Abstract
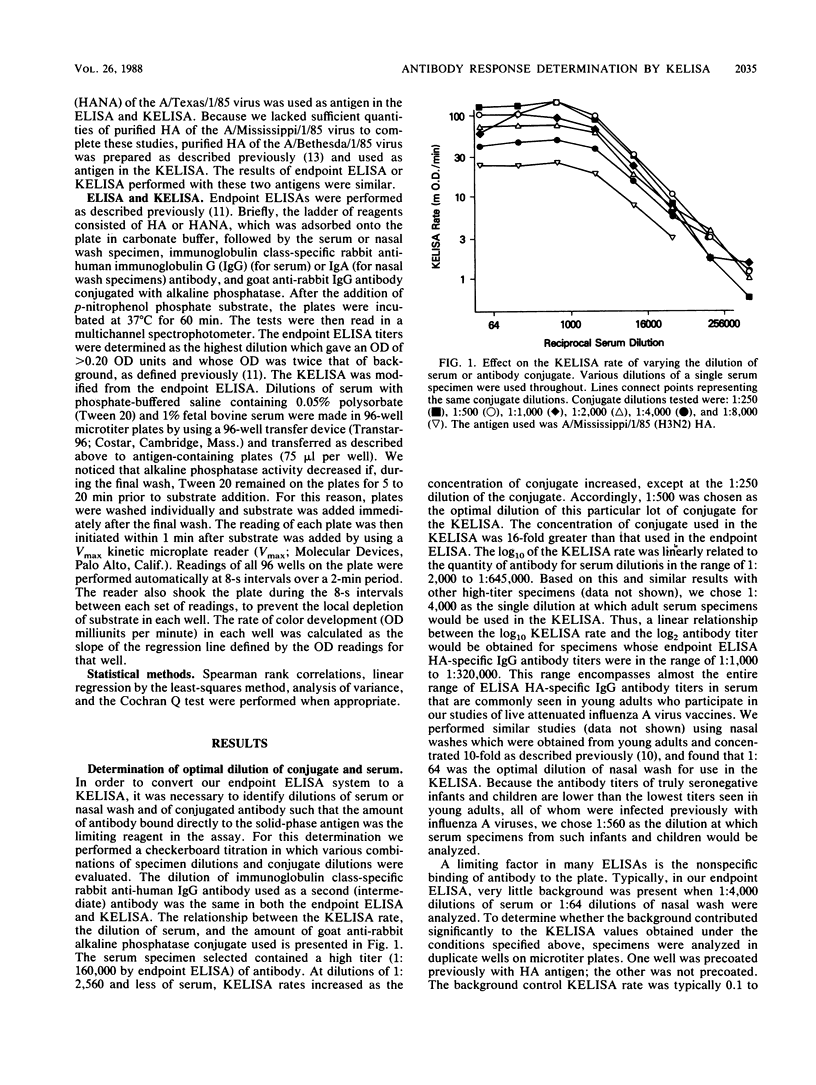
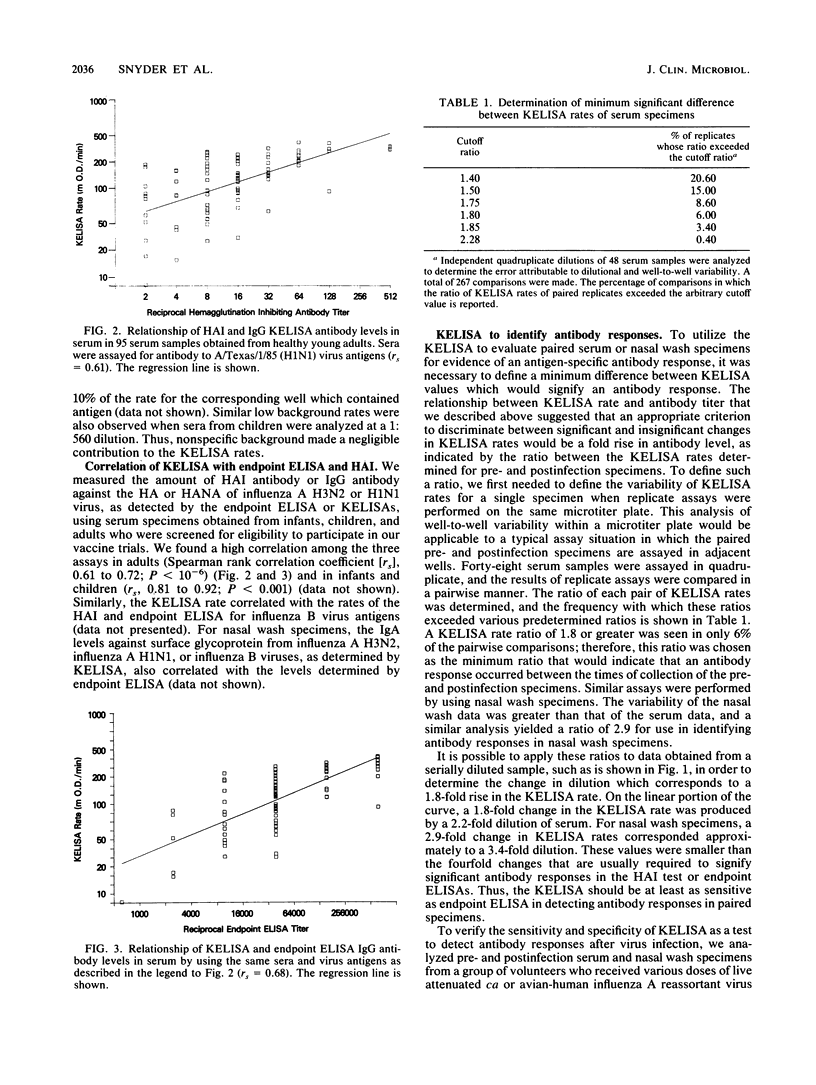
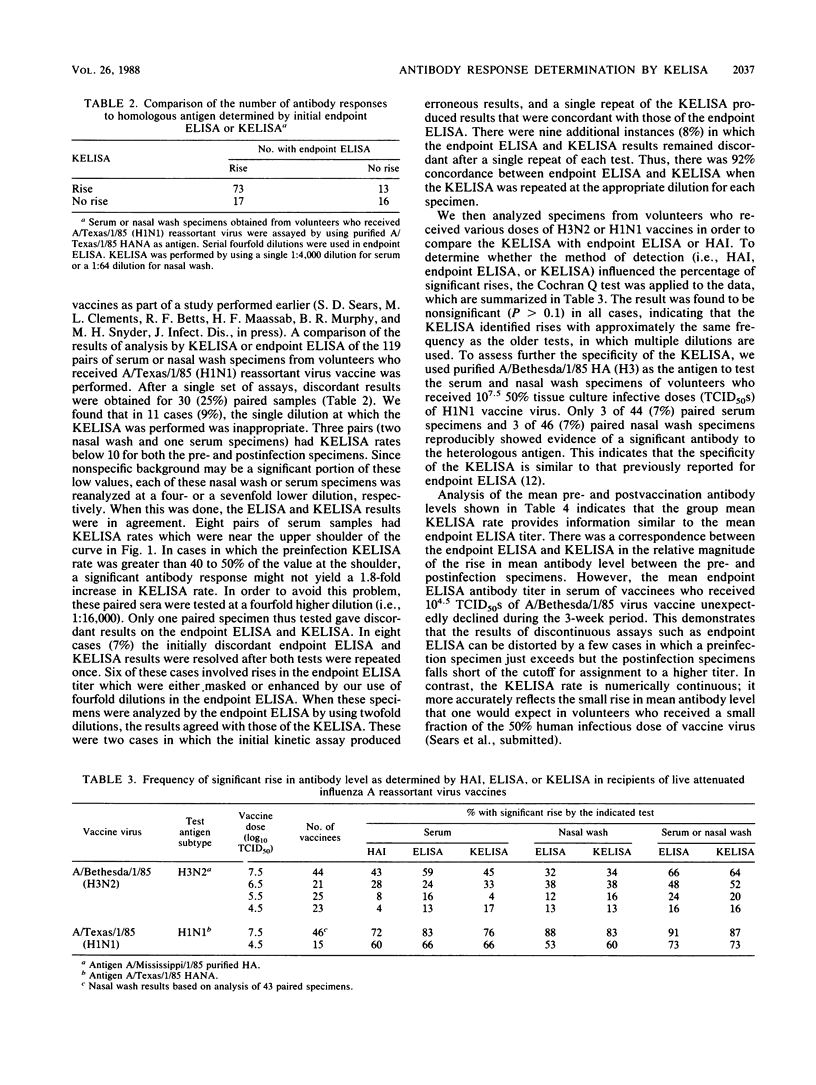
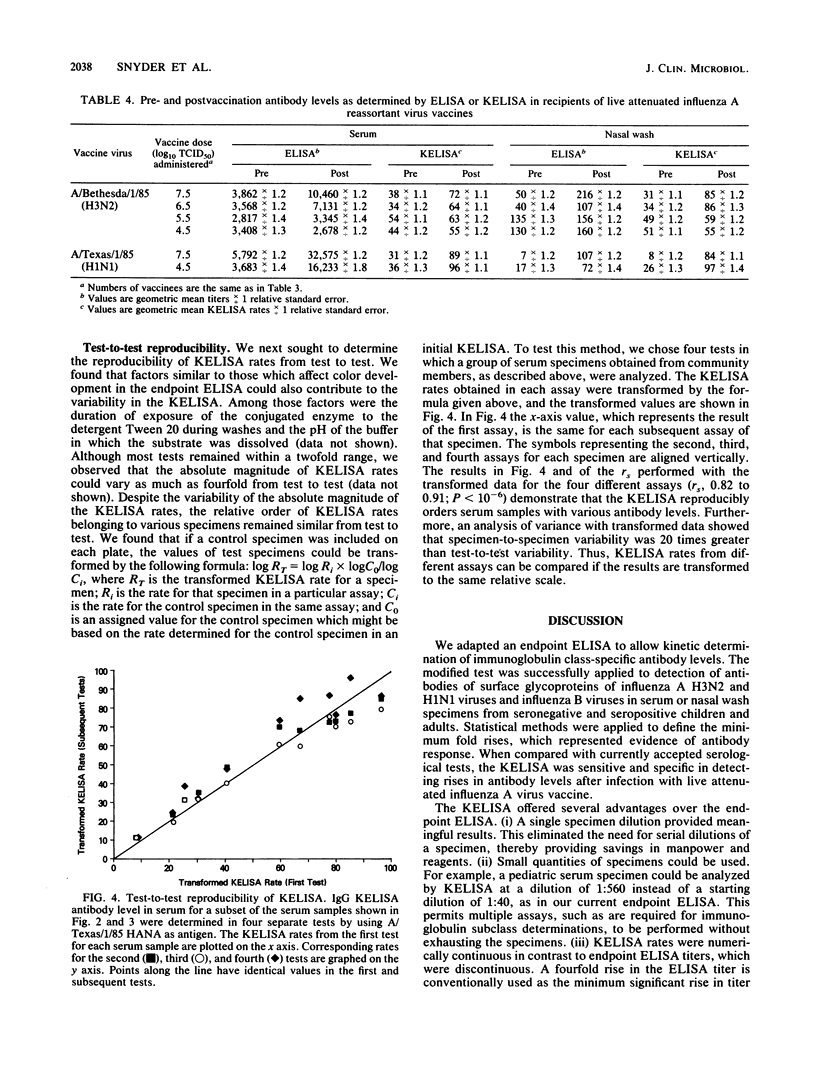
We modified an existing enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to be able to use new spectrophotometers which can measure the rate of color development in microtiter wells. This new kinetic-based ELISA (KELISA) required only a single dilution of specimen rather than the multiple dilutions required with endpoint ELISA. In addition, 10- to 100-fold-less specimen was required to perform the KELISA than the ELISA. The level of serum or nasal wash antibody against surface glycoproteins of influenza A or influenza B viruses determined by KELISA was reproducible and correlated highly with the results of endpoint ELISA or hemagglutination inhibition tests. The difference between the KELISA rates, which indicated than an antibody response to infection had occurred, was defined and was analogous to a 2.2-fold rise in titer for serum and a 3.4-fold rise in titer for nasal wash determined by endpoint ELISA. The KELISA was similar to endpoint ELISAs in its ability to detect rises in antibody level in paired serum or nasal wash specimens obtained from volunteers who received live attenuated influenza A reassortant virus vaccines. By eliminating the need for multiple dilutions, the use of KELISA offers the advantage of increasing the number of assays that can be performed by the same personnel compared with endpoint ELISA, while it maintains sensitivity and specificity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlough J. E., Jacobson R. H., Downing D. R., Marcella K. L., Lynch T. J., Scott F. W. Evaluation of a computer-assisted, kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of coronavirus antibodies in cats. