Abstract
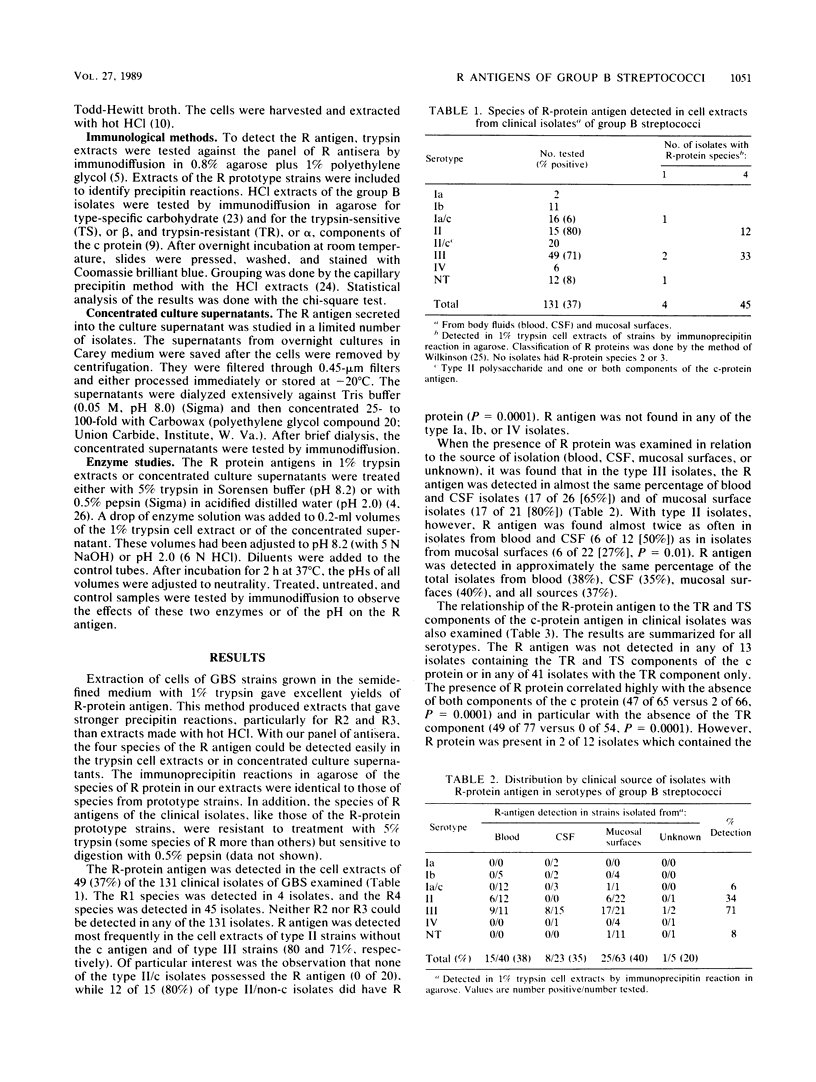
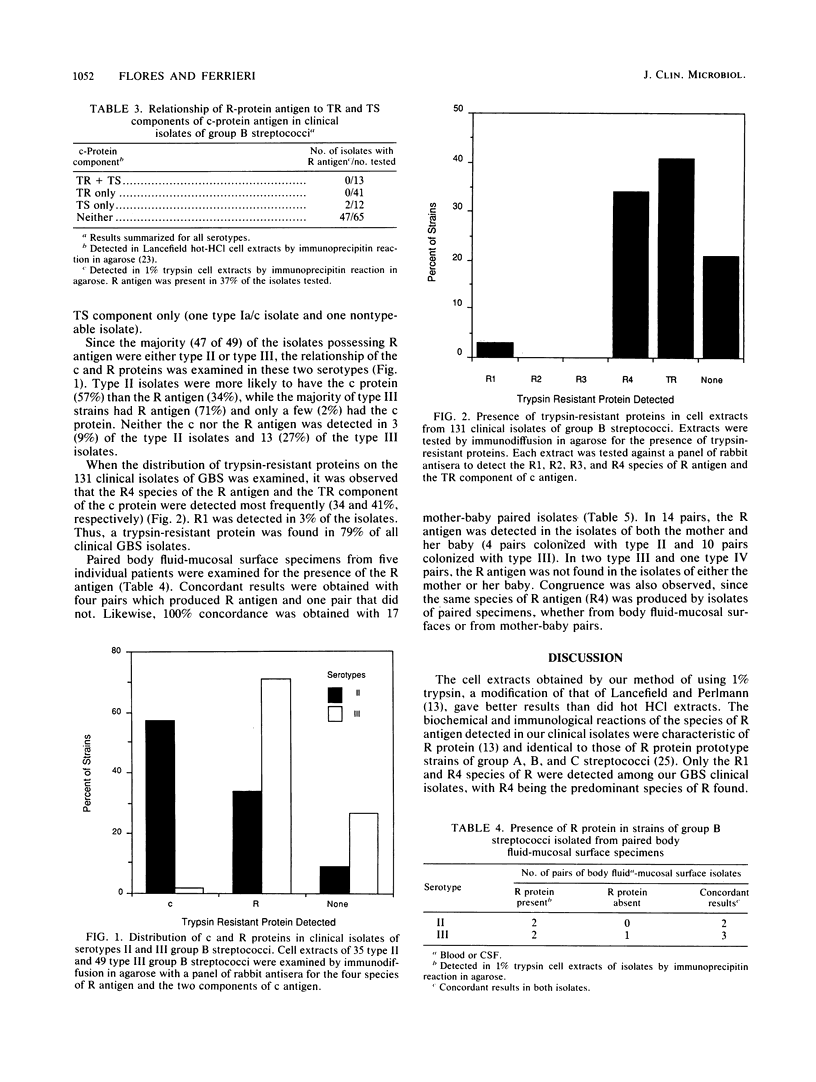
Clinical isolates of group B streptococci from body fluids and mucosal surfaces were examined for production of a trypsin-resistant antigen known as R protein. R protein was extracted with 1% trypsin from cells grown in a semidefined medium. The extracts were tested by immunodiffusion in agarose with a panel of antisera for detection and precise identification of the four species of R protein described by Wilkinson. R antigen was present in 49 of 131 (37%) of the strains tested. Analysis by serotype revealed that 0 of 2 type Ia, 0 of 11 Ib, 1 of 16 (6%) Ia/c, 12 of 15 (80%) II, 0 of 20 II/c, 35 of 49 (71%) III, 0 of 6 IV, and 1 of 12 (8%) nontypeable strains produced R antigen. Production of the R protein and the trypsin-resistant or alpha component of the c protein appeared to be mutually exclusive. R antigen was more prevalent in isolates from blood (50%) than in those from mucosal sites (27%) for type II strains; no difference was seen for type III strains from these sites. Concordant results were obtained with five paired body fluid-mucosal surface isolates from individual patients and with isolates from 17 mother-baby pairs. The most frequent species of R antigen was R4 (45 of 49), followed by R1 (4 of 49). These two species of R protein were biochemically (trypsin resistant and pepsin sensitive) and immunologically identical to the R-protein antigens produced by prototype strains of groups A, B, and C streptococci.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carey R. B., Eisenstein T. K., Shockman G. D., Greber T. F., Swenson R. M. Soluble group- and type-specific antigens from type III group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):195–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.195-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P. Surface-localized protein antigens of group B streptococci. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S363–S366. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores A. E., Ferrieri P. The type-specific polysaccharide and the R protein antigens of the L-phase from a group B, type III Streptococcus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Apr;259(2):165–178. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington J. C., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Pert J. H. Polymer-induced precipitation of antigen-antibody complexes: "precipiplex" reactions. Immunochemistry. 1971 May;8(5):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90504-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelínkoá J. Group B streptococci in the human population. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;76:127–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen N. E. Serotypes of group B streptococci in urogenital patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 1980;12(2):101–104. doi: 10.3109/inf.1980.12.issue-2.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Ferrieri P. Group B streptococcal Ibc protein antigen: distribution of two determinants in wild-type strains of common serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):506–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.506-510.