Abstract
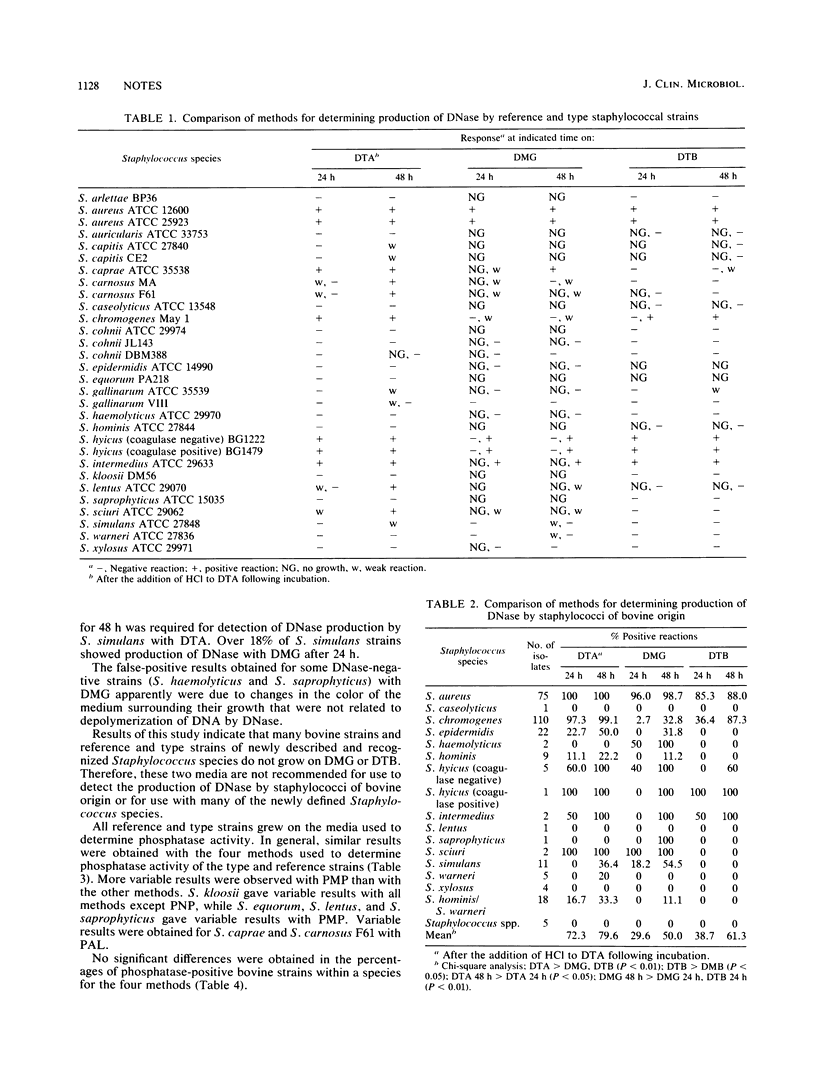
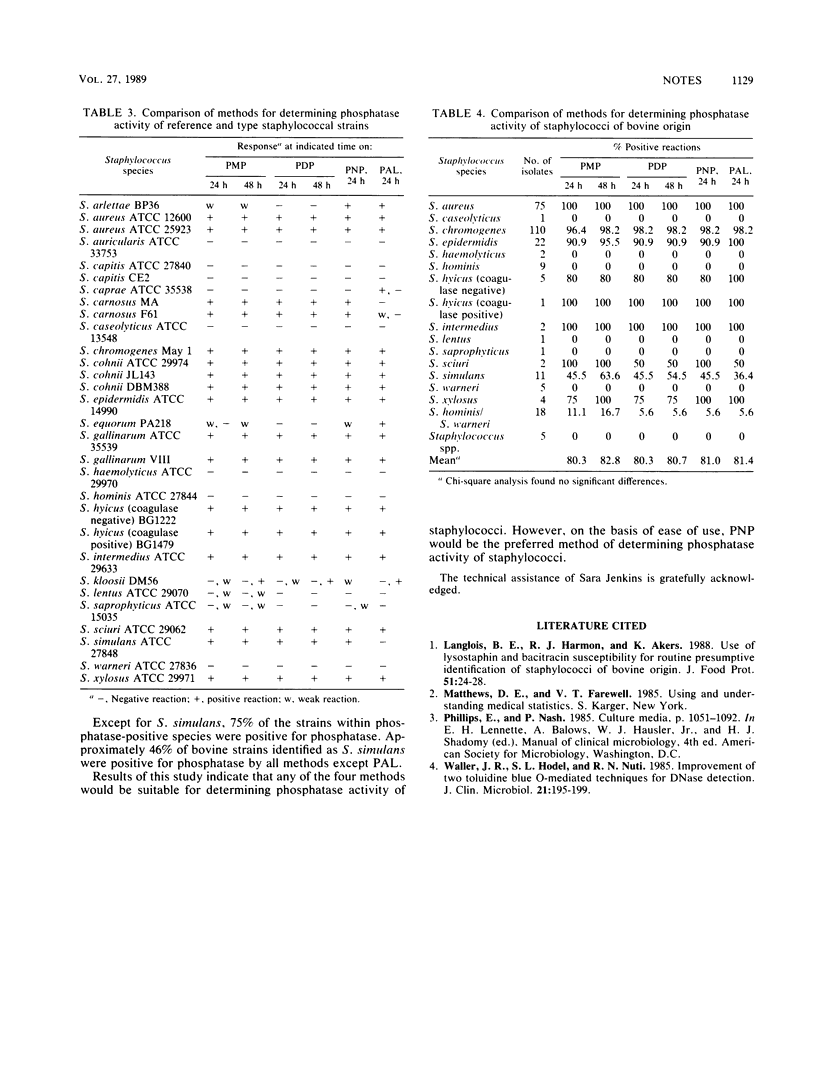
A greater percentage of DNase-positive strains was detected with DNase test agar than with DNase test agar containing 0.005% methyl green or 0.005% toluidine blue (P less than 0.01). No significant differences were obtained in the percentage of phosphatase-positive strains with the four methods compared. On the basis of ease of use, P agar containing para-nitrophenylphosphate disodium (0.495 mg/ml) would be the preferred method for determining phosphatase activity of staphylococci.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Waller J. R., Hodel S. L., Nuti R. N. Improvement of two toluidine blue O-mediated techniques for DNase detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):195–199. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.195-199.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


