Abstract
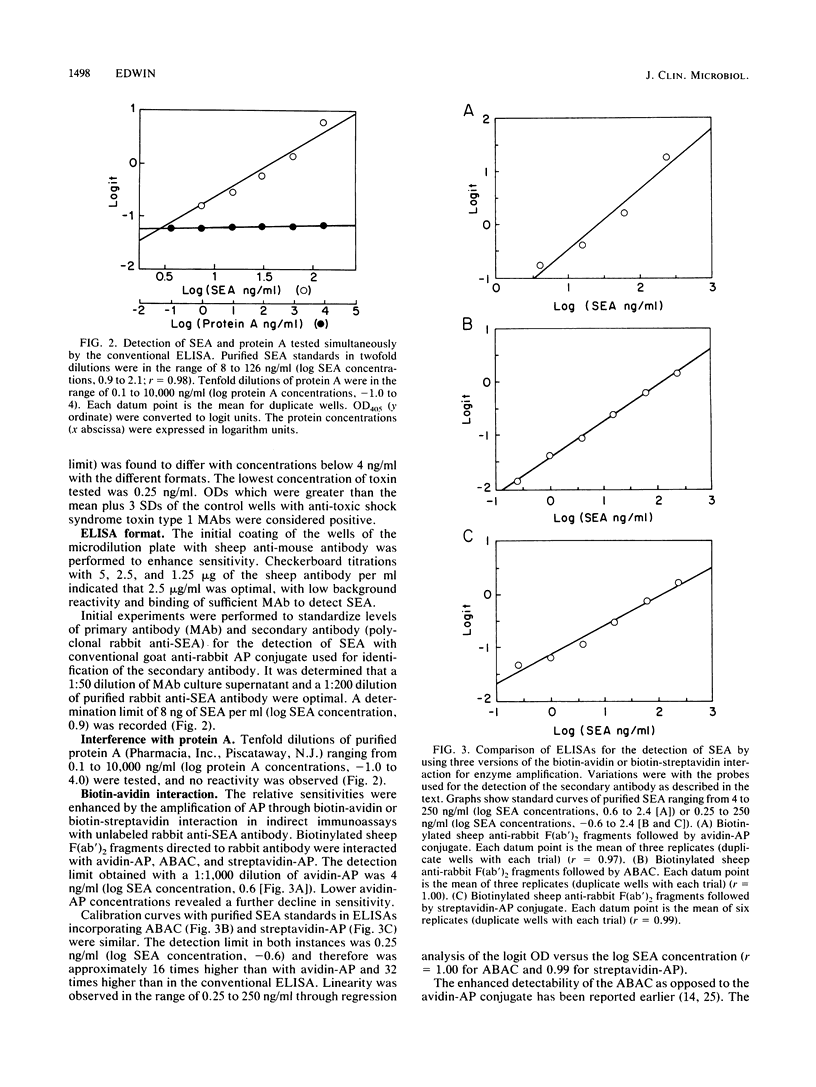
A sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) was developed by using monoclonal antibodies (MAb) to SEA as primary capture antibodies. The antigen was detected with purified rabbit anti-SEA antibody as the secondary antibody. The secondary antibody was identified by direct conjugation with biotin or via biotinylated sheep F(ab')2 fragments to rabbit antibody. The biotin was then reacted with avidin-alkaline phosphatase (AP) conjugate, avidin-biotin-AP conjugated complex, or streptavidin-AP conjugate. The enzyme was identified by using p-nitrophenylphosphate. The incorporation of the avidin-biotin-AP conjugated complex or streptavidin-AP conjugate augmented the sensitivity 32-fold over that of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay without these reagents. Controls were run by substitution of the anti-SEA MAb with unrelated MAb of the same isotype. Sample values were considered positive when the A405 exceeded those of the negative controls by 3 standard deviations (greater than 99% confidence interval). The toxin could be quantitated with purified SEA standards through linear regression analysis with lower detection limits of 4 ng/ml (r = 0.99) and 0.25 ng/ml (r greater than or equal to 0.98). Concentrations of protein A up to 10 micrograms/ml did not cause interference. Analyses of crude growth extracts of SEA-secreting strains of Staphylococcus aureus were reproducible and were expressed in terms of 95% confidence intervals. Lack of cross-reactivity was seen with extracts of other toxigenic and nontoxigenic strains of S. aureus. The assay can be completed in one working day, provided that MAb-coated plates are available.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M., Skutelsky E. Affinity cytochemistry: the localization of lectin and antibody receptors on erythrocytes via the avidin-biotin complex. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 1;68(2):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80445-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdal B. P., Olsvik O., Omland T. A sandwich ELISA method for detection of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Dec;89(6):411–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwin C., Tatini S. R., Maheswaran S. K. Nature and reactivity of staphylococcal enterotoxin A monoclonal antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1247–1252. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1247-1252.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwin C., Tatini S. R., Maheswaran S. K. Specificity and cross-reactivity of staphylococcal enterotoxin A monoclonal antibodies with enterotoxins B, C1, D, and E. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Dec;52(6):1253–1257. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.6.1253-1257.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwin C., Tatini S. R., Strobel R. S., Maheswaran S. K. Production of monoclonal antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1171–1175. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1171-1175.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Burkhard G. Measurement of staphylococcal protein A and detection of protein A-carrying staphylococcus strains by a competitive ELISA method. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Rüegg O. Comparative evaluation of different enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay systems for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, and D. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):34–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.34-38.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed R. C., Evenson M. L., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1349–1355. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1349-1355.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeuptle M. T., Aubert M. L., Djiane J., Kraehenbuhl J. P. Binding sites for lactogenic and somatogenic hormones from rabbit mammary gland and liver. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn I. F., Pickenhahn P., Lenz W., Brandis H. An avidin-biotin ELISA for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins A and B. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Aug 21;92(1):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90499-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzmann H., Richards F. M. Use of the avidin-biotin complex for specific staining of biological membranes in electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K., Wood S. W., Brinton C. C., Montibeller J. A., Finn F. M. Iminobiotin affinity columns and their application to retrieval of streptavidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4666–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Timmermans P., Nagel J. Interaction of staphylococcal protein A in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detecting staphylococcal antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Nov 26;55(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. G., Nickerson J. M., Fuller G. M. Two simple programs for the analysis of data from enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) assays on a programmable desk-top calculator. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 15;110(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins R., Gould S., Bergdoll M. Detecting the enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):946–950. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.946-950.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter M., Butler J. E. The immunochemistry of sandwich ELISAs. II. A novel system prevents the denaturation of capture antibodies. Immunol Lett. 1986 Nov 3;13(6):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Razdan M., Kuntsmann G., Aschenbach J. M., Evenson M. L., Bergdoll M. S. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and radioimmunoassays: comparison of monoclonal and polyclonal antibody systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):885–890. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.885-890.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J., Whitcomb L. S., Santosham M. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of bacterial antigens utilizing biotin-labeled antibody and peroxidase biotin--avidin complex. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):319–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