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Occurrence of R antigen specific for Group A type 3 streptococci. J Exp Med. 1958 Sep 1;108(3):329–341. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.3.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of a protein (R antigen) occurring in streptococci of group A, type 28 and in certain streptococci of other serological groups. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):83–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindén V., Christensen K. K., Christensen P. Correlation between low levels of maternal IgG antibodies to R protein and neonatal septicemia with group B streptococci carrying R protein. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;71(2):168–172. doi: 10.1159/000233382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindén V., Christensen K. K., Christensen P. The occurrence of R-protein among isolates of group B streptococci from human sources. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):153–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindén V. Mouse-protective effect of rabbit anti-R-protein antibodies against group B streptococci type II carrying R-protein. Lack of effect on type III carrying R-protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):145–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa S., Yaegashi T., Nakayama Y. Existence of 28R-antigen in a certain strain of group F streptococcus. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(5):263–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTISON I. H., MATTHEWS P. R., HOWELL D. G. The type classification of group-B streptococci, with special reference to bovine strains apparently lacking in type polysaccharide. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Ferrieri P. The relation of the Ibc protein antigen to the opsonization differences between strains of type II group B streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):672–681. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Kim Y. K., Ferrieri P. Effect of differences in antibody and complement requirements on phagocytic uptake and intracellular killing of "c" protein-positive and -negative strains of type II group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1243–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1243-1251.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Krause R. M., Lancefield R. C., Everly W., Lackland H. New approaches for the laboratory recognition of M types of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1298–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. Comparison of streptococcal R antigens. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):669–670. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.669-670.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Eagon R. G. Type-specific antigens of group B type Ic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):596–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.596-604.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


