Abstract
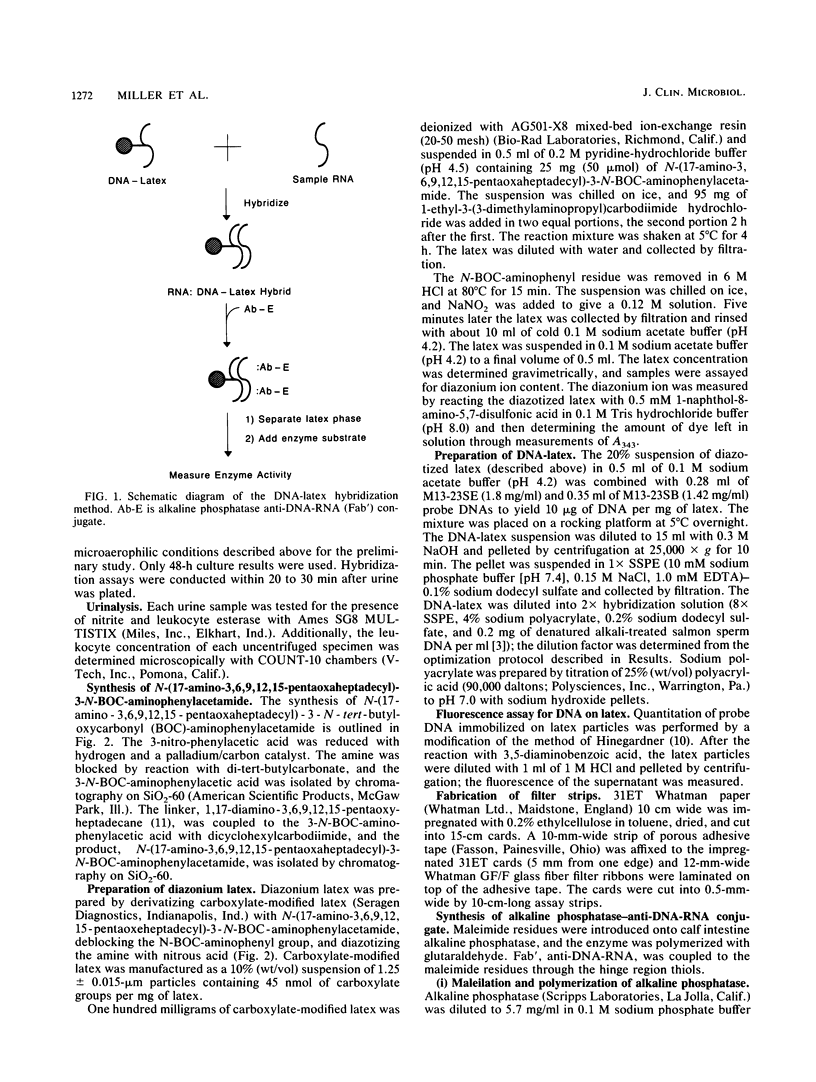
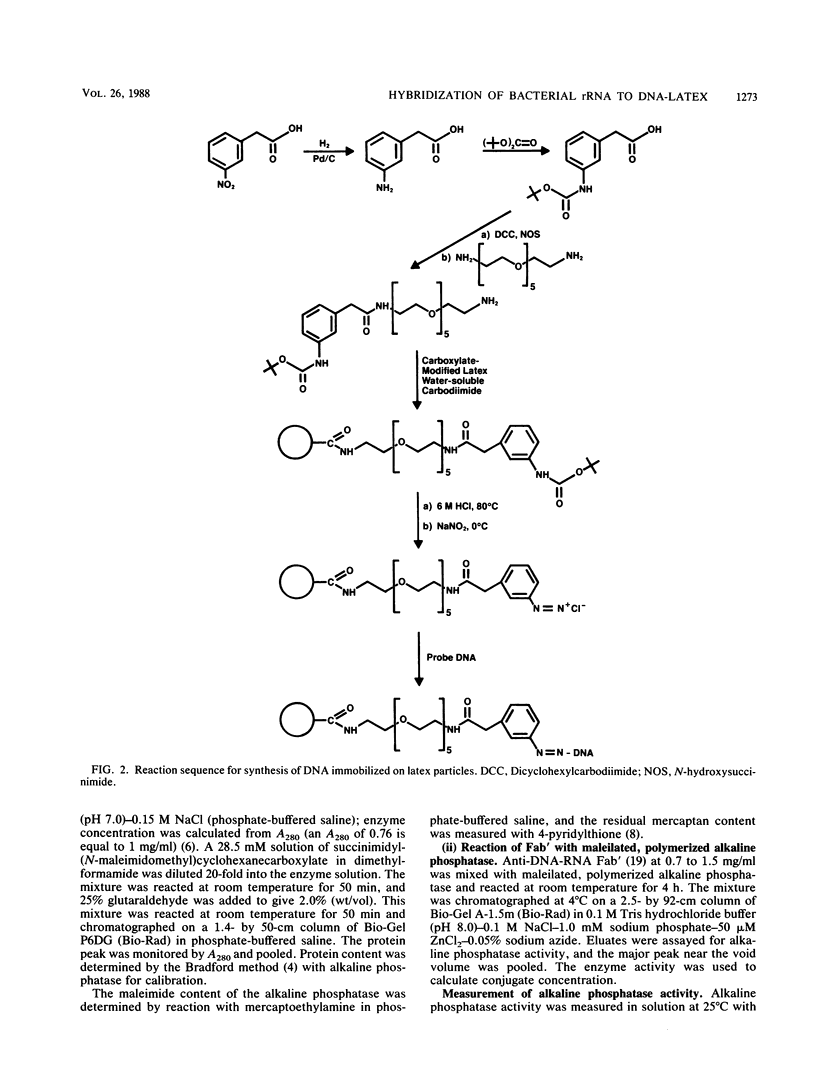
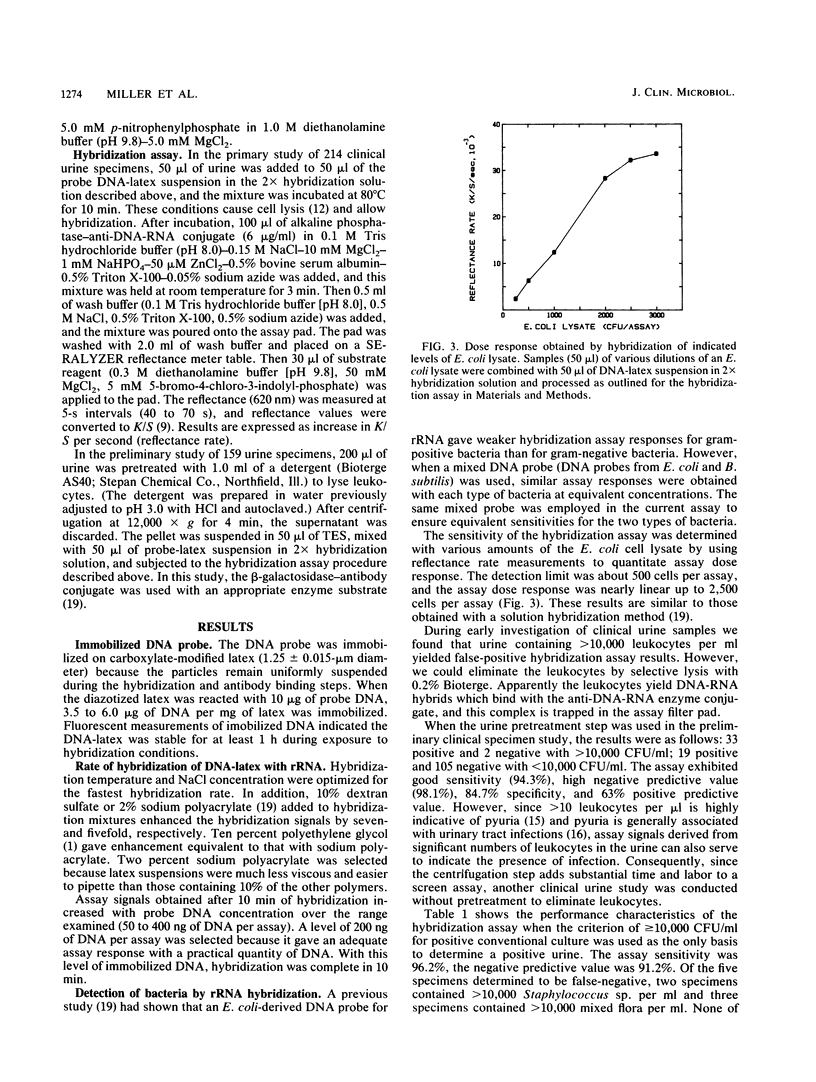
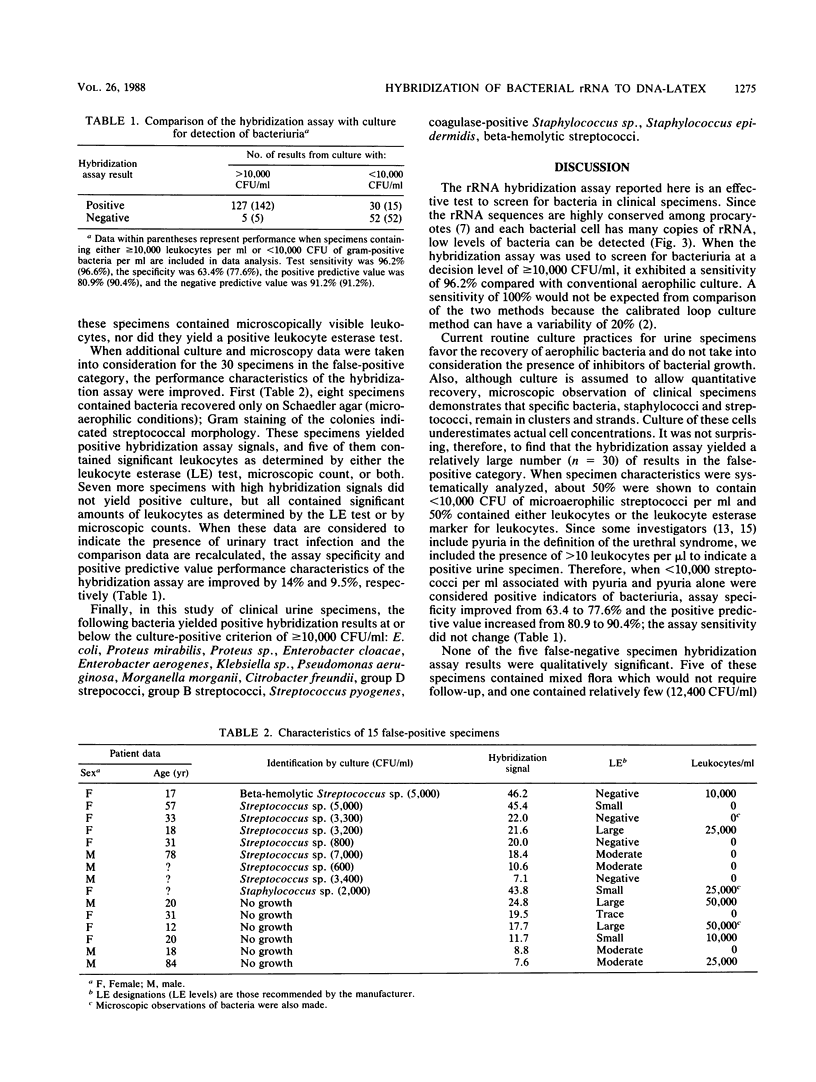
A novel nucleic acid hybridization assay with a DNA probe immobilized on 1.25-micron-diameter latex particles was developed. Hybridization of the immobilized probe DNA with sample rRNA was complete in 10 to 15 min. Alkaline phosphatase-labeled anti-DNA-RNA was allowed to bind to the DNA-RNA hybrids on the latex particles. Then the latex was collected on a small glass fiber filter pad, and bound alkaline phosphatase was quantitated by reflectance rate measurement. The method detected a broad range of bacterial species and had a detection limit of 500 cells per assay. The assay was used to screen urine samples for bacteriuria and had a sensitivity of 96.2% compared with conventional culture at a decision level of greater than or equal to 10(4) CFU/ml. The hybridization method could have broad application to the detection of bacteria and viruses.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguslawski S. J., Smith D. E., Michalak M. A., Mickelson K. E., Yehle C. O., Patterson W. L., Carrico R. J. Characterization of monoclonal antibody to DNA.RNA and its application to immunodetection of hybrids. