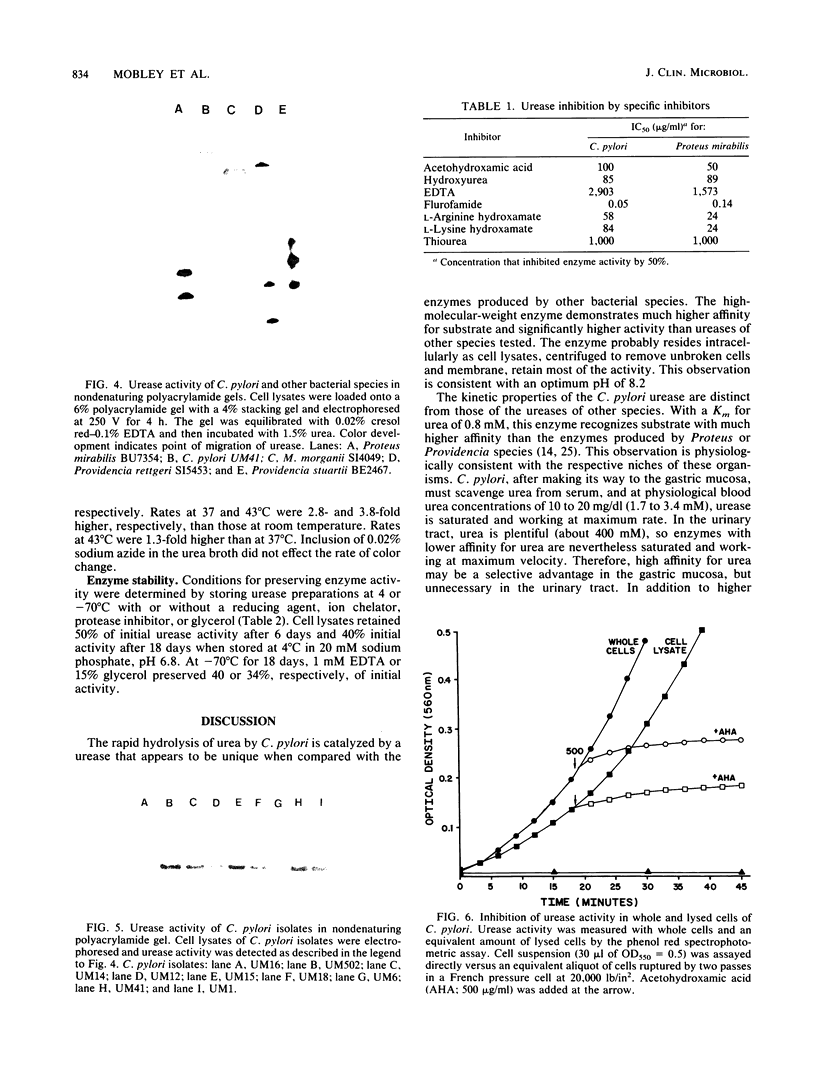
Campylobacter pylori, a suspected agent of gastritis and peptic ulceration, rapidly hydrolyzes urea. Because urease serves as the basis of detection of the organism in gastric biopsies and may represent an important virulence factor, biochemical characteristics of the enzyme were determined. C. pylori was isolated from antral biopsies from 10 patients with complaints of abdominal pain or history of peptic ulcer disease. All isolates were urease positive, with an average rate of hydrolysis by cell lysates being 36 +/- 28 mumol of NH3 per min per mg of protein, more than twice that of Proteus mirabilis and 10 times that of other urinary tract isolates. The enzyme had an apparent molecular weight of 625,000 +/- 15,000 by column chromatography, an isoelectric point of 5.9, a Km of 0.8 +/- 0.1 mM urea, an optimal temperature of 45 degrees C, and an optimal pH of 8.2. Ten isolates tested produced ureases with identical electrophoretic mobilities on nondenaturing 5% polyacrylamide activity gels. Acetohydroxamic acid (100 micrograms/ml), hydroxyurea (85 micrograms/ml), flurofamide (0.05 micrograms/ml), and EDTA (8 mM) inhibited enzyme activity by 50%. Cell lysates retained 50% of initial urease activity after 6 days and 40% activity after 18 days when stored at 4 degrees C in 20 mM sodium phosphate, pH 6.8. At -70 degrees C for 18 days, 1 mM EDTA or 15% glycerol preserved 40 or 34%, respectively, of initial activity. The urease of C. pylori appears to be biochemically unique from the enzymes of other common urease-producing species.
