Abstract
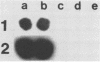
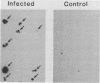
A 900-base-pair DNA fragment derived from a 9.5-kilobase plasmid in Yersinia pestis hybridized specifically with Y. pestis DNA. We demonstrated the feasibility of using this DNA fragment to detect plague bacilli directly in fleas, suggesting that this Y. pestis-specific DNA probe may be used for plague surveillance in the field. Additional applications for this DNA probe may include plague diagnosis and pathogenesis research.
Full text
PDF

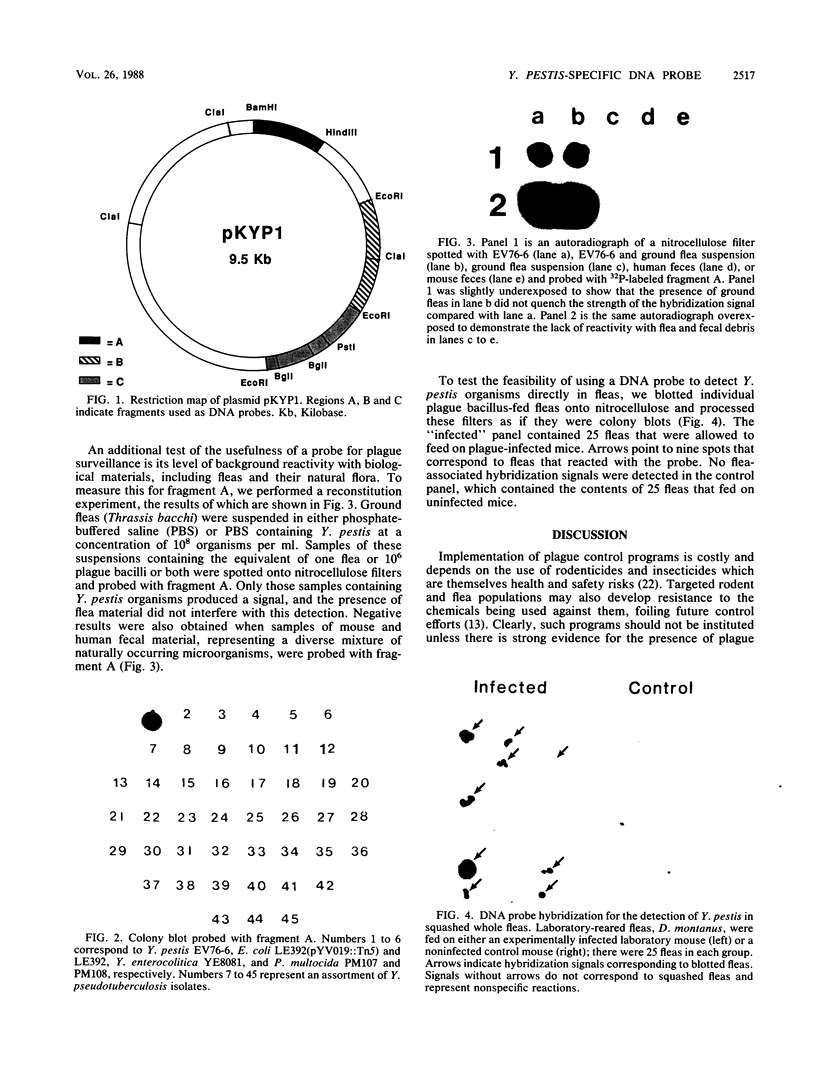


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Hakim A. H., Hull R. Studies towards the development of chemically synthesized non-radioactive biotinylated nucleic acid hybridization probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9965–9976. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEN-GURION R., HERTMAN I. Bacteriocin-like material produced by Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):289–297. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley E. D., Brubaker R. R., Janssen W. A., Surgalla M. J. Pesticins. 3. Expression of coagulase and mechanism of fibrinolysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):19–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.19-26.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley E. D., Surgalla M. J. Pesticinogeny: a characteristic useful for presumptive identification and isolation of Pasteurella pestis. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):915–918. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.915-918.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R., Beesley E. D., Surgalla M. J. Pasteurella pestis: Role of Pesticin I and Iron in Experimental Plague. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., SHIMADA T., SUYEMOTO W., WHEELER C. M., YAMAKAWA Y. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in various flea species. III. Transmission of avirulent strains of Past. pestis by Xenopsylla cheopis. J Infect Dis. 1956 Jul-Aug;99(1):72–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/99.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., WHEELER C. M., SUYEMOTO W., SHIMADA T., YAMAKAWA Y. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in various flea species. I. Infection of flea species with avirulent strains of Past. pestis. J Infect Dis. 1956 Jan-Feb;98(1):103–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/98.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh D. C. Specific effect of temperature upon transmission of the plague bacillus by the oriental rat flea, Xenopsylla cheopis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Mar;20(2):264–273. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goncharov E. K., Mishan'kin B. N., Sorokin V. M. Restriktsionnaia karta plazmidy pestitsinogennosti pYP1 Yersinia pestis. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1986 Apr;(4):28–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson B. W., Kartman L., Prince F. M. Pasteurella pestis detection in Fleas by fluorescent antibody staining. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(5):709–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., WINTER C. C. Rapid identification of Pasteurella pestis with fluorescent antibody. III. Staining Pasteurella pestis in tissue impression smears. J Infect Dis. 1959 May-Jun;104(3):288–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/104.3.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Tirapat C., Chaicumpa W., Sakuldaipeara T., Falkow S. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization using three enterotoxin gene probes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):863–869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Falkow S. Virulence-associated plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., KARTMAN L., McMANUS A. G. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. II. Experimental blocking of Xenopsylla cheopis with an avirulent strain of P. pestis. Science. 1954 Dec 31;120(3131):1101–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3131.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan T. J., Tsuchiya K. R., Carter L. G. Isolation of pathogens other than Yersinia pestis during plague investigations. J Wildl Dis. 1979 Oct;15(4):505–510. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-15.4.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter D. B., Gerloff R. K. Deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization among some species of the genus Pasteurella. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1838–1839. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1838-1839.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Tiemeier D. C., Polsky F., Edgell M. H., Seidman J. G., Leder A., Enquist L. W., Norman B., Leder P. Cloning specific segments of the mammalian genome: bacteriophage lambda containing mouse globin and surrounding gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4406–4410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. C., MOODY M. D. Rapid identification of Pasteurella pestis with fluorescent antibody. I. Production of specific antiserum with whole cell Pasteurella pestis antigen. J Infect Dis. 1959 May-Jun;104(3):274–280. doi: 10.1093/infdis/104.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. C., MOODY M. D. Rapid identification of Pasteurella pestis with fluorescent antibody. II. Specific identification of Pasteurella pestis in dried smears. J Infect Dis. 1959 May-Jun;104(3):281–287. doi: 10.1093/infdis/104.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. E., Gordon D., Poland J. D., Barnes A. M. Recommendations for the control of Yersinia pestis infections. Recommendations from the CDC. Infect Control. 1980 Sep-Oct;1(5):324–329. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700053273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. E., Harrison D. N., Quan T. J., Mullins J. L., Barnes A. M., Cavanaugh D. C. Atypical plague bacilli isolated from rodents, fleas, and man. Am J Public Health. 1978 Mar;68(3):262–264. doi: 10.2105/ajph.68.3.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]