Abstract
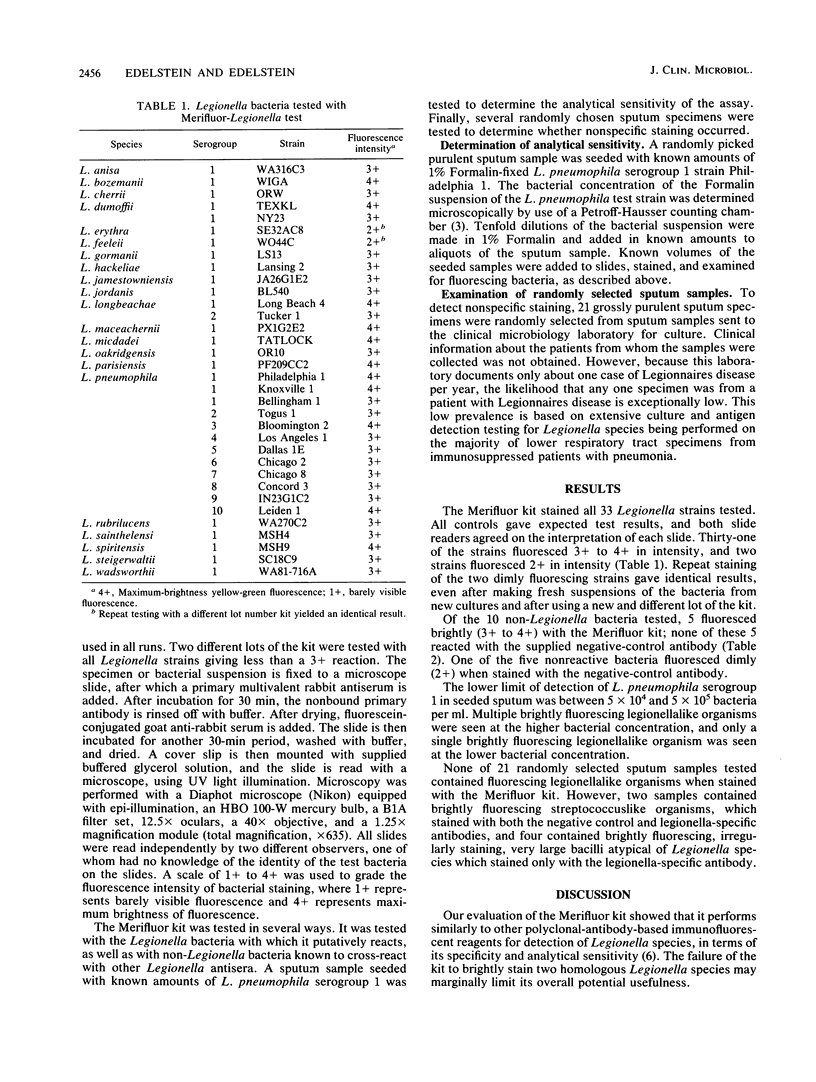
We evaluated a 33-valent polyclonal indirect immunofluorescent-reagent kit (Merifluor-Legionella; Meridian Diagnostics Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio) made for the detection of Legionella species by testing bacterial isolates, seeded sputum, and negative sputum samples. Use of the reagent according to the directions of the manufacturer gave false-negative staining of homologous culture isolates due to a prozone phenomenon; this was solved by diluting test strain suspensions. After this change in testing protocol was made, the reagent gave bright fluorescent staining with 31 of the 33 Legionella strains with which it supposedly reacts. Strongly reacting Legionella strains included the type strains of L. pneumophila serogroups 1 to 10, L. longbeachae serogroups 1 and 2, and serogroup 1 of L. anisa, L. bozemanii, L. cherrii, L. dumoffii, L. gormanii, L. hackeliae, L. jamestowniensis, L. jordanis, L. maceachernii, L. micadedi, L. oakridgensis, L. rubrilucens, L. sainthelensi, L. spiritensis, L. steigerwaltii, and L. wadsworthii. Type strains of L. erythra and L. feeleii fluoresced only dimly with the reagent. Of 10 non-Legionella bacteria known to cross-stain with other polyvalent antisera, 5 also cross-reacted with the Merifluor reagent; these included 3 Bacteroides fragilis and 2 Pseudomonas fluorescens strains. The lower limit of detection of L. pneumophila serogroup 1 in seeded sputum was about 5 x 10(4) to 5 x 10(5) cells per ml. None of 21 randomly collected sputum specimens tested contained fluorescing legionellalike organisms, but 6 specimens did contain brightly fluorescing bacteria atypical in morphology for Legionella species. The Merifluor-Legionella kit appears to perform as well as other polyclonal immunofluorescent reagents used for detection of Legionella species. Because of the cross-reactions observed, which are common to all polyclonal reagents, utilization of this reagent for either bacterial identification or detection must be performed in combination with culture.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridge J. A., Edelstein P. H. Oropharyngeal colonization with Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1108–1112. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1108-1112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., Bibb W. F., McKinney R. M. Retrospective examination of lung tissue specimens for the presence of Legionella organisms: comparison of an indirect fluorescent-antibody system with direct fluorescent-antibody testing. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):468–472. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.468-472.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cercenado E., Edelstein P. H., Gosting L. H., Sturge J. C. Legionella micdadei and Legionella dumoffii monoclonal antibodies for laboratory diagnosis of Legionella infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2163–2167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2163-2167.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Improved semiselective medium for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from contaminated clinical and environmental specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):298–303. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.298-303.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Laboratory diagnosis of infections caused by legionellae. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;6(1):4–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02097182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., McKinney R. M., Meyer R. D., Edelstein M. A., Krause C. J., Finegold S. M. Immunologic diagnosis of Legionnaires' disease: cross-reactions with anaerobic and microaerophilic organisms and infections caused by them. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):652–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C., Edelstein P. H., Goldstein L. C., Sturge J. C., Plorde J. J. Comparison of cross-staining reactions by Pseudomonas spp. and fluorescein-labeled polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies directed against Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):647–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.647-649.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Drasar V., Thacker W. L., Benson R. F., Schindler J., Potuznikova B., Mayberry W. R., Brenner D. J. Legionella moravica sp. nov. and Legionella brunensis sp. nov. isolated from cooling-tower water. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Jul-Aug;139(4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


