Abstract
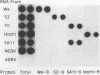
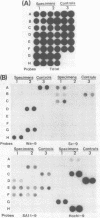
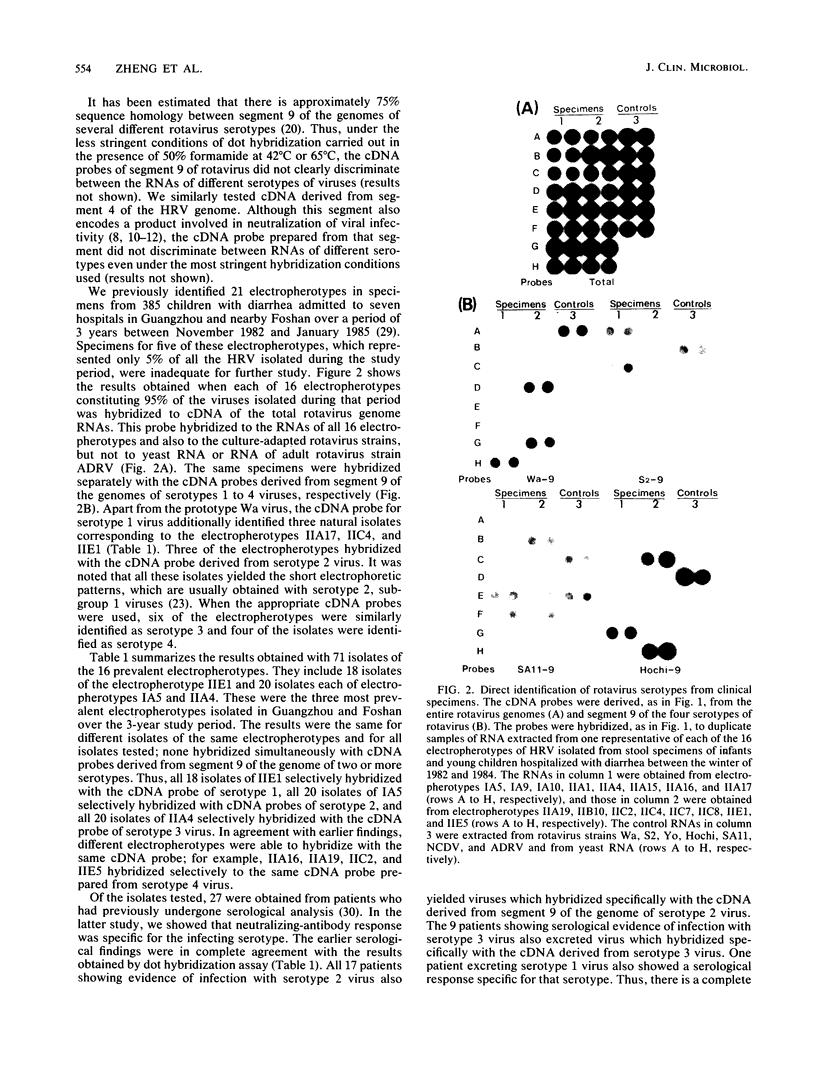
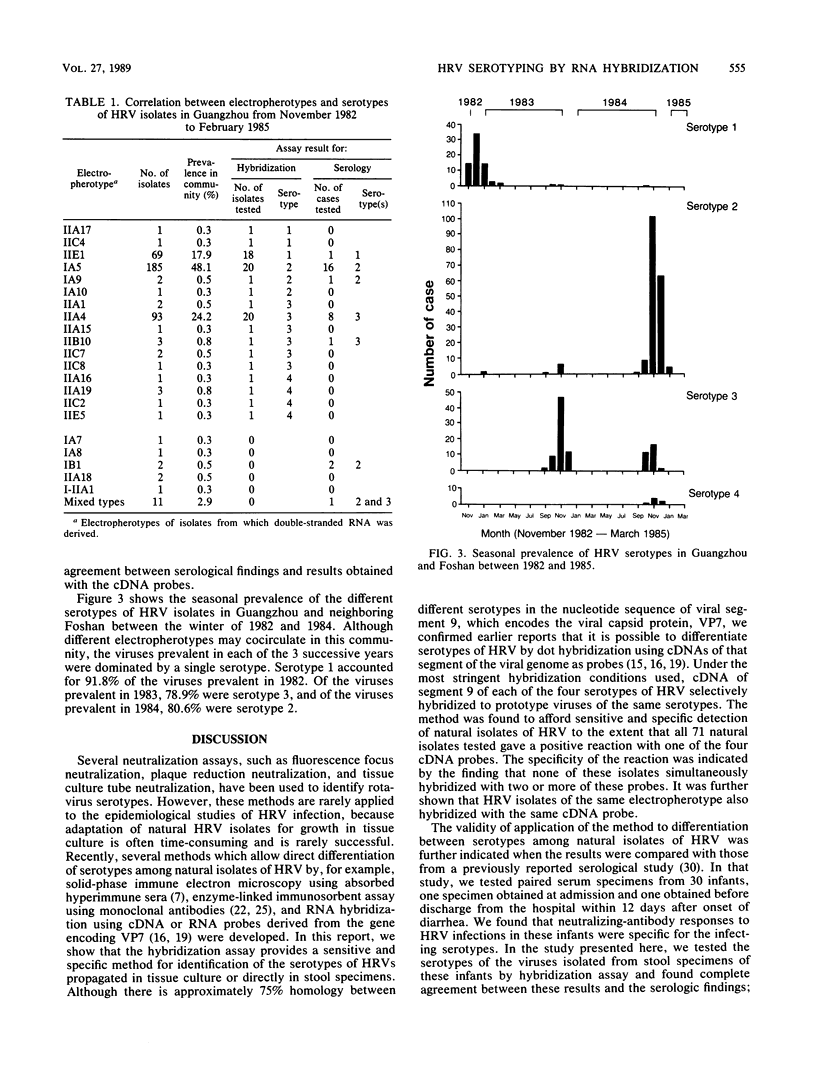
Under stringent hybridization conditions, cDNA of segment 9 of the rotavirus genome, which codes for the viral protein VP7, permitted differentiation of serotypes of culture-grown rotaviruses and natural isolates of human rotaviruses directly from clinical specimens. This was evident for the following reasons. (i) The cDNA of one serotype selectively hybridized with the RNA of the same serotype of culture-grown rotaviruses. (ii) Natural isolates of the virus thus identified as serotype 2 were also those which gave the short electrophoretic pattern characteristic of the genome of serotype 2, subgroup 1 viruses. Isolates having the long electrophoretic pattern characteristic of the genome of subgroup 2 viruses were identified as serotype 1, 3, or 4 by this method. (iii) For patients who had previously undergone serological analysis, the serotypes being excreted were the same serotypes against which there was the most marked serum neutralizing antibody response. Although the virus population was genetically diverse, the preponderance of the population prevalent in Guangzhou and Foshan in each of the three successive years between 1982 and 1985 comprised a single serotype. The dominant serotype changed from one year to another, but there was minimal cocirculation of different serotypes in this community. All virus isolates belonged to serotype 1,2,3, or 4, and there was no evidence to suggest that the other human rotavirus serotypes were prevalent in this community.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beards G. M., Pilfold J. N., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus serotypes by serum neutralisation. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):231–237. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Oldham G. Avirulent rotavirus infections protect calves from disease with and without inducing high levels of neutralizing antibody. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2311–2317. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Yokoyama T., Nakata S., Morita Y., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Nakao T. Protective effect of naturally acquired homotypic and heterotypic rotavirus antibodies. Lancet. 1986 Aug 23;2(8504):417–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Hoshino Y., Bell L. M., Groff J., Hess G., Bachman P., Offit P. A. Rotavirus isolate WI61 representing a presumptive new human serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1757–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1757-1762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Estes M. K., Rangelova S. M., Shindarov L. M., Melnick J. L., Graham D. Y. Detection of antigenically distinct rotaviruses from infants. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):523–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.523-526.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Passarani N., Battaglía M., Percivalle E. Rapid serotyping of human rotavirus strains by solid-phase immune electron microscopy. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):273–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.273-278.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. Gene coding assignments for growth restriction, neutralization and subgroup specificities of the W and DS-1 strains of human rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):313–320. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Analysis by plaque reduction neutralization assay of intertypic rotaviruses suggests that gene reassortment occurs in vivo. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):290–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.290-294.