Abstract
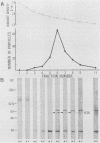
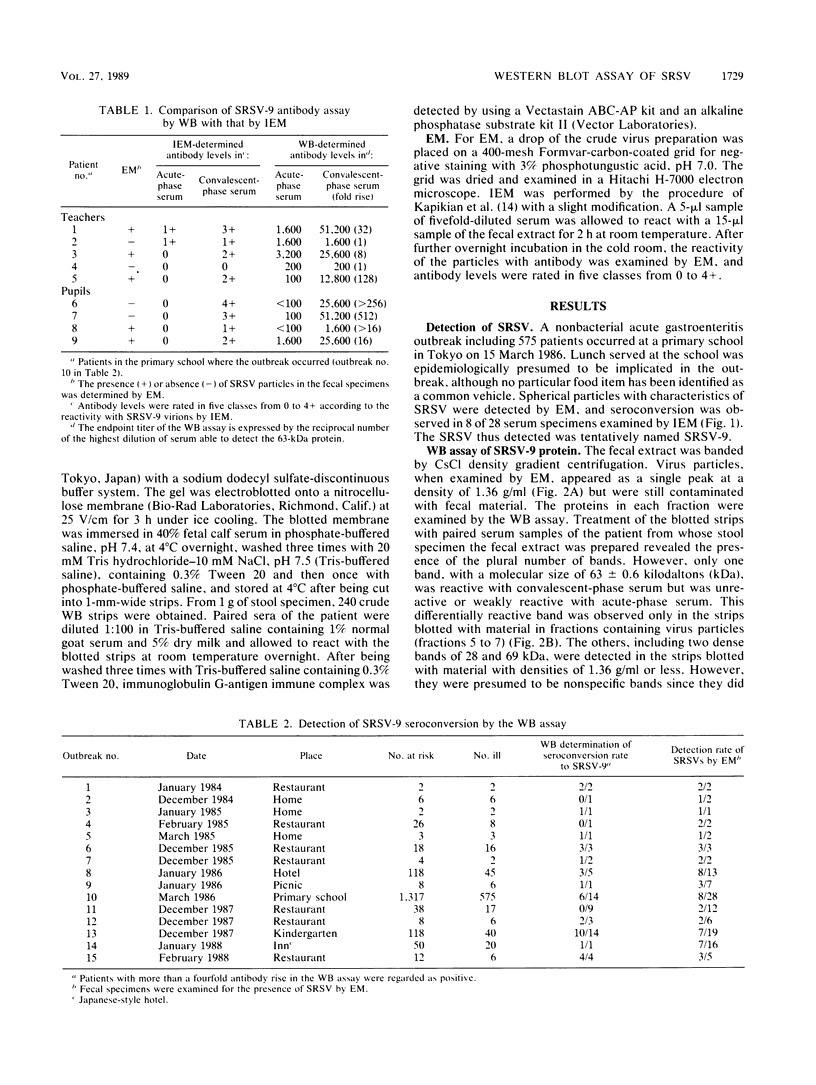
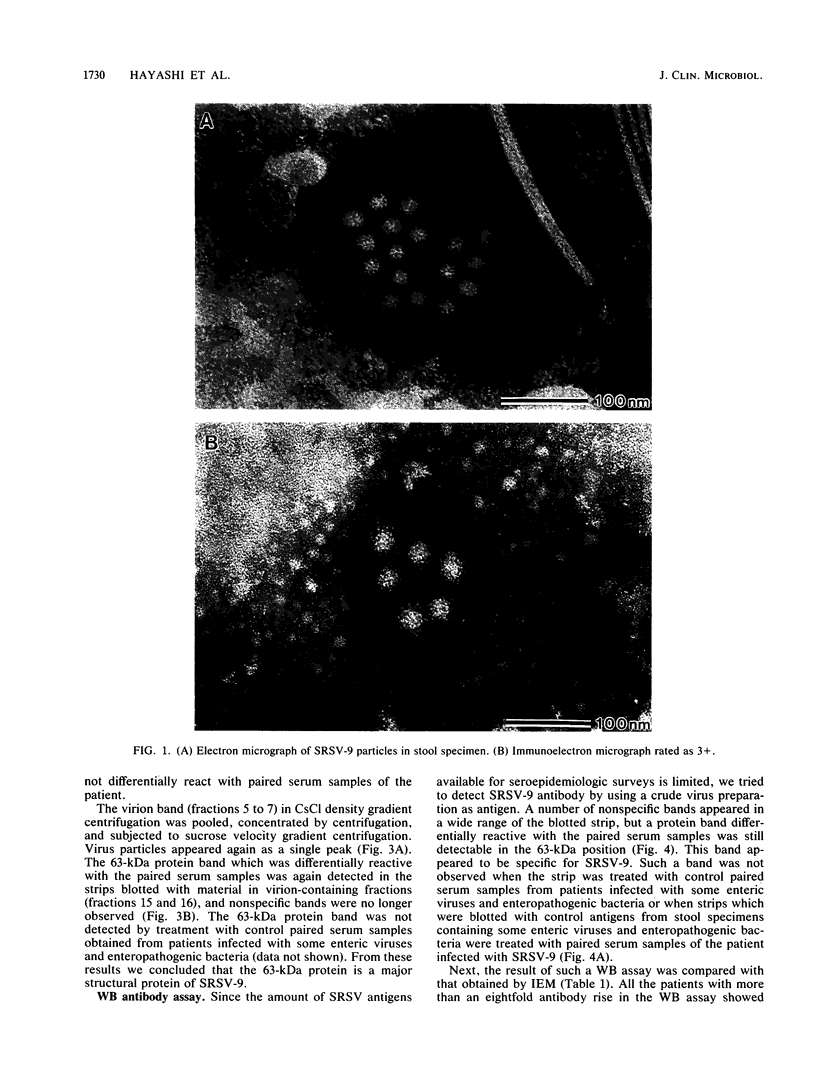
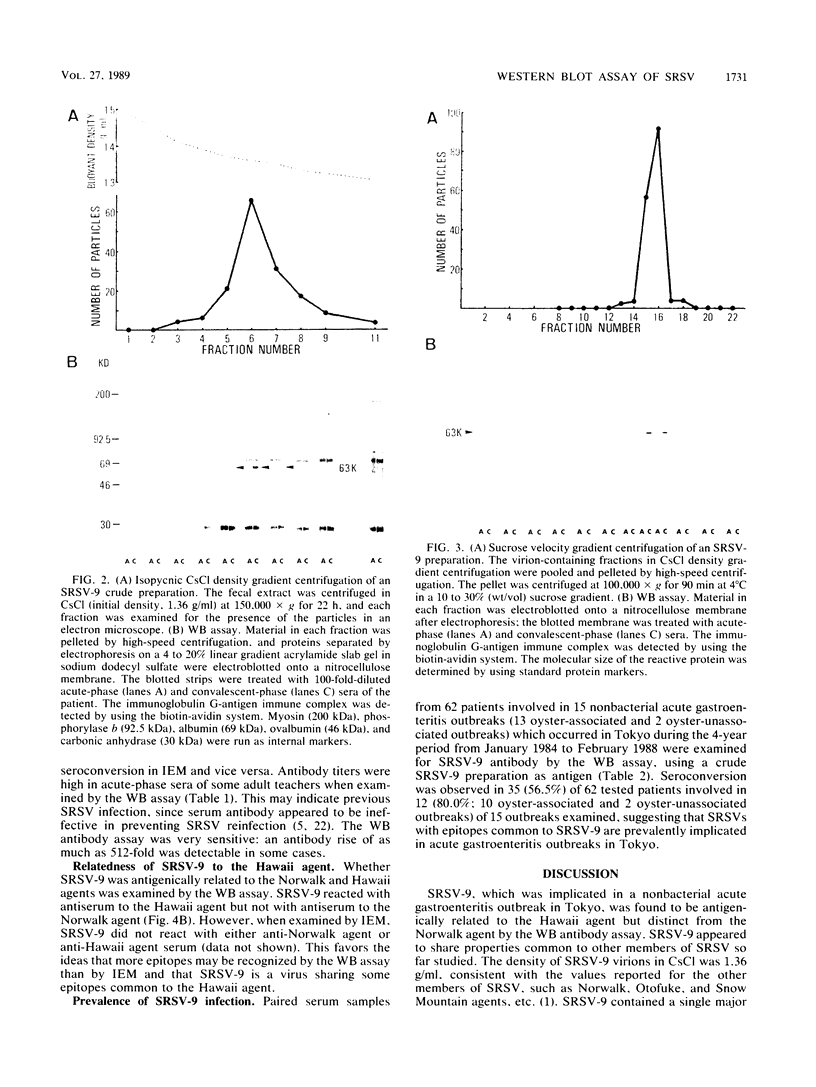
Small, round-structured virus (SRSV) was detected in a stool specimen of a patient during an acute gastroenteritis outbreak in Tokyo and was tentatively named SRSV-9. SRSV-9 was purified by sucrose velocity gradient centrifugation after CsCl density gradient centrifugation. The buoyant density of SRSV-9 appeared to be 1.36 g/ml in CsCl. A Western blot (immunoblot) assay using the biotin-avidin system revealed that SRSV-9 was antigenically related to the Hawaii agent but distinct from the Norwalk agent and contained a single major structural protein with a molecular size of 63.0 +/- 0.6 kilodaltons. The prevalence of SRSV-9 infection in Tokyo was surveyed by the Western blot antibody assay by using a crude virus preparation as the antigen. Seroconversion was observed in 56.5% of the patients involved in the outbreaks from which SRSV was detected by electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleton H. Small round viruses: classification and role in food-borne infections. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;128:108–125. doi: 10.1002/9780470513460.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caul E. O., Appleton H. The electron microscopical and physical characteristics of small round human fecal viruses: an interim scheme for classification. J Med Virol. 1982;9(4):257–265. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890090403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubitt W. D., Blacklow N. R., Herrmann J. E., Nowak N. A., Nakata S., Chiba S. Antigenic relationships between human caliciviruses and Norwalk virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):806–814. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R. Human viral gastroenteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):157–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.157-179.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Nowak N. A., Blacklow N. R. Immunoglobulin M responses to the Norwalk virus of gastroenteritis. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):463–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.463-468.