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):202–217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.202-217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishai F. R., Galli R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to influenza A and B and parainfluenza type 1 in sera of patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):648–656. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.648-656.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg N., Masel D., Stoler M. Disparities in estimates of IgG bound to normal platelets. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):200–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delia S., Russo V., Vullo V., Aceti A., Ferone U. Determination of specific antibodies to influenza by ELISA. Lancet. 1977 Jun 25;1(8026):1364–1364. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92575-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Smith S. J., Noble G. R. Sensitivity and specificity of enzyme immunoassay for serodiagnosis of influenza A virus infections. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):644–651. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon M. W., Phillips D. J., Reimer C. B., Kendal A. P. Isotype-specific enzyme immunoassay for influenza antibody with monoclonal antibodies to human immunoglobulins. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):913–916. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.913-916.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Jr, Feldman S., Thompson J. M., Mahoney J. D., Wright P. F. Comparison of long-term systemic and secretory antibody responses in children given live, attenuated, or inactivated influenza A vaccine. J Med Virol. 1985 Dec;17(4):325–335. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambre C., Kasturi K. N. A microplate immunoenzyme assay for anti-influenza antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews H. M., Walls K. W., Huong A. Y. Microvolume, kinetic-dependent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for amoeba antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):221–224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.221-224.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Clements M. L., Tierney E. L., Black R. E., Stienberg J., Chanock R. M. Dose response of influenza A/Washington/897/80 (H3N2) avian-human reassortant virus in adult volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):225–229. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Phelan M. A., Nelson D. L., Yarchoan R., Tierney E. L., Alling D. W., Chanock R. M. Hemagglutinin-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies to influenza A and B viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):554–560. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.554-560.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Tierney E. L., Barbour B. A., Yolken R. H., Alling D. W., Holley H. P., Jr, Mayner R. E., Chanock R. M. Use of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect serum antibody responses of volunteers who received attenuated influenza A virus vaccines. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.342-347.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. A., Mayner R. E., Bucher D. J., Ennis F. A. Purification of influenza virus glycoproteins for the preparation and standardization of immunological potency testing reagents. J Biol Stand. 1980;8(3):233–242. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(80)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solano W., Giambrone J. J., Panangala V. S. Comparison of a kinetic-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (KELISA) and virus-neutralization test for infectious bursal