Abstract
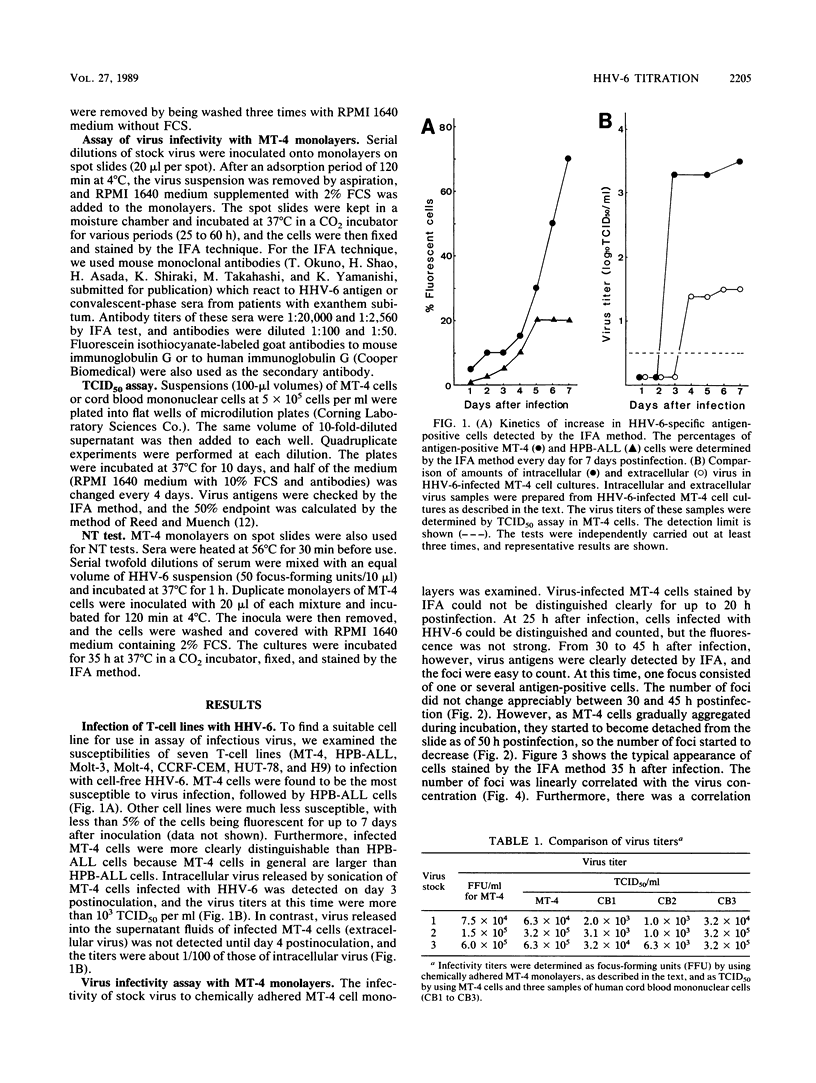
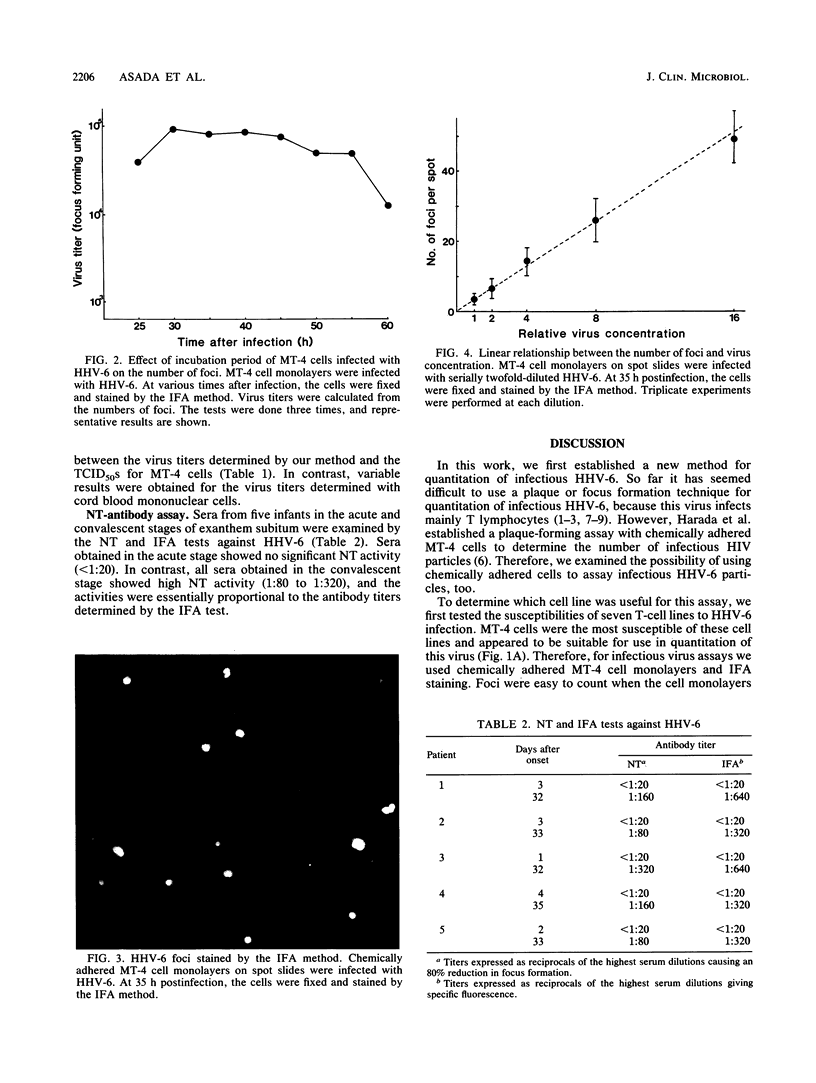
The susceptibilities of seven T-cell lines to human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) infection were examined. MT-4 cells were the most susceptible of these lines to infection with this virus. Therefore, chemically adhered MT-4 cell monolayers were used for infectious HHV-6 assay by indirect immunofluorescent-antibody (IFA) staining. When cell monolayers were fixed 30 to 45 h postinfection, the foci stained with IFA were easy to count and a linear relationship was observed between the number of foci and the virus concentration. MT-4 cell monolayers were also used for a focus reduction neutralizing-antibody test. In this test, sera from patients in the convalescent stage of exanthem subitum all showed significant neutralizing activity (1:80 to 1:320), whereas sera from patients in the acute stage of disease showed no detectable neutralizing activity. The titers of neutralizing antibody correlated well with the levels of anti-HHV-6 antibodies detected by IFA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ablashi D. V., Salahuddin S. Z., Josephs S. F., Imam F., Lusso P., Gallo R. C., Hung C., Lemp J., Markham P. D. HBLV (or HHV-6) in human cell lines. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):207–207. doi: 10.1038/329207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agut H., Guetard D., Collandre H., Dauguet C., Montagnier L., Miclea J. M., Baurmann H., Gessain A. Concomitant infection by human herpesvirus 6, HTLV-I, and HIV-2. Lancet. 1988 Mar 26;1(8587):712–712. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91520-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing R. G., Sewankambo N., Serwadda D., Honess R., Crawford D., Jarrett R., Griffin B. E. Isolation of human lymphotropic herpesviruses from Uganda. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):390–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou S., Gompels U. A., Craxton M. A., Honess R. W., Ward K. DNA homology between a novel human herpesvirus (HHV-6) and human cytomegalovirus. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):63–64. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of HTLV-III/LAV in HTLV-I-carrying cells MT-2 and MT-4 and application in a plaque assay. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):563–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2992081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Pellett P., Stewart J., Goldsmith C., Sanderlin K., Black J., Warfield D., Feorino P. Characteristics of human herpesvirus-6. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1271–1273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusso P., Markham P. D., Tschachler E., di Marzo Veronese F., Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Pahwa S., Krohn K., Gallo R. C. In vitro cellular tropism of human B-lymphotropic virus (human herpesvirus-6). J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1659–1670. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusso P., Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Gallo R. C., Di Marzo Veronese F., Markham P. D. Diverse tropism of HBLV (human herpesvirus 6) Lancet. 1987 Sep 26;2(8561):743–743. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J. Membrane and other phenotypes of leukemia cells. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;132E:215–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder R. S., Briggs M., Cameron C. H., Honess R., Robertson D., Whittle H. A novel lymphotropic herpesvirus. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):390–392. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Okuno T., Shiraki K., Takahashi M., Kondo T., Asano Y., Kurata T. Identification of human herpesvirus-6 as a causal agent for exanthem subitum. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