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R., Reichman R. C., Roessner K. D., Tralka T. S., Schooley R. T., Gary W., Morens D. Detection by immune electron microscopy of the Snow Mountain agent of acute viral gastroenteritis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):184–189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R., Roessner K. D., Treanor J. J., Reichman R. C., Phillips M., Madore H. P. Radioimmunoassay for detection of the Snow Mountain Agent of viral gastroenteritis. J Med Virol. 1986 May;19(1):11–18. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gary G. W., Jr, Kaplan J. E., Stine S. E., Anderson L. J. Detection of Norwalk virus antibodies and antigen with a biotin-avidin immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):274–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.274-278.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J. R., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., McAuliffe V. J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Proteins of Norwalk virus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.994-999.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Valdesuso J., Kalica A. R., London W. T., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Solid-phase microtiter radioimmunoassay for detection of the Norwalk strain of acute nonbacterial, epidemic gastroenteritis virus and its antibodies. J Med Virol. 1978;2(2):97–108. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Nowak N. A., Blacklow N. R. Detection of Norwalk virus in stools by enzyme immunoassay. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Dolin R., Thornhill T. S., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1075–1081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1075-1081.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogasaka R., Nakamura S., Chiba S., Sakuma Y., Terashima H., Yokoyama T., Nakao T. The 33- to 39-nm virus-like particles, tentatively designed as Sapporo agent, associated with an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis. J Med Virol. 1981;8(3):187–193. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890080305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore H. P., Treanor J. J., Dolin R. Characterization of the Snow Mountain agent of viral gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.487-492.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore H. P., Treanor J. J., Pray K. A., Dolin R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for Snow Mountain and Norwalk agents of viral gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):456–459. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.456-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. L., Guzewich J. J., Hanrahan J. P., Stricof R., Shayegani M., Deibel R., Grabau J. C., Nowak N. A., Herrmann J. E., Cukor G. Widespread outbreaks of clam- and oyster-associated gastroenteritis. Role of Norwalk virus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):678–681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. M., Grohmann G. S., Christopher P. J., Lopez W. A., Davey G. R., Millsom R. H. An Australia-wide outbreak of gastroenteritis from oysters caused by Norwalk virus. Med J Aust. 1979 Oct 6;2(7):329–333. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1979.tb104133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi I., Yamazaki K., Minekawa Y., Nishimura H., Kitaura T. Three-year survey of the epidemiology of rotavirus, enteric adenovirus, and some small spherical viruses including "Osaka-agent" associated with infantile diarrhea. Biken J. 1985 Jun;28(1-2):9–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrino T. A., Schreiber D. S., Trier J. S., Kapikian A. Z., Blacklow N. R. Clinical immunity in acute gastroenteritis caused by Norwalk agent. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jul 14;297(2):86–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197707142970204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine S., Okada S., Hayashi Y., Ando T., Terayama T., Yabuuchi K., Miki T., Ohashi M. Prevalence of small round structured virus infections in acute gastroenteritis outbreaks in Tokyo. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(3):207–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Urasawa T. Virus-like particle, 35 to 40 nm, associated with an institutional outbreak of acute gastroenteritis in adults. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):730–736. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.730-736.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashima H., Chiba S., Sakuma Y., Kogasaka R., Nakata S., Minami R., Horino K., Nakao T. The polypeptide of a human calicivirus. Arch Virol. 1983;78(1-2):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF01310853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill T. S., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Dolin R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Detection by immune electron microscopy of 26- to 27-nm viruslike particles associated with two family outbreaks of gastroenteritis. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):20–27. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]