Abstract
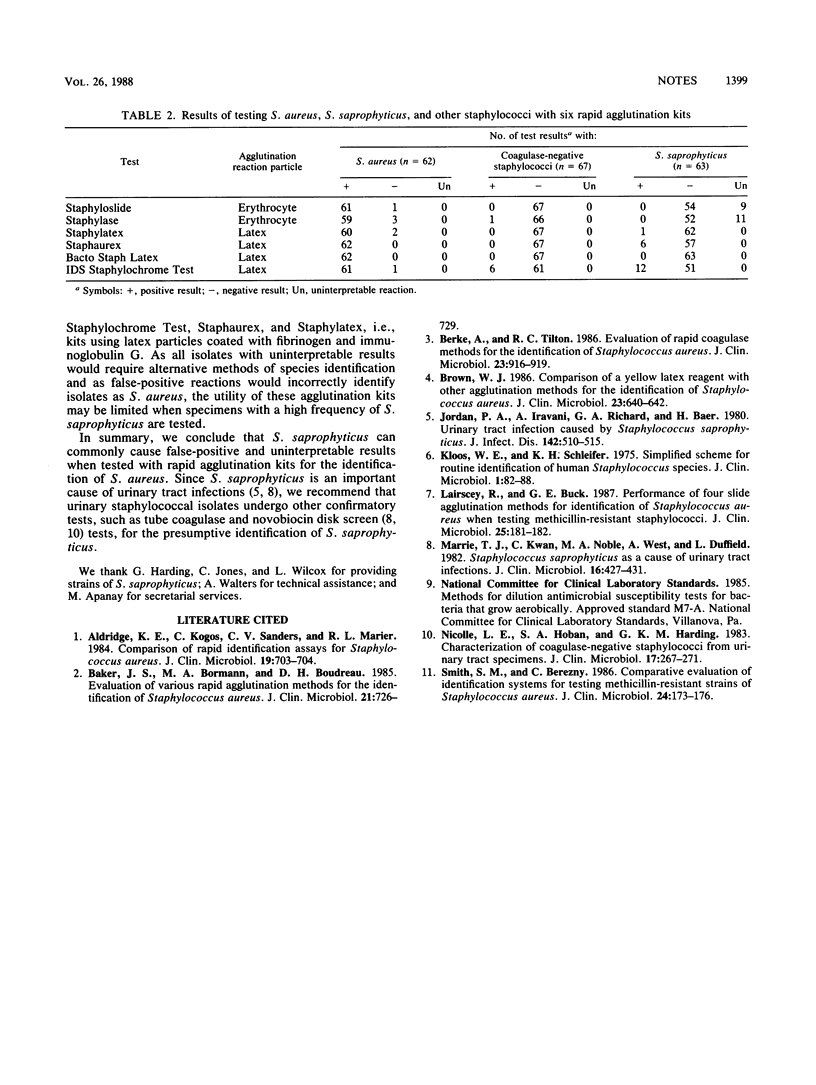
Six rapid agglutination tests for identification of Staphylococcus aureus were evaluated by using 62 strains of S. aureus, 63 strains of S. saprophyticus, and 67 strains of other coagulase-negative staphylococci. S. saprophyticus was responsible for 19 of 26 false-positive results and 20 uninterpretable reactions. Thus, urinary staphylococcal isolates that are positive by rapid agglutination tests may require other confirmatory tests for the identification of possible S. saprophyticus.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Kogos C., Sanders C. V., Marier R. L. Comparison of rapid identification assays for Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):703–704. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.703-704.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. S., Bormann M. A., Boudreau D. H. Evaluation of various rapid agglutination methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):726–729. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.726-729.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke A., Tilton R. C. Evaluation of rapid coagulase methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):916–919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.916-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J. Comparison of a yellow latex reagent with other agglutination methods for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):640–642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.640-642.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. A., Iravani A., Richard G. A., Baer H. Urinary tract infection caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):510–515. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lairscey R., Buck G. E. Performance of four slide agglutination methods for identification of Staphylococcus aureus when testing methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):181–182. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.181-182.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Kwan C., Noble M. A., West A., Duffield L. Staphylococcus saprophyticus as a cause of urinary tract infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):427–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.427-431.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolle L. E., Hoban S. A., Harding G. K. Characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci from urinary tract specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):267–271. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.267-271.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Berezny C. Comparative evaluation of identification systems for testing methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):173–176. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.173-176.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


