Abstract
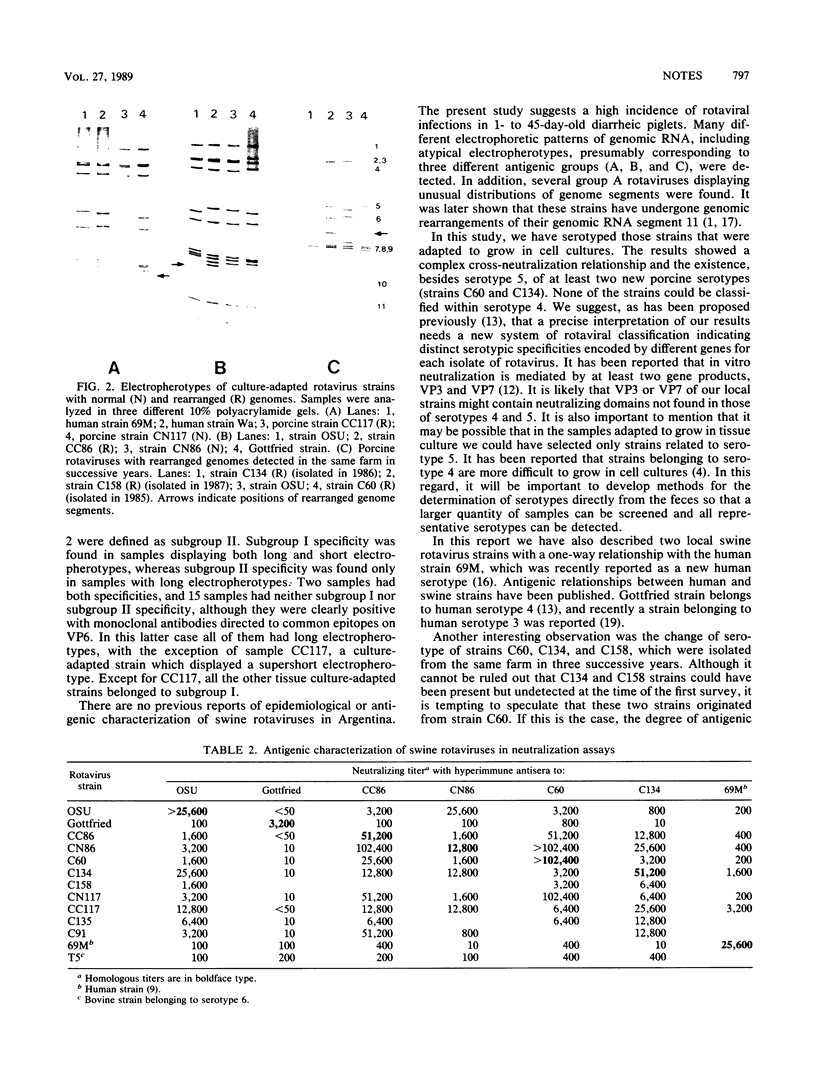
Fecal samples from 156 diarrheic piglets were collected from several herds located in two main breeding areas of Argentina. Rotaviruses were detected in 60 samples (38.4%) by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and in 55 samples by a group A-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). All samples which were positive by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and negative by ELISA had elicited atypical electropherotypes resembling those of group B or C. ELISA-positive samples showing genome rearrangements were also detected (R.C. Bellinzoni, N.M. Mattion, O.R. Burrone, S.A. González, J.L. La Torre, and E.A. Scodeller, J. Clin. Microbiol. 25:952-954, 1987; N.M. Mattion, S.A. González, O.R. Burrone, R.C. Bellinzoni, J.L. La Torre, and E.A. Scodeller, J. Gen. Virol. 69:695-698, 1988). By subgrouping with monoclonal antibodies, it was found that of 32 positive samples, 13 belonged to subgroup I, 2 belonged to subgroup II, 2 samples had both specificities, and 15 samples were neither subgroup I nor subgroup II (non-I/II). In addition, 10 samples were adapted to grow in tissue culture, cloned, and serotyped by means of neutralization assays. Two samples were classified as serotype 5, and none of them were classified as serotype 4. The other strains showed only a one-way relationship with serotype 5 and can be tentatively classified as new porcine serotypes. Two samples with rearranged genomes had a one-way relationship with antiserum to human strain 69M, which displays a supershort electropherotype and was classified as a new human serotype (S. Matsuno, A. Hasegawa, A. Mukoyama, and S. Inouye, J. Virol. 54:623-624, 1985). At one farm, similar rearranged strains were detected during three successive years. Serotype changes were found between the isolates of the first and the second year, suggesting that a high degree of antigenic variability went on during continuous circulation of these strains in the field.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellinzoni R. C., Mattion N. M., Burrone O., Gonzalez A., La Torre J. L., Scodeller E. A. Isolation of group A swine rotaviruses displaying atypical electropherotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):952–954. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.952-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Saif L. J., Cross R. F., Agnes A. G., Theil K. W. Rotavirus as a cause of diarrhea in pigs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Feb 15;172(4):458–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J. Isolation and serotyping of porcine rotaviruses and antigenic comparison with other rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.105-111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Brown J. F. Prevalence of antibody to typical and atypical rotaviruses in pigs. Vet Rec. 1985 Jan 12;116(2):50–50. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.2.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Battaglia M., Milenesi G., Passarani N., Percivalle E., Cattaneo E. Serotyping of cell culture-adapted subgroup 2 human rotavirus strains by neutralization. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):722–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.722-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Inouye S., Matsuno S., Yamaoka K., Eko R., Suharyono W. Isolation of human rotaviruses with a distinct RNA electrophoretic pattern from Indonesia. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(6):719–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Gorziglia M., Valdesuso J., Askaa J., Glass R. I., Kapikian A. Z. An equine rotavirus (FI-14 strain) which bears both subgroup I and subgroup II specificities on its VP6. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):488–496. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Banks C. E., James H. D., Jr, Flores J., Chanock R. M. Antigenic characterization of human and animal rotaviruses by immune adherence hemagglutination assay (IAHA): evidence for distinctness of IAHA and neutralization antigens. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):415–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.415-425.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattion N., González S. A., Burrone O., Bellinzoni R., La Torre J. L., Scodeller E. A. Rearrangement of genomic segment 11 in two swine rotavirus strains. J Gen Virol. 1988 Mar;69(Pt 3):695–698. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-3-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagesha H. S., Holmes I. H. New porcine rotavirus serotype antigenically related to human rotavirus serotype 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):171–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.171-174.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Lyoo Y. S., Andrews J. J., Hill H. T. Isolation of two new serotypes of porcine rotavirus from pigs with diarrhea. Arch Virol. 1988;100(1-2):139–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01310917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigolo de San Juan C., Bellinzoni R. C., Mattion N., La Torre J., Scodeller E. A. Incidence of group A and atypical rotaviruses in Brazilian pig herds. Res Vet Sci. 1986 Sep;41(2):270–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J. In vitro detection of porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus) and its antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):844–846. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.844-846.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralization. Arch Virol. 1977;53(4):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01315627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utrera V., Mazzali de Ilja R., Gorziglia M., Esparza J. Epidemiological aspects of porcine rotavirus infection in Venezuela. Res Vet Sci. 1984 May;36(3):310–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J., Hall G. A., Jones J. M., Jackson G. The isolation of reovirus-like agents (rota-viruses) from acute gastroenteritis of piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):203–209. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]