Abstract
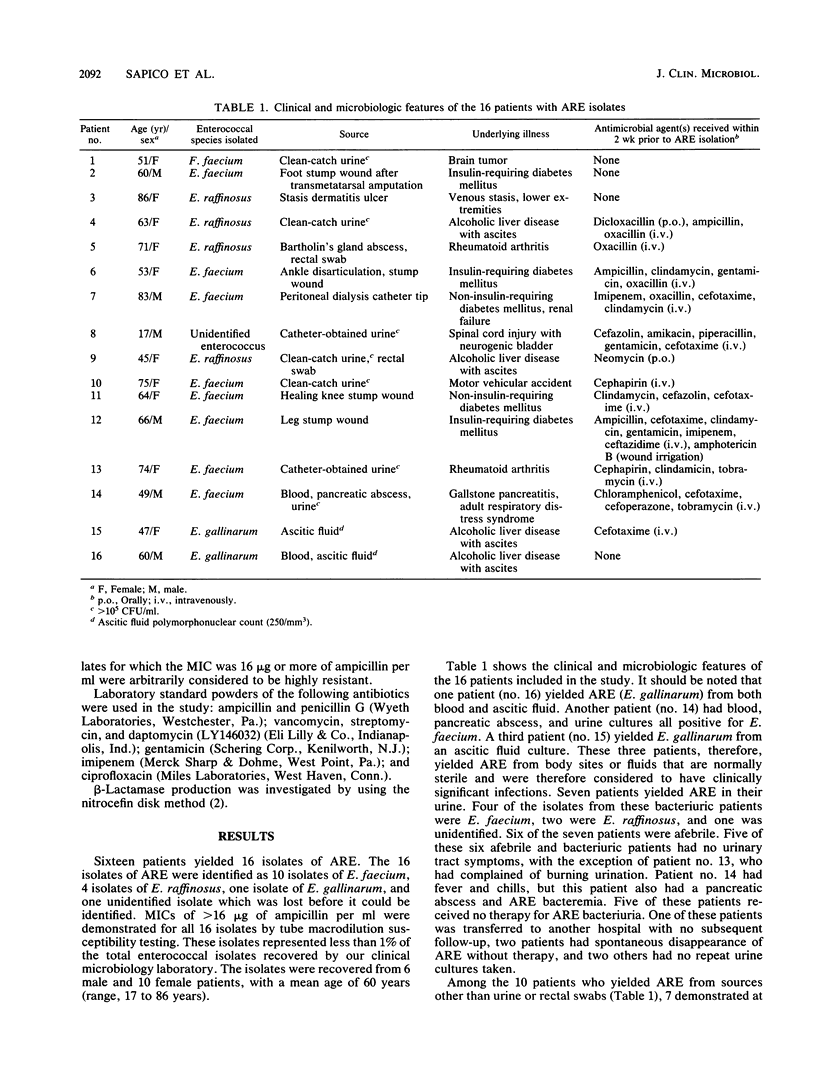
Sixteen clinical isolates of ampicillin-resistant enterococci (ARE) were recovered from the microbiology laboratory of a 450-bed rehabilitation medical center from January 1981 to September 1987. These isolates were detected when a disk diffusion test using 10 micrograms of ampicillin on a blood agar plate revealed no zones of inhibition. Tube macrodilution tests yielded an MIC of greater than or equal to 16 micrograms of ampicillin per ml. None of the isolates were penicillinase producers by the chromogenic cephalosporin disk test. Ten isolates were Enterococcus faecium, four isolates were E. raffinosus, one isolate was E. gallinarum, and one isolate was not identified (lost). There were 6 male and 10 female patients. The sources of isolates were urine (n = 7), wound (n = 5), ascitic fluid (n = 2), blood (n = 2), peritoneal catheter tip (n = 1), Bartholin's cyst abscess (n = 1), rectal swab (n = 2), and pancreatic abscess (n = 1). The organism was isolated from multiple sites in 4 patients, was a pure culture isolate in 5 patients, and was part of a polymicrobial flora in 11 patients. Six patients were diabetic, and four had liver cirrhosis. All but four patients had received at least one antibiotic within 3 weeks of ARE isolation. The MICs (micrograms per milliliter) for 50 and 90% of isolates tested, respectively, were as follows: ampicillin, 64 and 64; penicillin, 128 and greater than 128; vancomycin, 1 and 2; gentamicin, 4 and 16; ciprofloxacin, 1.6 and 3.2; imipenem, 128 and greater than 128; and daptomycin (LY146032), 1.6 and 6.4. ARE may be an emerging pathogen in the hospitalized patient population.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. P., Barry A. L., Benner E. J. A simple, rapid test to differentiate penicillin-susceptible from penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Dec;122(6):544–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.6.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Ayers L. W., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Antibacterial activities of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, oxolinic acid, cinoxacin, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):633–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P. M., Shaw W. V., Jacob A. E. Plasmid-mediated mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycoside-aminocyclitol antibiotics and to chloramphenicol in group D streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):716–725. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Streptococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):295–301. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Collins M. D. Identification of Enterococcus species isolated from human infections by a conventional test scheme. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):731–734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.731-734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Grossato A., Rossi L., Cheng Y. R., Satta G. Transition from resistance to hypersusceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics associated with loss of a low-affinity penicillin-binding protein in a Streptococcus faecium mutant highly resistant to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):678–683. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann S. A., Moellering R. C., Jr The enterococcus: "putting the bug in our ears". Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):757–761. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Bougueleret L., El-Solh N., Bieth G., Delbos F. High-level, plasmid-borne resistance to gentamicin in Streptococcus faecalis subsp. zymogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):686–689. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D. Enterococci. Biologic and epidemiologic characteristics and in vitro susceptibility. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Oct 25;142(11):2006–2009. doi: 10.1001/archinte.142.11.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. J., Weiser M., Gottschall S., Randall E. L. Identification of Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium and susceptibility studies with newly developed antimicrobial agents. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):787–790. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.787-790.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Korfhagen T. R., Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Swartz M. N. Aminoglycoside-inactivating enzymes in clinical isolates of Streptococcus faecalis. An explanation for resistance to antibiotic synergism. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):480–486. doi: 10.1172/JCI109149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Duval J., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Enterococcus faecium. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 21;319(3):157–161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807213190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston W. K., Elliott A. M., Cobbs C. G. In vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787) against resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Serratia marcescens, and Enterococcus spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):114–116. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lleó M. M., Canepari P., Cornaglia G., Fontana R., Satta G. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of beta-lactams against Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecium are associated with saturation of different penicillin-binding proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1618–1626. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mederski-Samoraj B. D., Murray B. E. High-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniter P. M., Patterson T. F., Johnson M. A., Andriole V. T. Activity of LY146032 in vitro and in experimental enterococcal pyelonephritis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1199–1203. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Korzeniowski O. M., Sande M. A., Wennersten C. B. Species-specific resistance to antimocrobial synergism in Streptococcus faecium and Streptococcus faecalis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):203–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Medrek T., Weinberg A. N. Prevalence of high-level resistance to aminoglycosides in clinical isolates of enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Church D. A., Wanger A., Zscheck K., Levison M. E., Ingerman M. J., Abrutyn E., Mederski-Samoraj B. Comparison of two beta-lactamase-producing strains of Streptococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):861–864. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Mederski-Samoraj B., Foster S. K., Brunton J. L., Harford P. In vitro studies of plasmid-mediated penicillinase from Streptococcus faecalis suggest a staphylococcal origin. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):289–293. doi: 10.1172/JCI112289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachamkin I., Axelrod P., Talbot G. H., Fischer S. H., Wennersten C. B., Moellering R. C., Jr, MacGregor R. R. Multiply high-level-aminoglycoside-resistant enterococci isolated from patients in a university hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1287–1291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1287-1291.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. E., Masecar B. L., Zervos M. J. Characterization and comparison of two penicillinase-producing strains of Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):122–124. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico F. L., Ginunas V. J., Canawati H. N., Montgomerie J. Z. LY146032, alone and in combination with gentamicin, for the treatment of enterococcal pyelonephritis in the rat model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):81–83. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H. Interaction of ciprofloxacin with ampicillin and vancomycin for Streptococcus faecalis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;9(4):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford H. D., De Maine J. B., Kirby W. M. Antibiotic synergism of enterococci. Relation to inhibitory concentrations. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Aug;126(2):255–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., McDonald A., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of group D streptococcus (enterococcus) to 21 antibiotics in vitro, with special reference to species differences. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Dec;258(6):416–430. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196912000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Solliday J. A., Crossley K. B. Susceptibilities of enterococci to twelve antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):532–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuominen R. K., Männistö P. T., Pohto P., Solkinen A., Vuorela A. Absorption of erythromycin acistrate and erythromycin base in the fasting and non-fasting state. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jun;21 (Suppl 500):45–55. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_d.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttley A. H., Collins C. H., Naidoo J., George R. C. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):57–58. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Calderwood S. B., Moellering R. C., Jr, Tomasz A. Studies on the mechanism of intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in group D streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):813–822. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos M. J., Kauffman C. A., Therasse P. M., Bergman A. G., Mikesell T. S., Schaberg D. R. Nosocomial infection by gentamicin-resistant Streptococcus faecalis. An epidemiologic study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):687–691. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