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Flores J., Greenberg H. B. Identification of the rotaviral gene that codes for hemagglutination and protease-enhanced plaque formation. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Approaches to immunization of infants and young children against gastroenteritis due to rotaviruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):459–469. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Imai M., Bellamy A. R., Ikegami N., Furuichi Y., Summers D., Nuss D. L., Deibel R. Diagnosis of rotavirus infection with cloned cDNA copies of viral genome segments. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):509–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.509-512.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Imai M., Ikegami N., Bellamy A. R., Summers D., Nuss D. L., Deibel R., Furuichi Y. cDNA probes of individual genes of human rotavirus distinguish viral subgroups and serotypes. J Virol Methods. 1987 Mar;15(4):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Offit P. A., Estes M. K. Identification of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome segment 3 product. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Flores J., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genetic relatedness among human rotavirus genes coding for VP7, a major neutralization protein, and its application to serotype identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1269–1274. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1269-1274.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. A., Iwamoto A., Ikegami N., Nomoto A., Furuichi Y. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the serotype-specific antigen of human (Wa) rotavirus: comparison with the homologous genes from simian SA11 and UK bovine rotaviruses. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):860–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.860-862.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simhon A., Chrystie I. L., Totterdell B. M., Banatvala J. E., Rice S. J., Walker-Smith J. A. Sequential rotavirus diarrhoea caused by virus of same subgroup. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1174–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90627-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. S., Kum W. W., Lam B., Yeung C. Y., Ng M. H. Molecular epidemiology of human rotavirus infection in children in Hong Kong. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):660–664. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.660-664.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Morita Y., Greenberg H. B., Urasawa S. Direct serotyping of human rotavirus in stools by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using serotype 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-specific monoclonal antibodies to VP7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Zheng S. L., Rosen B. I., Knight N., Gourley N. E., Ramig R. F. Protection between different serotypes of bovine rotavirus in gnotobiotic calves: specificity of serum antibody and coproantibody responses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1052–1058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1052-1058.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James H. D., Jr, Pittman A. L., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Direct isolation in cell culture of human rotaviruses and their characterization into four serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.310-317.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B. J., Han S. X., Yan Y. K., Liang X. R., Ma G. Z., Yang Y., Ng M. H. Development of neutralizing antibodies and group A common antibodies against natural infections with human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1506–1512. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1506-1512.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]