Abstract
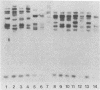
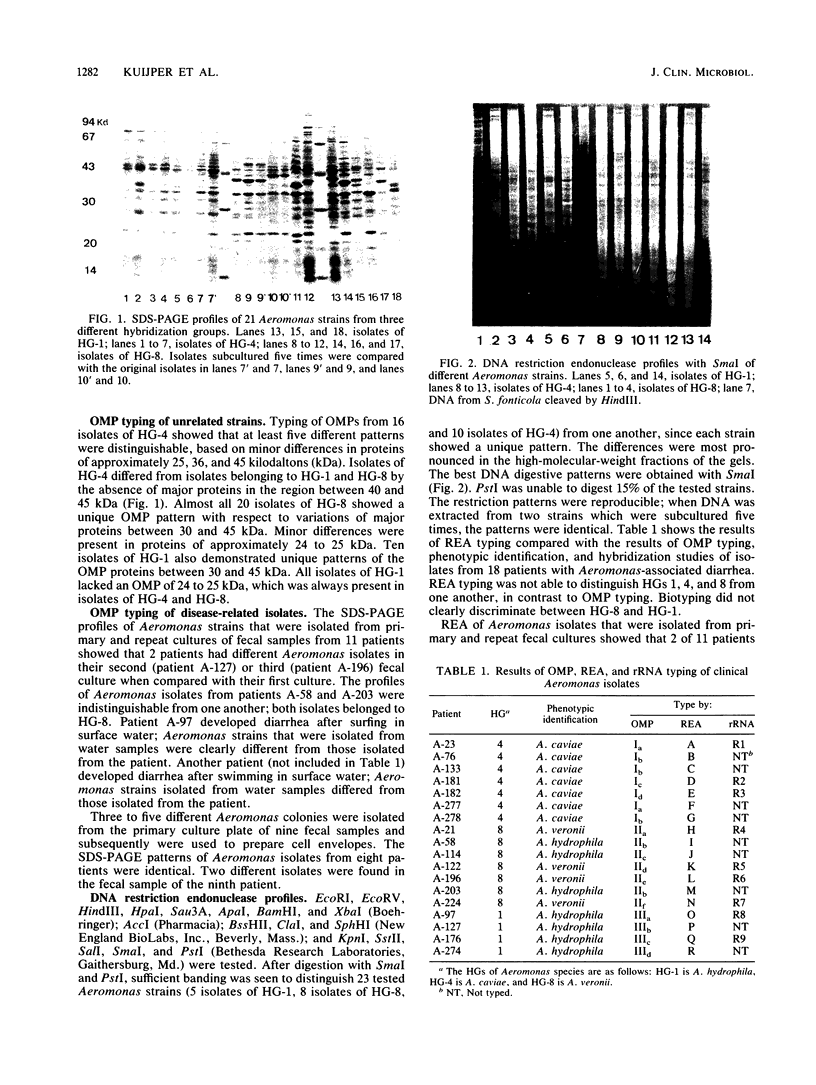
The outer membrane protein (OMP) composition (OMP typing) of 46 fecal Aeromonas strains from hybridization groups (HGs) 1 (A. hydrophila; n = 10), 4 (A. caviae; n = 16), and 8 (A. veronii; n = 20) were examined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis as a phenotypic typing method. Almost every isolate of HG-1 and HG-8 had a unique OMP profile, in contrast to isolates of HG-4, which were separated into five different OMP types. It was possible to recognize HGs 1, 4, and 8 by OMP profiles. Twenty-three Aeromonas strains from HGs 1 (n = 5), 4 (n = 10), and 8 (n = 8) were tested by whole-cell DNA restriction endonuclease analysis (REA) as a genetic typing method. All strains tested by REA (with SmaI) had different DNA digestion patterns. Although additional DNA-rRNA hybridization analyses with SmaI and 16S and 23S rRNAs from Escherichia coli showed a reduction in the number of restriction bands to 8 to 13 hybridized fragments, the discriminative value was less when compared with that obtained by REA. The individual differences found by REA were used to analyze whether patients remained colonized by the same Aeromonas strain. Of 11 patients with diarrhea, 2 had a different isolate on repeat culture. In addition, one of nine tested fecal samples contained two Aeromonas isolates with different REA patterns. These results indicate that during diarrheal disease the intestinal tract may be colonized simultaneously with different Aeromonas isolates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chattopadhyay B. Aeromonas in hospital. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7(2):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B. D., Houang E. C., Lee J. V. Clustering of aeromonas hydrophila septicaemia. Lancet. 1981 Nov 28;2(8257):1232–1232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Kane J. G., Garagusi V. F. Human aeromonas infections: a review of the literature and a case report of endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., MacDonald K. L., Steigerwalt A. G., Fanning G. R., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas veronii, a new ornithine decarboxylase-positive species that may cause diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):900–906. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.900-906.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Schell W. L., Fanning G. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas intestinal infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):683–689. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Dixon A., Raucher B., Clark R. B., Bottone E. J. Value of blood agar for primary plating and clinical implication of simultaneous isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas caviae from a patient with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1221–1222. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1221-1222.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Duffey P. S. Mesophilic aeromonads in human disease: current taxonomy, laboratory identification, and infectious disease spectrum. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):980–997. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Reitano M., Bottone E. J. Biotyping of Aeromonas isolates as a correlate to delineating a species-associated disease spectrum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):44–47. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.44-47.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Steigerwalt A. G., Schoenmakers B. S., Peeters M. F., Zanen H. C., Brenner D. J. Phenotypic characterization and DNA relatedness in human fecal isolates of Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.132-138.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langenberg W., Rauws E. A., Widjojokusumo A., Tytgat G. N., Zanen H. C. Identification of Campylobacter pyloridis isolates by restriction endonuclease DNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):414–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.414-417.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellersh A. R., Norman P., Smith G. H. Aeromonas hydrophila: an outbreak of hospital infection. J Hosp Infect. 1984 Dec;5(4):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(84)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millership S. E., Chattopadhyay B. Aeromonas hydrophila in chlorinated water supplies. J Hosp Infect. 1985 Mar;6(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6701(85)80021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer N. P. Clinical significance of Aeromonas species isolated from patients with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2044–2048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2044-2048.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Arlet G., Goullet P. Septicémies à Aeromonas hydrophila. Aspects épidémiologiques. Quinze observations. Presse Med. 1984 May 5;13(19):1203–1205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Goullet P. Epidemiological complexity of hospital aeromonas infections revealed by electrophoretic typing of esterases. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Feb;98(1):5–14. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800061665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines H. D., Cook F. V. Pneumonia and bacteremia due to Aeromonas hydrophila. Chest. 1981 Sep;80(3):264–267. doi: 10.1378/chest.80.3.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statner B., Jones M. J., George W. L. Effect of incubation temperature on growth and soluble protein profiles of motile Aeromonas strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):392–393. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.392-393.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Millership S. E., Tabaqchali S. Typing of Aeromonas species by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of radiolabelled cell proteins. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Sep;24(2):113–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-2-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd Aeromonas hydrophila in clinical bacteriologic specimens. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):611–614. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. L., Wiseman S. L., Kitchens C. S. Aeromonas hydrophila bacteremia in ambulatory immunocompromised hosts. Am J Med. 1980 Feb;68(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]