Abstract
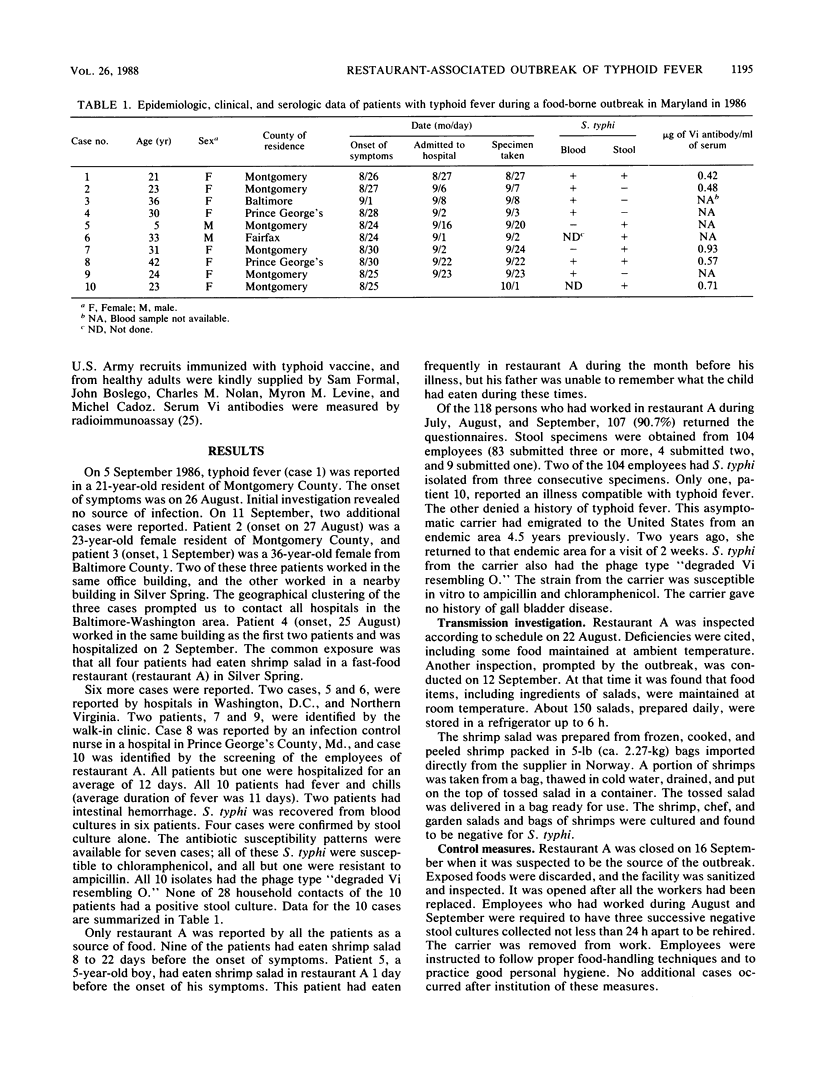
Ten cases of typhoid fever occurred between 24 August and 1 September 1986 in the vicinity of Silver Spring, Md. Shrimp salad served in a fast-food restaurant was implicated as the source of infection. Stool cultures were obtained from 104 employees, and serum Vi antibodies were assayed in 97 of the employees. Salmonella typhi was isolated from stool cultures of an 18-year-old asymptomatic female employee, who was a food handler. A high level of Vi antibodies (79.0 micrograms/ml), measured by radioimmunoassay, was found in her serum. She had emigrated from an endemic area at the age of 14 years and had visited that endemic area 2 years previously. The causal relation between the carrier and the 10 cases of typhoid fever was confirmed by a common bacteriophage type, denoted "degraded Vi resembling O," in the S. typhi isolates. This phage type is rare in the western hemisphere but common in the endemic area from which the carrier had emigrated. The high level of Vi antibody in the asymptomatic carrier, in contrast to the lower levels in the convalescent- and postimmunization-phase sera, facilitated the identification of the source infection in this outbreak. This radioimmunoassay offers a rapid and standardized method for identifying carriers of S. typhi.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya I. L., Lowe C. U., Thapa R., Gurubacharya V. L., Shrestha M. B., Cadoz M., Schulz D., Armand J., Bryla D. A., Trollfors B. Prevention of typhoid fever in Nepal with the Vi capsular polysaccharide of Salmonella typhi. A preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 29;317(18):1101–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710293171801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOKKENHEUSER V., SMIT P., RICHARDSON N. A CHALLENGE TO THE VALIDITY OF THE VI TEST FOR THE DETECTION OF CHRONIC TYPHOID CARRIERS. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1964 Sep;54:1507–1513. doi: 10.2105/ajph.54.9.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Tsang R. S. Vi serology in screening of typhoid carriers: improved specificity by detection of Vi antibodies by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):261–267. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleberg N. C., Barrett T. J., Fisher H., Porter B., Hurtado E., Hughes J. M. Identification of a carrier by using Vi enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay serology in an outbreak of typhoid fever on an Indian reservation. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1320–1322. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1320-1322.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. E., Baine W. B., Nitzkin J. L., Saslaw M. S., Pollard R. A., Jr Epidemiology of Salmonella typhi infection in a migrant labor camp in Dade County, Floida. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Bacteriophage types of Salmonella typhi in the United States from 1974 through 1981. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):172–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.172-174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., LAMB E. Estimation of Vi antibody employing erythrocytes treated with purified Vi antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Apr;82(4):593–598. