Abstract
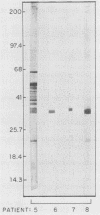
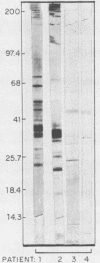
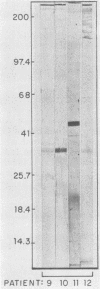
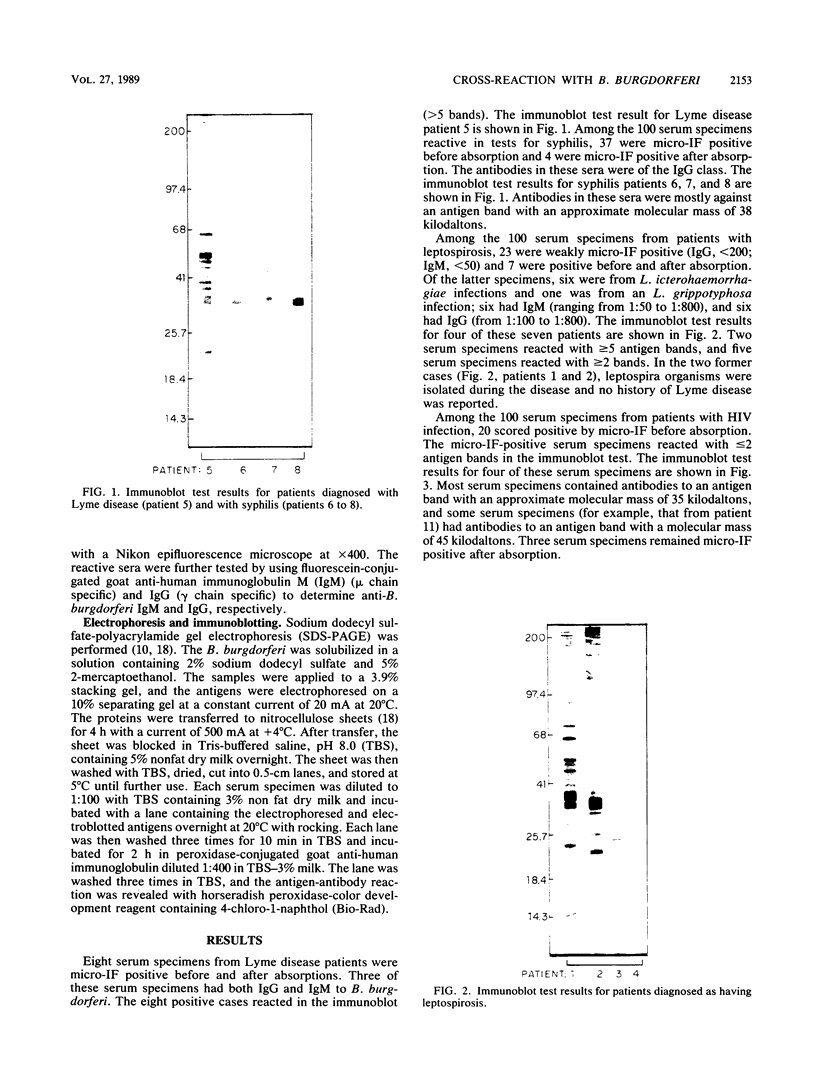
We have studied the cross-reaction with Borrelia burgdorferi of sera positive for leptospirosis, syphilis, or human immunodeficiency virus by using the microimmunofluorescence test (micro-IF). The percentage of sera reactive in the micro-IF before absorption varied from 7 to 37% and was reduced to 3 to 8% after absorption with a commercial Reiter treponemal antigen. The cross-reaction of sera positive for syphilis or human immunodeficiency virus was distinguished from the homologous reaction with sera from patients with Lyme disease in the immunoblot test results. However, the cross-reaction could not always be distinguished from the homologous reaction with sera from patients with leptospirosis whose sera scored positive in the micro-IF for B. burgdorferi.
