Abstract
Most individuals infected with Entamoeba histolytica are reported to be clinically asymptomatic. On the basis of the electrophoretic migration of hexokinase and phosphoglucomutase isoenzymes, two groups of E. histolytica isolates have been classified. Those derived from symptomatic cases were found to have fast-migrating hexokinase bands and were labeled pathogenic. The others, isolated from cyst passers, had (in most cases) slow-migrating bands and were called nonpathogenic. Differences between these two groups of E. histolytica were found recently at the DNA level. Two sets of different DNA probes derived from tandemly repeated sequences present in extrachromosomal circular DNA elements in each group of E. histolytica were characterized. Using these probes with procedures for direct hybridization of trophozoites on nylon membranes, we could correctly correlate hexokinase electromobility with the DNA hybridization signal of 81 different isolates of E. histolytica. The advantages of using DNA probes lie in their sensitivity (fewer than 200 trophozoites can be detected) and specificity. The probes hybridized only with amebae from the E. histolytica species and not with other enteric protozoa and can be useful as a diagnostic tool.
Full text
PDF
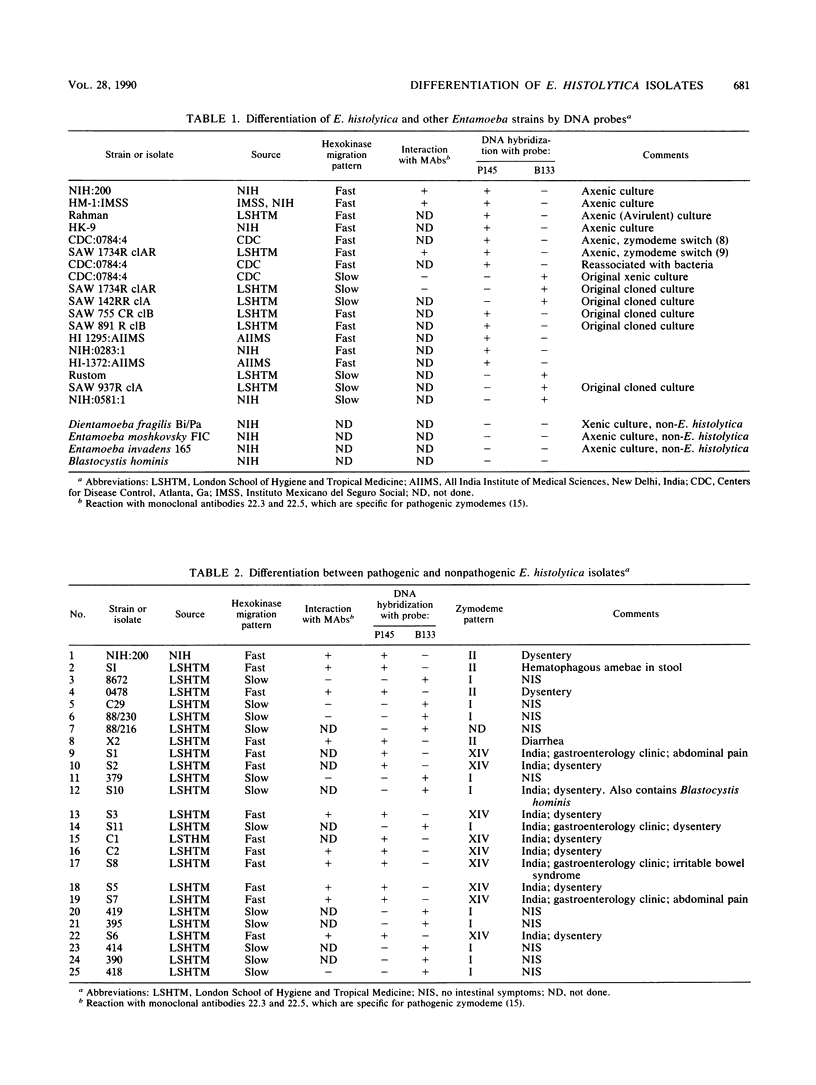
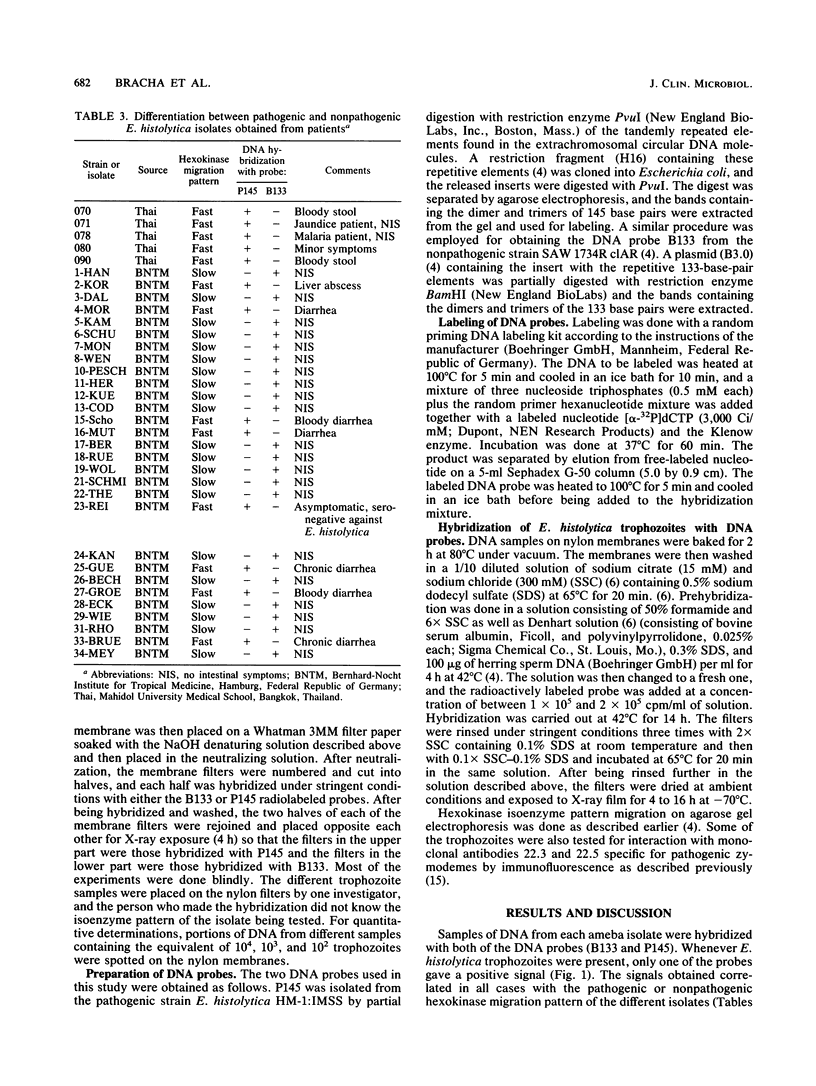
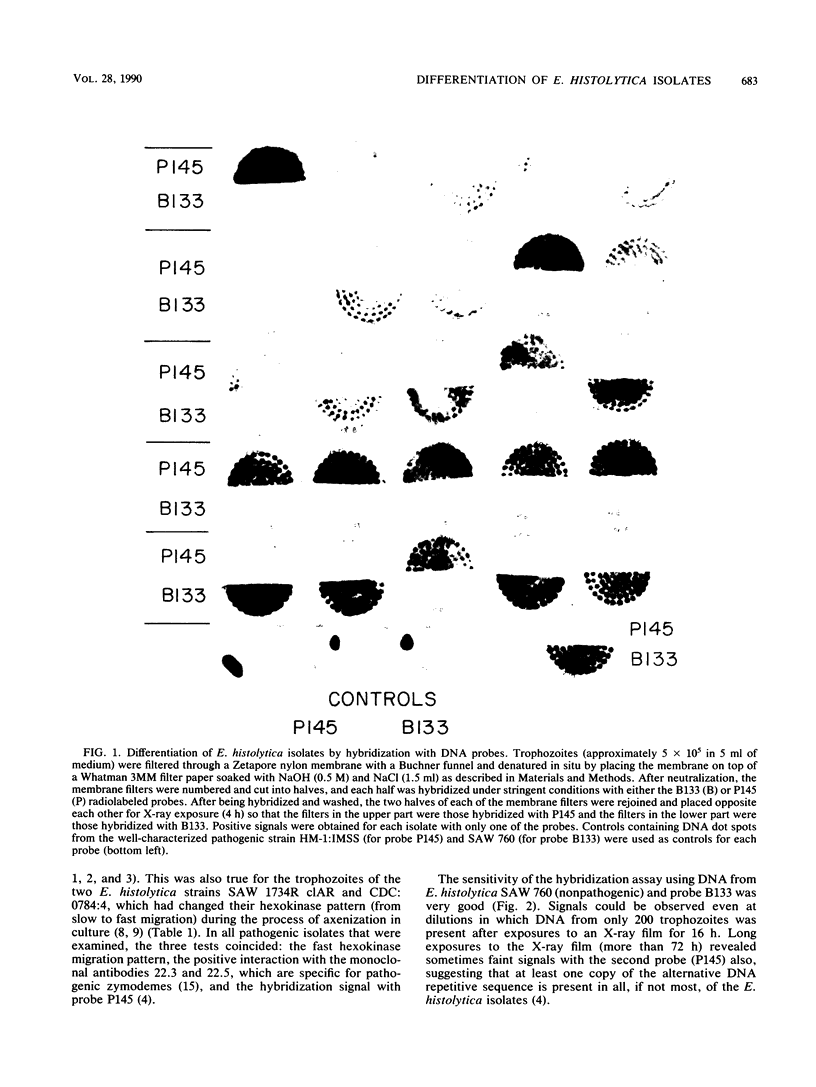

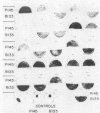
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel L. I., Giladi M., Huber M., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. DNA probes specific for Entamoeba histolytica possessing pathogenic and nonpathogenic zymodemes. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):926–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.926-931.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Koller B., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S., Garfinkel L. Entamoeba histolytica ribosomal RNA genes are carried on palindromic circular DNA molecules. