Abstract
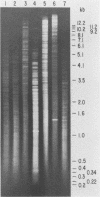
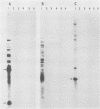
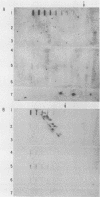
A repetitive sequence element was cloned from the primary etiological agent causing bovine leptospirosis in North America, Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis. This element was used to design a sensitive diagnostic probe which distinguishes hardjo-bovis from other pathogenic leptospires which commonly infect domestic animals in North America and discriminates between hardjo-bovis and the reference strain for serovar hardjo, hardjoprajitno. By using this probe, it was possible to identify infected cattle shedding hardjo-bovis in their urine. This is the first practical demonstration of a cloned DNA probe for leptospirosis, and it provides a sensitive method for studying the transmission and pathogenesis of L. interrogans infections. Control measures for L. interrogans infections may now be improved by rapidly and efficiently identifying infected animals.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botchan M. R. Bovine satellite I DNA consists of repetitive units 1,400 base pairs in length. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):288–292. doi: 10.1038/251288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Jr, Sulzer C. R., Pursell A. R. Improved microtechnique for the leptospiral microscopic agglutination test. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):976–980. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.976-980.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., O'Brien J. J., Bryson D. G., Mackie D. P. Bovine leptospirosis: some clinical features of serovar hardjo infection. Vet Rec. 1985 Aug 3;117(5):101–104. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.5.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., O'Brien J. J., Neill S. D., Bryson D. G. Bovine leptospirosis: experimental serovar hardjo infection. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Mar;11(3):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., O'Brien J. J., Neill S. D., Hanna J. Bovine leptospirosis: serological findings in aborting cows. Vet Rec. 1982 Feb 20;110(8):178–180. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.8.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., O'Brien J. J., Neill S., Hanna J., Bryson D. G. The isolation of a leptospire from an aborted bovine fetus. Vet Rec. 1976 Dec 4;99(23):458–459. doi: 10.1136/vr.99.23.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., Thiermann A. B. Isolation of leptospires from the genital tracts of Iowa cows. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Aug;47(8):1694–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Brom S., Martínez E., Piñero D., Romero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Reiterated DNA sequences in Rhizobium and Agrobacterium spp. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5782–5788. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5782-5788.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén L., Westin G., Shabo R., Aslund L., Perlmann H., Persson T., Wigzell H., Pettersson U. Analysis of clinical specimens by hybridisation with probe containing repetitive DNA from Plasmodium falciparum. A novel approach to malaria diagnosis. Lancet. 1984 Mar 10;1(8376):525–528. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90929-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göbel U. B., Geiser A., Stanbridge E. J. Oligonucleotide probes complementary to variable regions of ribosomal RNA discriminate between Mycoplasma species. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1969–1974. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B. DNA probe for detection of the Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo genotype hardjo-bovis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2236–2238. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2236-2238.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. B., Thiermann A. B., Foley J. Genetic and antigenic differences of serologically indistinguishable leptospires of serovar hardjo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2094–2097. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2094-2097.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. B., Wilton B. E., Robinson A. J. Identification of Leptospira serovars by restriction-endonuclease analysis. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):163–166. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michna S. W. Leptospirosis. Vet Rec. 1970 Apr 25;86(17):484–496. doi: 10.1136/vr.86.17.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar B. D., Chappel R. J., Adler B. Detection of leptospires in biological fluids using DNA hybridisation. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Oct;15(1-2):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction enzymes and their isoschizomers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15 (Suppl):r189–r217. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.suppl.r189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Doolittle W. F. Unusual physical organization of the Halobacterium genome. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):384–389. doi: 10.1038/295384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim B. K., Piessens W. F., Wirth D. F. A DNA probe cloned in Escherichia coli for the identification of Brugia malayi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 May;19(2):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra W. J., Schoone G. J., Ligthart G. S., ter Schegget J. Detection of Leptospira interrogans in clinical specimens by in situ hybridization using biotin-labelled DNA probes. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Apr;133(4):911–914. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-4-911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra W. J., Schoone G. J., ter Schegget J. Detection of leptospiral DNA by nucleic acid hybridisation with 32P- and biotin-labelled probes. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Aug;22(1):23–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B. Bovine leptospirosis: bacteriologic versus serologic diagnosis of cows at slaughter. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Dec;44(12):2244–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B. Experimental leptospiral infections in pregnant cattle with organisms of the Hebdomadis serogroup. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):780–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Foley J. W., White F. H., Kingscote B. F. Reclassification of North American leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroups Mini and Sejroe by restriction endonuclease analysis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Moseley S. L., Kingscote B. New method for classification of leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroup pomona by restriction endonuclease analysis: serovar kennewicki. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.585-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Zaal J., Schoone G. J., Terpstra W. J. DNA hybridization with hardjobovis-specific recombinant probes as a method for type discrimination of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):567–574. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. H., Sulzer K. R., Engel R. W. Isolations of Leptospira interrogans serovars hardjo, balcanica, and pomona from cattle at slaughter. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jul;43(7):1172–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]