Full text
PDF



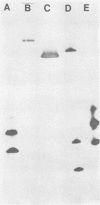
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck G. E., Gourley W. K., Lee W. K., Subramanyam K., Latimer J. M., DiNuzzo A. R. Relation of Campylobacter pyloridis to gastritis and peptic ulcer. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):664–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. G., Correa P., Offerhaus J., Rodriguez E., Janney F., Hoffmann E., Fox J., Hunter F., Diavolitsis S. Ultrastructure of the gastric mucosa harboring Campylobacter-like organisms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;86(5):575–582. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen W. B. Urea Decomposition as a Means of Differentiating Proteus and Paracolon Cultures from Each Other and from Salmonella and Shigella Types. J Bacteriol. 1946 Oct;52(4):461–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.4.461-466.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm B., Sherman P., Cutz E., Karmali M. Association of Campylobacter pylori on the gastric mucosa with antral gastritis in children. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1557–1561. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge J., Lessells A. M., Jones D. M. Antibody to spiral organisms on gastric mucosa. Lancet. 1984 Jun 2;1(8388):1237–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91716-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Armstrong J. A., Marshall B. J. Campylobacter pyloridis, gastritis, and peptic ulceration. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Apr;39(4):353–365. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.4.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Blincow E. D., Warren J. R., Waters T. E., Sanderson C. R., Easton L. Evaluation of cultural techniques for isolating Campylobacter pyloridis from endoscopic biopsies of gastric mucosa. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Oct;38(10):1127–1131. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.10.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Klein P. D., Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Alpert L. C., Opekun A. R., Boutton T. W. Campylobacter pylori detected noninvasively by the 13C-urea breath test. Lancet. 1987 May 23;1(8543):1174–1177. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M. Prevention of infected urinary stones by urease inhibition. Invest Urol. 1973 Nov;11(3):228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M., Gargan R. A. Rapid screening for urease inhibitors. Invest Urol. 1979 Mar;16(5):327–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Borody T. J., Gal A., Lee A. Campylobacter pyloridis gastritis I: Detection of urease as a marker of bacterial colonization and gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Apr;82(4):292–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Hennessy W. B., Borody T. J., Carrick J., Ralston M., Brady L., Lee A. Campylobacter pyloridis gastritis II: Distribution of bacteria and associated inflammation in the gastroduodenal environment. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Apr;82(4):297–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Lee A. Campylobacter pyloridis, urease, hydrogen ion back diffusion, and gastric ulcers. Lancet. 1986 Jul 5;2(8497):15–17. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92561-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Mobley H. L. Genetic and biochemical diversity of ureases of Proteus, Providencia, and Morganella species isolated from urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2198–2203. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2198-2203.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Eldridge J., Fox A. J., Sethi P., Whorwell P. J. Antibody to the gastric campylobacter-like organism ("Campylobacter pyloridis")--clinical correlations and distribution in the normal population. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Aug;22(1):57–62. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Lessells A. M., Eldridge J. Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1002–1006. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOBASHI K., HASE J., UEHARA K. Specific inhibition of urease by hydroxamic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 4;65:380–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J. Campylobacter pyloridis and gastritis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):650–657. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., McGechie D. B., Rogers P. A., Glancy R. J. Pyloric Campylobacter infection and gastroduodenal disease. Med J Aust. 1985 Apr 15;142(8):439–444. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb113444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R., Francis G. J., Langton S. R., Goodwin C. S., Blincow E. D. Rapid urease test in the management of Campylobacter pyloridis-associated gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):200–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty C. A., Wise R. Rapid diagnosis of Campylobacter-associated gastritis. Lancet. 1985 Jun 22;1(8443):1443–1444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91865-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millner O. E., Jr, Andersen J. A., Appler M. E., Benjamin C. E., Edwards J. G., Humphrey D. T., Shearer E. M. Flurofamide: a potent inhibitor of bacterial urease with potential clinical utility in the treatment of infection induced urinary stones. J Urol. 1982 Feb;127(2):346–350. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)53779-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Jones B. D., Jerse A. E. Cloning of urease gene sequences from Providencia stuartii. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):161–169. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.161-169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., McIntyre D., Rose T., Nicholson G. Rapid diagnosis of Campylobacter pyloridis infection. Lancet. 1986 Jan 18;1(8473):149–149. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Nicholson G. Ingestion of Campylobacter pyloridis causes gastritis and raised fasting gastric pH. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Nicholson G., Lloyd G., Haines D., Rogers A., Taylor D. Seroepidemiology of Campylobacter pyloridis. N Z Med J. 1986 Sep 10;99(809):657–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Martin S. R., Borman P. Rapid urea hydrolysis by gastric Campylobacters. Lancet. 1985 Jan 12;1(8420):111–111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathbone B. J., Wyatt J. I., Worsley B. W., Shires S. E., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Heatley R. V., Losowsky M. S. Systemic and local antibody responses to gastric Campylobacter pyloridis in non-ulcer dyspepsia. Gut. 1986 Jun;27(6):642–647. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.6.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W., Bradford N. C., Simpson D. S. The ureases of Proteus strains in relation to virulence for the urinary tract. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Nov;13(4):507–512. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-4-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer H. W., Newell D. G. Immunological identification of Campylobacter pyloridis in gastric biopsy tissue. Lancet. 1985 Jul 6;2(8445):38–38. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. J., Rodman J. S., Peterson C. M. A randomized double-blind study of acetohydroxamic acid in struvite nephrolithiasis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 20;311(12):760–764. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409203111203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]