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 15;32(2-3):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Palomo A., Gonzalez-Robles A., De la Torre M. Selective agglutination of pathogenic strains of Entamoeba histolytica induced con A. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 10;245(145):186–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio245186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Chayen A., Aust-Kettis A., Diamond L. S. Entamoeba histolytica: effect of growth conditions and bacterial associates on isoenzyme patterns and virulence. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Aug;62(1):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Wexler A., Chayen A. Changes in isoenzyme patterns of a cloned culture of nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica during axenization. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):827–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.827-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. E., Bischoff J. M. Classification of Entamoeba species by means of electrophoretic properties of amebal enzymes. J Parasitol. 1968 Jun;54(3):594–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L. The laboratory diagnosis of human parasitic amoebae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson J., Acuna-Soto R., Reed S., Biagi F., Wirth D. DNA hybridization probe for clinical diagnosis of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):671–676. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.671-676.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Jackson T. F., Simjee A. Biochemical homogeneity of Entamoeba histolytica isolates, especially those from liver abscess. Lancet. 1982 Jun 19;1(8286):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E. Electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(2):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan W. D., Chiodini P. L., Spice W. M., Moody A. H., Ackers J. P. Immunological differentiation of pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. Lancet. 1988 Mar 12;1(8585):561–563. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]