Abstract
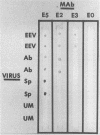
A panel of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) was prepared and used to develop an enzyme immunodot assay for the rapid identification and presumptive serotyping of aquatic birnaviruses. Comparison of the reaction patterns of these MAbs with representative virus isolates indicated that one MAb recognizes a serogroup-reactive epitope and can therefore be used for identification of all serogroup A aquatic birnaviruses, the predominant serotype worldwide. Other MAbs exhibited more restrictive specificities, permitting the presumptive serotyping of viruses of the three recognized serotypes and the identification of some individual strains. This assay, in which MAbs are used, is more efficient in terms of time, cost, and case of performance and provides significant advantages in specificity and standardization compared with currently used tests.
Full text
PDF

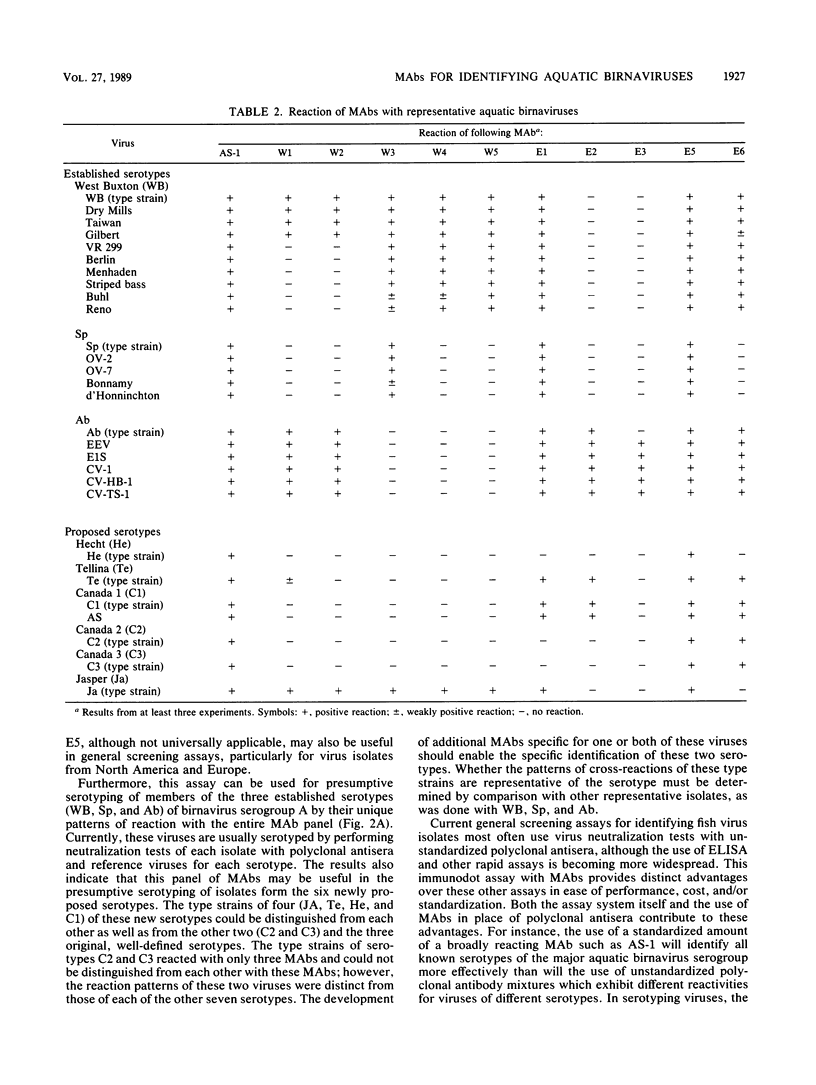


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caswell-Reno P., Reno P. W., Nicholson B. L. Monoclonal antibodies to infectious pancreatic necrosis virus: analysis of viral epitopes and comparison of different isolates. J Gen Virol. 1986 Oct;67(Pt 10):2193–2205. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-10-2193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon P. F., Hill B. J. Rapid detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):321–330. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobos P., Hill B. J., Hallett R., Kells D. T., Becht H., Teninges D. Biophysical and biochemical characterization of five animal viruses with bisegmented double-stranded RNA genomes. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):593–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.593-605.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lannan C. N., Winton J. R., Fryer J. L. Fish cell lines: establishment and characterization of nine cell lines from salmonids. In Vitro. 1984 Sep;20(9):671–676. doi: 10.1007/BF02618871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. D., Gower D. A. Genomic and phenotypic divergence among three serotypes of aquatic birnaviruses (infectious pancreatic necrosis virus). Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister P. E., Schill W. B. Immunoblot assay: a rapid and sensitive method for identification of salmonid fish viruses. J Wildl Dis. 1986 Oct;22(4):468–474. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-22.4.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson B. L., Caswell P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identification of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):469–472. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.469-472.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson B. L., Henchal E. A. Rapid identification of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus in infected cell cultures by immunoperoxidase techniques. J Wildl Dis. 1978 Oct;14(4):465–469. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-14.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper D., Nicholson B. L., Dunn J. Immunofluorescent study of the replication of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus in trout and Atlantic salmon cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):249–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.249-254.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonstegard R. A., McDermott L. A., Sonstegard K. S. Isolation of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus from white suckers (Catastomus commersoni). Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):174–175. doi: 10.1038/236174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood B. O., Smale C. J., Brown F., Hill B. J. Relationship of a virus from Tellina tenuis to infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):93–109. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF K., SNIESZKO S. F., DUNBAR C. E., PYLE E. Virus nature of infectious pancreatic necrosis in trout. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 May;104:105–108. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf K., Mann J. A. Poikilotherm vertebrate cell lines and viruses: a current listing for fishes. In Vitro. 1980 Feb;16(2):168–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02831507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolski S. C., Roberson B. S., Hetrick F. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the Sp strain of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jun;12(1-4):373–381. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90143-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]