Abstract
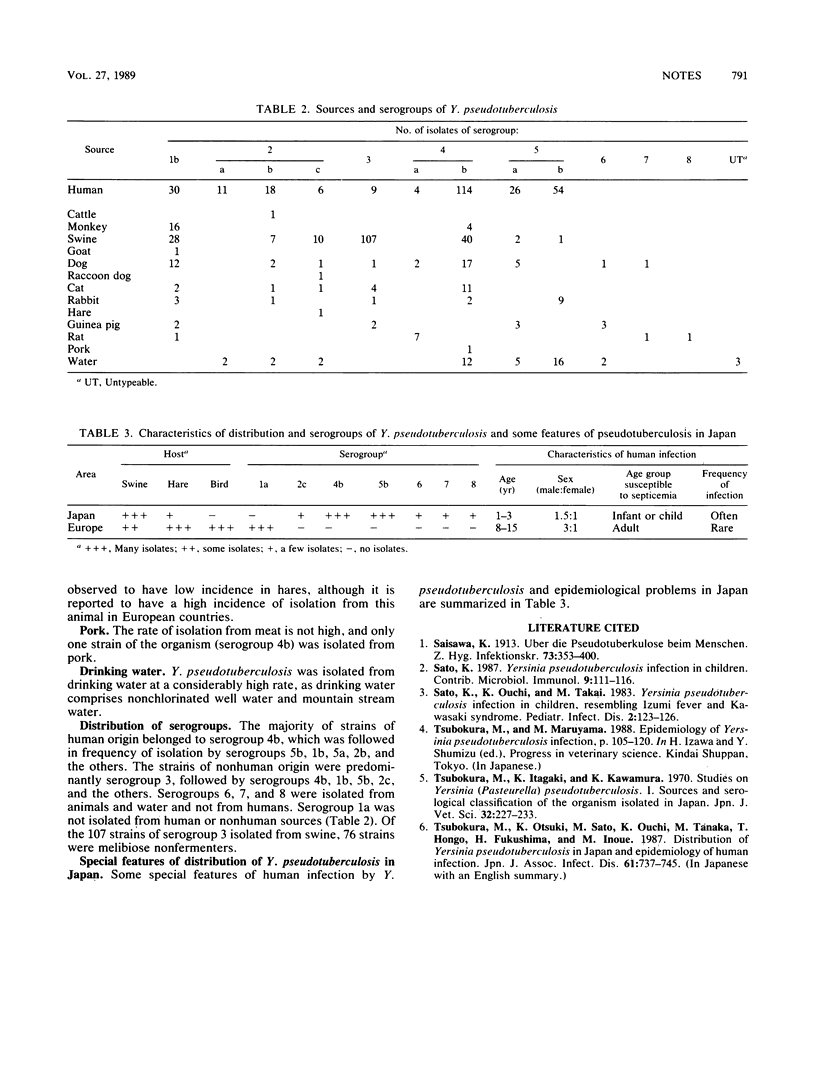
The incidence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis isolation from humans, animals, water, and pork in Japan is presented on the basis of a review of the literature and serotyping of 633 strains referred to our laboratory. Most of the strains belonged to serogroup 4b, followed in frequency of isolation by serogroups 3, 1b, 5b, 5a, and the others, whereas serogroup 1a has not been detected. Although strains were isolated from 11 species of animals, none were isolated from birds.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Sato K., Ouchi K., Taki M. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection in children, resembling Izumi fever and Kawasaki syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;2(2):123–126. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198303000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection in children. Clinical manifestations and epidemiology. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:111–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubokura M., Itagaki K., Kawamura K. Studies on Yersinia (Pasteurella) pseudotuberculosis. I. Sources and serological classification of the organism isolated in Japan. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1970 Oct;32(5):227–233. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.32.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubokura M., Otsuki K., Sato K., Ouchi K., Tanaka M., Hongo T., Fukushima H., Inoue M. [Distribution of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in Japan and epidemiology of human infection]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1987 Jul;61(7):737–745. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.61.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