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 1;89(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Rake A. V., Johnson K. E. Batch procedure for thermal elution of DNA from hydroxyapatite. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):447–459. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90199-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Chappelet-Tordo D., Lazdunski M. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Physical properties and quaternary structure. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1783–1788. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassetti D. R., Murray J. F., Jr Determination of sulfhydryl groups with 2,2'- or 4,4'-dithiodipyridine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinegardner R. T. An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell R., Pead L., Sanderson R. A. Fastidious bacteria and the urethral syndrome: a 2-year clinical and bacteriological study of 51 women. Lancet. 1983 Dec 3;2(8362):1277–1280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollice M., Yang H. L. Use of nonradioactive DNA probes for the detection of infectious bacteria. Clin Lab Med. 1985 Sep;5(3):463–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E. Measurement of pyuria and its relation to bacteriuria. Am J Med. 1983 Jul 28;75(1B):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Wagner K. F., Amsel R., Alexander E. R., Turck M., Counts G. W., Holmes K. K. Causes of the acute urethral syndrome in women. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 21;303(8):409–415. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008213030801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf S. F., Haines L., Fisch J., Kremsky J. N., Dougherty J. P., Jacobs K. Rapid hybridization kinetics of DNA attached to submicron latex particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2911–2926. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood E. G., Dillon H. C., Jr A prospective study of group B streptococcal bacteriuria in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Jul 1;140(5):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(81)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yehle C. O., Patterson W. L., Boguslawski S. J., Albarella J. P., Yip K. F., Carrico R. J. A solution hybridization assay for ribosomal RNA from bacteria using biotinylated DNA probes and enzyme-labeled antibody to DNA:RNA. Mol Cell Probes. 1987 Jun;1(2):177–193. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(87)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


