Abstract
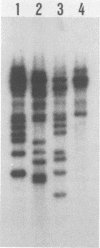
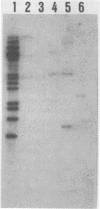
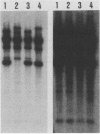
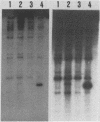
Three cloned segments of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA which are promising as clinical probes were identified. An MboI digest of DNA from a clinical isolate of M. tuberculosis was cloned into bacteriophage M13. To identify recombinants specific for the M. tuberculosis complex, plaque lifts were hybridized with M. bovis and M. kansasii DNA. Recombinants which selectively hybridized with M. bovis DNA were characterized by probing slot blots and restriction digests of DNA from various mycobacteria. Three recombinants that did not hybridize to a significant extent with DNA from nontuberculous mycobacteria were identified. These three probes are of special interest because they are each repeated multiple (10 to 16) times in the M. tuberculosis chromosome. These probes were also shown to be useful for fingerprinting strains for epidemiological studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Qasba P. K. Alkaline transfer of DNA to plastic membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford J. T., Bates J. H. Isolation of plasmids from mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):979–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.979-981.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Hindler J. A., Berlin O. G., Bruckner D. A. Rapid identification of Mycobacterium avium complex in culture using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1442–1445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1442-1445.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Crawford J. T., Bates J. H. Genetic relatedness among strains of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Analysis of restriction fragment heterogeneity using cloned DNA probes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jun;133(6):1065–1068. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.6.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez R., Hanna B. A. Evaluation of Gen-Probe DNA hybridization systems for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;8(2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadival G. V., Mazarelo T. B., Chaparas S. D. Sensitivity and specificity of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the detection of antigen in tuberculous meningitis cerebrospinal fluids. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):901–904. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.901-904.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Edwards F. F. Rapid identification using a specific DNA probe of Mycobacterium avium complex from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1551–1552. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1551-1552.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krambovitis E., McIllmurray M. B., Lock P. E., Hendrickse W., Holzel H. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis by latex particle agglutination. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1229–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92792-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappuoli R., Perugini M., Ratti G. DNA element of Corynebacterium diphtheriae with properties of an insertion sequence and usefulness for epidemiological studies. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):308–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.308-312.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. C., McMillan C., Coyle M. B. Whole chromosomal DNA probes for rapid identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1239–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1239-1243.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C. Diagnostic deoxyribonucleic acid probes for infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):82–101. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yáez M. A., Coppola M. P., Russo D. A., Delaha E., Chaparas S. D., Yeager H., Jr Determination of mycobacterial antigens in sputum by enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):822–825. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.822-825.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]