disease virus. I. Quantitation of antibody in white Leghorn hens. Avian Dis. 1985 Jul-Sep;29(3):662–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solano W., Giambrone J. J., Panangala V. S. Comparison of a kinetic-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (KELISA) and virus-neutralization test for infectious bursal disease virus. II. Decay of maternal antibody in progeny from white Leghorns receiving various vaccination regimens. Avian Dis. 1986 Jan-Mar;30(1):126–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalnik S., Cowles J., Cox M. T., Baker D., Holt J., Blumberg N. A new technique in quantitative immunohematology: solid-phase kinetic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Vox Sang. 1983;45(6):440–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Hancock K., Maddison S. E., Beatty A. L., Moss D. M. Demonstration of species-specific and cross-reactive components of the adult microsomal antigens from Schistosoma mansoni and S. japonicum (MAMA and JAMA). J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2607–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Wilson B. C., Peralta J. M. Quantitative, single-tube, kinetic-dependent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (k-ELISA). Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:391–403. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff J. H., 3rd, Bradley R. E. An optimized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitative diagnosis of bovine fascioliasis. J Parasitol. 1986 Jun;72(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Immunological response to infection with human reovirus-like agent: measurement of anti-human reovirus-like agent immunoglobulin G and M levels by the method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.540-546.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