Full text
PDF
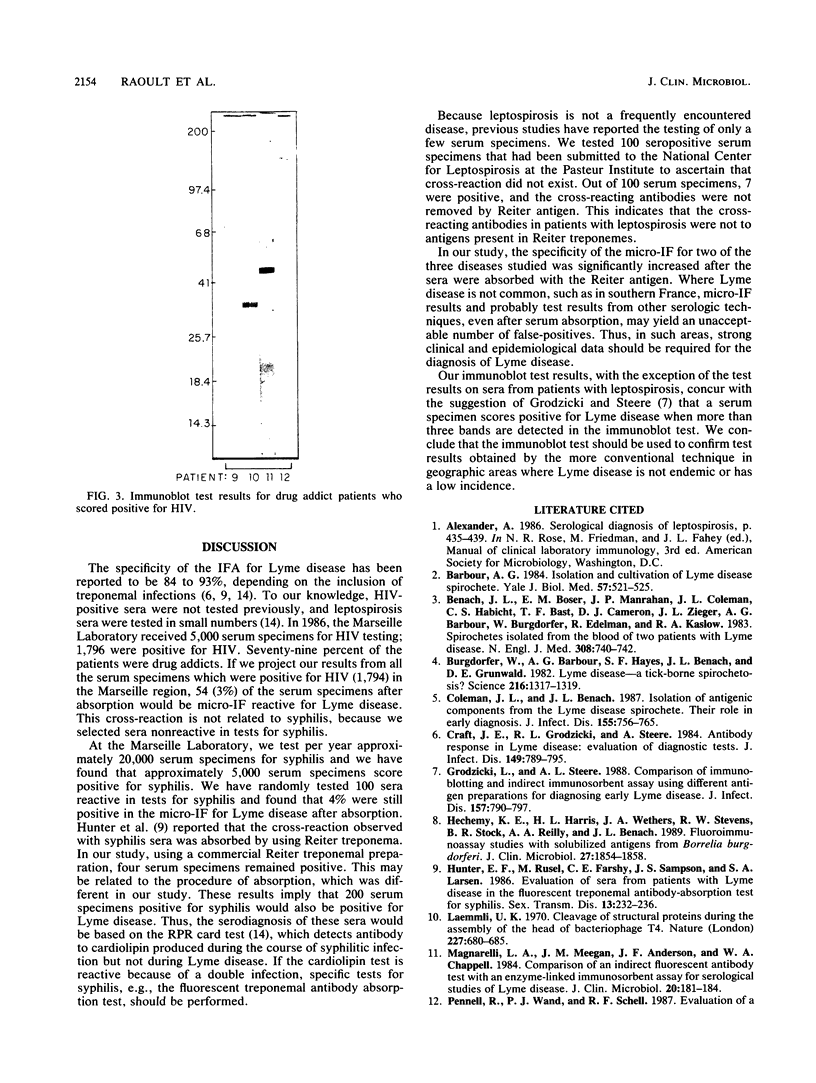

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Antibody response in Lyme disease: evaluation of diagnostic tests. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):789–795. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Harris H. L., Wethers J. A., Stevens R. W., Stock B. R., Reilly A. A., Benach J. L. Fluoroimmunoassay studies with solubilized antigens from Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1854–1858. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1854-1858.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. F., Russell H., Farshy C. E., Sampson J. S., Larsen S. A. Evaluation of sera from patients with Lyme disease in the fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption test for syphilis. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):232–236. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Meegan J. M., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Comparison of an indirect fluorescent-antibody test with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological studies of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.181-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennell D. R., Wand P. J., Schell R. F. Evaluation of a quantitative fluorescence immunoassay (FIAX) for detection of serum antibody to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2218–2220. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2218-2220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Hechemy K. E., Lecam C., Enea M., Tamalet J. Réactions croisées dans la maladie de Lyme. Intérêt du Western blot. Presse Med. 1988 Mar 19;17(10):485–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell H., Sampson J. S., Schmid G. P., Wilkinson H. W., Plikaytis B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect immunofluorescence assay for Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Bartenhagen N. H., Spieler P. N., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Hutchinson G. J., Green J., Snydman D. R., Taylor E. The clinical spectrum and treatment of Lyme disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):453–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernstedt G., Eriksson G., Enfors W., Jörbeck H., Svenungsson B., Sköldenberg B., Granström M. Erythema chronicum migrans in Sweden: clinical manifestations and antibodies to Ixodes ricinus spirochete measured by indirect immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986;18(3):217–224. doi: 10.3109/00365548609032330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Schierz G., Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V. European erythema migrans disease and related disorders. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):463–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]