Abstract
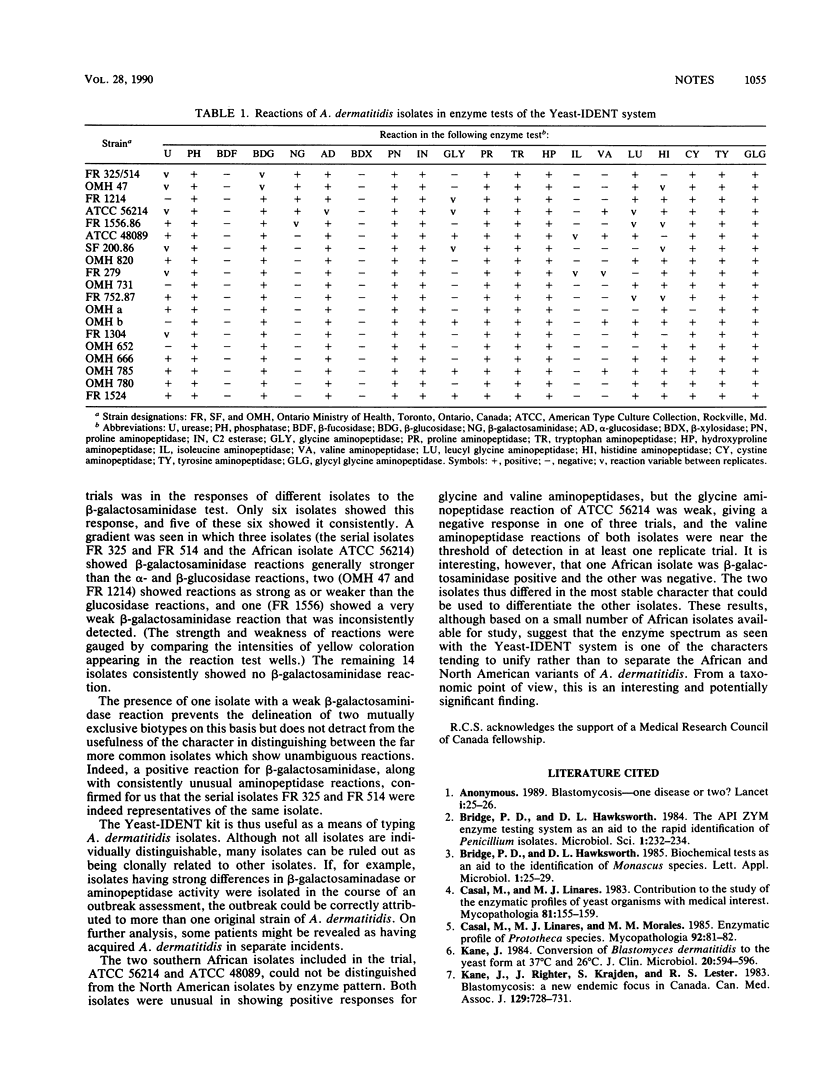
Enzyme profiling was investigated as a means of recognizing biotypes and individual strains of Ajellomyces dermatitidis (anamorph, Blastomyces dermatitidis). Eighteen North American and 2 African representatives were tested with the Yeast-IDENT enzymatic activity profiling system (Analytab Products, Plainview, N.Y.). Significant variation was found between isolates, particularly in beta-galactosaminidase activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridge P. D., Hawksworth D. L. The API ZYM enzyme testing system as an aid to the rapid identification of Penicillium isolates. Microbiol Sci. 1984 Dec;1(9):232–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal M., Linares M. J. Contribution to the study of the enzymatic profiles of yeast organisms with medical interest. Mycopathologia. 1983 Mar 22;81(3):155–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00436820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. Conversion of Blastomyces dermatitidis to the yeast form at 37 degrees C and 26 degrees C. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):594–596. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.594-596.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J., Righter J., Krajden S., Lester R. S. Blastomycosis: a new endemic focus in Canada. Can Med Assoc J. 1983 Oct 1;129(7):728–731. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. G., Weeks R. J., Padhye A. A. Detection of two Blastomyces dermatitidis serotypes by exoantigen analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):110–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.110-114.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B. S., Vergeront J. M., DiSalvo A. F., Kaufman L., Davis J. P. Two outbreaks of blastomycosis along rivers in Wisconsin. Isolation of Blastomyces dermatitidis from riverbank soil and evidence of its transmission along waterways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Dec;136(6):1333–1338. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.6.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Rega M. E., Watson R. R., Campbell C. C. Identification of yeast phase of pathogenic fungi by the specificity of their aminopeptidase(s). Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):132–141. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Biotyping of medically important fungi. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1985;1:155–171. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9547-8_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeil C., Bouillard C., Miegeville M., Morin O., Marjolet M. The echinulate conidia of Blastomyces dermatitidis Gilchrist and Stokes and the taxonomic status of this species. Mykosen. 1982 May;25(5):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1982.tb02750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