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanata C. F., Levine M. M., Ristori C., Black R. E., Jimenez L., Salcedo M., Garcia J., Sotomayor V. Vi serology in detection of chronic Salmonella typhi carriers in an endemic area. Lancet. 1983 Aug 20;2(8347):441–443. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau D. F., Melly M. A., Hash J. H. Surface polysaccharide from Staphylococcus aureus M that contains taurine, D-aminogalacturonic acid, and D-fucosamine. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):913–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.913-922.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEILL W. A., MARTIN J. D., BELDEN E. A., TROTTER W. Y. A widespread epidemic of typhoid fever traced to a common exposure. N Engl J Med. 1958 Oct 2;259(14):667–672. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195810022591403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C. M., Feeley J. C., White P. C., Jr, Hambie E. A., Brown S. L., Wong K. H. Evaluation of a new assay for Vi antibody in chronic carriers of Salmonella typhi. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):22–26. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.22-26.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C. M., LaBorde E. A., Howell R. T., Robbins J. B. Identification of Salmonella typhi in faecal specimens by an antiserum-agar method. J Med Microbiol. 1980 May;13(2):373–377. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C. M., White P. C., Jr, Feeley J. C., Hambie E. A., Brown S. L., Wong K. H. Vi serology in the detection of typhoid carriers. Lancet. 1981 Mar 14;1(8220 Pt 1):583–585. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Blake P. A. Typhoid fever in the United States, 1975 and 1976. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):124–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarasombath S., Rungpitarangsi B., Danchaivijitr S., Chearskul S., Komolpit P., Sukosol T. Counterimmunoelectrophoresis in the serological diagnosis of typhoid fever. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1983 Mar;1(1):20–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Ferreccio C., Robbins J. B., Tsai C. M., Schulz D., Cadoz M., Goudeau A., Levine M. M. Safety and immunogenicity of two Salmonella typhi Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):342–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Pollard R. A., Blake P. A. Typhoid in the United States and the risk to the international traveler. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):599–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. P., Shandera W. X., Betz T. G., Schraitle K., Chaffee L., Lopez L., Henley R., Rothe C. N., Bell R. F., Blake P. A. Typhoid fever in San Antonio, Texas: an outbreak traced to a continuing source. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):553–557. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torin D. E., Betts S. L., McClenahan J. B., Phillips G. M., Shikamura M. T. A typhoid fever outbreak on a university campus. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Nov;124(5):606–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


