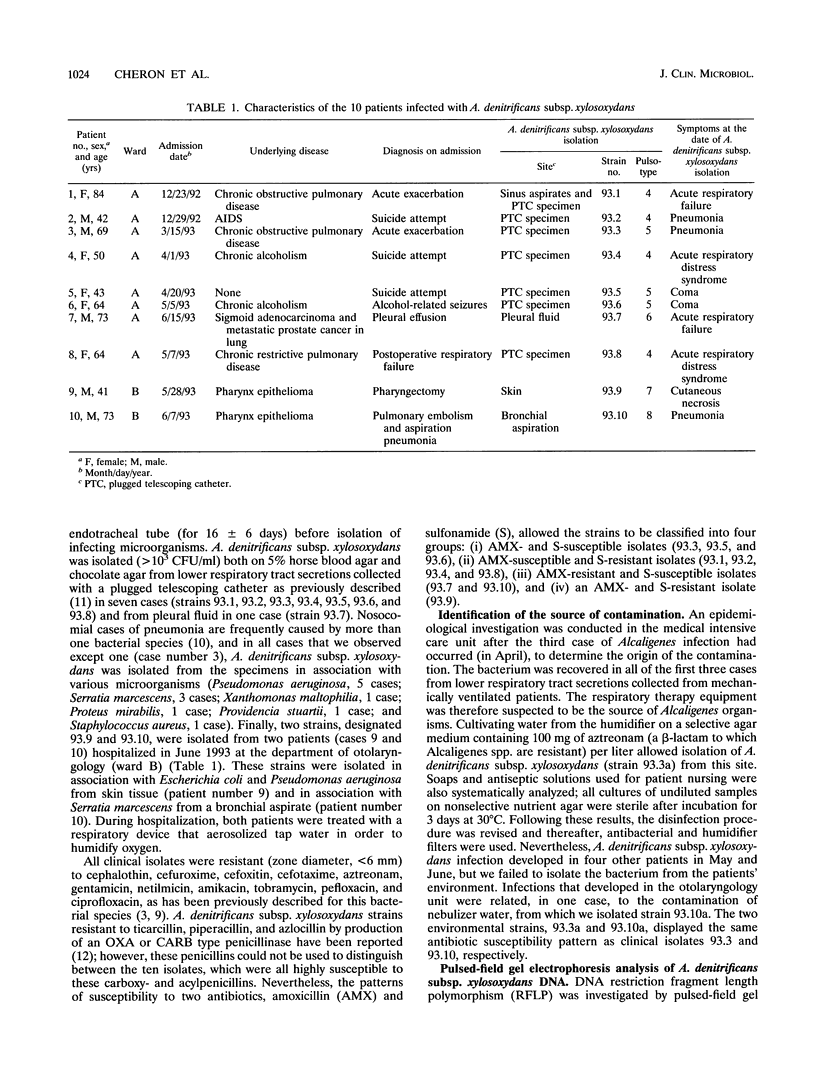
Abstract
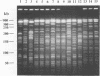
We demonstrate that DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism determined by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is very useful in the investigation of the epidemiology of hospital-acquired infections caused by Alcaligenes denitrificans subsp. xylosoxydans. This approach showed that hospital-acquired infections caused by this opportunistic pathogen over a 6-month period in 10 patients hospitalized in an intensive care unit and a surgical unit were not a true outbreak. In addition, this molecular typing method established that the respiratory therapy equipment was the source of the contamination of two patients.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahrn-Hansen B., Alstrup P., Dessau R., Fuursted K., Knudsen A., Olsen H., Oxhøj H., Petersen A. R., Siboni A., Siboni K. Outbreak of infection with Achromobacter xylosoxidans from contaminated intravascular pressure transducers. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Jul;12(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Hansen W., Freney J., Yourassowsky E. In vitro susceptibility of Alcaligenes denitrificans subsp. xylosoxidans to 24 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):276–278. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouby A., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bouziges N., Bourg G., Mesnard R., Bouvet P. J. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for investigation of hospital outbreaks of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1588–1591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1588-1591.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiyama S., Ohta M., Shimokata K., Kato N., Takeuchi J. Genomic DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as an epidemiological marker for study of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2690–2695. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2690-2695.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand C., Anaissie E. Bacteremia due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans in patients with cancer. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;14(2):479–484. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.2.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham L. H., Brun-Buisson C., Legrand P., Rauss A., Verra F., Brochard L., Lemaire F. Diagnosis of nosocomial pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. Comparison of a plugged telescoping catheter with the protected specimen brush. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 May;143(5 Pt 1):1055–1061. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.5_Pt_1.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A., Mensah K., Fournier G., Freney J. Two resistance phenotypes to beta-lactams of Alcaligenes denitrificans subsp. xylosoxydans in relation to beta-lactamase types. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Apr;25(4):698–700. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.4.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reina J., Antich M., Siquier B., Alomar P. Nosocomial outbreak of Achromobacter xylosoxidans associated with a diagnostic contrast solution. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Aug;41(8):920–921. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.8.920-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reverdy M. E., Freney J., Fleurette J., Coulet M., Surgot M., Marmet D., Ploton C. Nosocomial colonization and infection by Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):140–143. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.140-143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Miguel V. V., Lavery J. P., York J. C., Lisse J. R. Achromobacter xylosoxidans septic arthritis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Nov;34(11):1484–1485. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeta S., Yasunaga Y., Honzumi K., Okamura H., Kumata R., Endo S. Cerebral ventriculitis associated with Achromobacter xylosoxidans. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;31(2):156–161. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear J. B., Fuhrer J., Kirby B. D. Achromobacter xylosoxidans (Alcaligenes xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans) bacteremia associated with a well-water source: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):598–599. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.598-599.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh R. D., Klein N. C., Cunha B. A. Achromobacter xylosoxidans osteomyelitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;16(1):176–178. doi: 10.1093/clinids/16.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]