Abstract
Kaempferol is the major flavonol in green tea and exhibits many biomedically useful properties such as antioxidative, cytoprotective and anti-apoptotic activities. To elucidate its effects on the skin, we investigated the transcriptional profiles of kaempferol-treated HaCaT cells using cDNA microarray analysis and identified 147 transcripts that exhibited significant changes in expression. Of these, 18 were up-regulated and 129 were down-regulated. These transcripts were then classified into 12 categories according to their functional roles: cell adhesion/cytoskeleton, cell cycle, redox homeostasis, immune/defense responses, metabolism, protein biosynthesis/modification, intracellular transport, RNA processing, DNA modification/ replication, regulation of transcription, signal transduction and transport. We then analyzed the promoter sequences of differentially-regulated genes and identified over-represented regulatory sites and candidate transcription factors (TFs) for gene regulation by kaempferol. These included c-REL, SAP-1, Ahr-ARNT, Nrf-2, Elk-1, SPI-B, NF-κB and p65. In addition, we validated the microarray results and promoter analyses using conventional methods such as real-time PCR and ELISA-based transcription factor assay. Our microarray analysis has provided useful information for determining the genetic regulatory network affected by kaempferol, and this approach will be useful for elucidating gene-phytochemical interactions.
Keywords: keratinocytes, kaempferol, NF-κB, oligonucleotide array sequence analysis, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, transcription factors
Introduction
Camellia sinensis is the plant used to make green tea. It is believed to provide a number of beneficial medicinal effects and the flavonoids are probably the most important of its many bioactive substances in this respect. These include the biologically-active polyphenols, which exhibit anti-carcinogenic, antiinflammatory, cytostatic, apoptotic, anti-oxidant and anti-angiogenic activities (Ahmad and Mukhtar, 1999; 2001; Park and Dong, 2003). The majority of flavonoids from green tea are catechins such as epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin (EGC), epicatechin gallate (ECG) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), the latter being the focus of most research. EGCG not only selectively induces apoptosis in tumor cells and abnormal human epidermal keratinocytes, it also inhibits UVB-induced AP-1 expression and accelerates keratinocyte differentiation and wound healing (Hsu, 2005).
Recently, the flavonoid kaempferol was obtained from C. sinensis seeds by enzymatic cleavage of a sugar group (Sekine et al., 1991; Park et al., 2006). Kaempferol represents 22-29% of the total dietary flavonoid intake from a variety of diets (de Vries et al., 1997) and is easily absorbed by the digestive tract. Its antioxidative properties have been demonstrated in cell-free systems, as well as in a variety of cell types. It exhibits strong radical-scavenging activity (Murota et al., 2002) and inhibits formation of superoxide anion radicals by xanthine oxidase (Selloum et al., 2001). Chemical stress-induced ROS production is decreased by kaempferol in various cell types (Wang et al., 1999; Samhan-Arias et al., 2004). Kaempferol has also been shown to have cytoprotective and anti-apoptotic activities (Wang et al., 1999; Samhan-Arias et al., 2004) and to inhibit damage to DNA by certain hormones (Dobrzynska et al., 2004) and H2O2 (Noroozi et al., 1998). Although these activities have been reported in several studies, little is known about the effect of kaempferol on gene expression and regulation in the skin.
DNA microarray analysis allows simultaneous monitoring of expression of multiple genes in different cells and tissues (Brown and Botstein, 1999). Its applications for pharmaceutical and clinical research include identification of disease-related genes, as well as targets for therapeutic drugs (Alizadeh et al., 2000). In this study, we used DNA microarray analysis to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of kaempferol on the skin. We investigated changes in the transcriptional profiles of immortalized human keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) following treatment with kaempferol. We then used bioinformatics tools to analyze the promoter sequences of differentially-regulated genes in order to identify common transcription regulators. Using this approach, we identified a genetic regulatory network that responds to kaempferol.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
The spontaneously-transformed human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT (N.E. Fusenig, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany) (Boukamp et al., 1998) was grown in DMEM containing 10% FBS and antibiotics (100 µg ml-1 streptomycin and 100 IU ml-1 penicillin). Cells (1 × 105) were grown in tissue culture flasks (75 cm2) at 37℃ in 5% CO2 and 95% air for 24 h, followed by serum starvation for 24 h. Kaempferol was then added and the cells were incubated for the time periods indicated. Control cultures were maintained in medium supplemented with a 1 : 10,000 dilution of vehicle (DMSO), which produced no apparent growth or differentiation effects.
NHEKs were derived from neonatal foreskin as previously described (Gibson et al.,1996). Briefly, epidermis was isolated from newborn foreskins by incubation in Dispase, and a suspension of keratinocytes was obtained by incubation in 10 mM EDTA and subsequent trypsinization. Cells thus obtained were cultured with serum-free keratinocyte growth medium (KGM, Clonetics, San Diego, CA) and used for experiments after 2 or 3 passages.
RNA preparation
Following kaempferol treatment, HaCaT cells were washed twice with PBS and total RNA was isolated using Trizol reagent (GibcoBRL Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY), according to the manufacturer's instructions. The RNA concentration was determined photometrically and its quality was observed using agarose gel electrophoresis.
cDNA microarray analysis
We used a human 10K cDNA microarray that comprised 10,336 cDNA spots, as described previously (Lee et al., 2002a). Housekeeping genes and yeast DNA were spotted as negative controls. cDNA microarray analyses were performed four times for each time point. Fluorescence-labeled cDNA probes were prepared from 20 µg total RNA using an Amino Allyl cDNA labeling kit (Ambion, Austin, TX), as described previously (Ahn et al., 2004). The Cy3- and Cy5-labeled cDNA probes, corresponding to control and kaempferol-treated cells, respectively, were mixed and hybridized to the microarrays at 55℃ for 16 h. The two fluorescent images (Cy3 and Cy5) were scanned separately using a GMS 418 Array Scanner (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) and image data were analyzed with the ImaGene v. 4.2 (Biodiscovery, Santa Monica, CA) and MAAS (Gaiagene, Seoul, Korea) software packages (Kim et al., 2001). For each hybridization, emission signal data were normalized by multiplying the Cy3 signal values by the mean Cy3 to Cy5 signal intensity ratios for all spots on the array. Values ≥ 2-fold higher than background intensity were considered significant. We calculated the median value of the gene expression ratio from four independently-repeated microarray experiments, then used modified t-tests (significance analysis of microarrays, SAM) to evaluate the statistical significance of changes in gene expression (Tusher et al., 2001). Significant genome-wide changes in expression were selected at SAM(d) = 0.66 and we adopted a 2.0-fold change cutoff, based on our previous experience. Genes exhibiting significant differences in expression level were classified into Gene Ontology (GO)-based functional categories (Ashburner et al., 2000; The Gene Ontology. http://www.geneontology.org), with some modifications. We applied hierarchical clustering to genes using the weighted pair-group method with a centroid average, as implemented in the CLUSTER program (Eisen et al., 1998). The results were analyzed using Tree View software (M. Eisen; http://www.microarrays.org/software).
Real time RT-PCR
We selected a subset of differentially-expressed genes for independent confirmation of microarray results. We performed SYBR green-based real-time RT-PCR using the gene encoding β-actin as an internal reference. Reverse transcription was performed on 4 µg total RNA in a 25 µl reaction mixture containing MuLV reverse transcriptase (2.5 U), RNAse inhibitor (1 U), 5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, (pH 8.3), 2.5 µM oligo (dT) primer and 1 mM dNTPs. The reaction mixture was incubated at 42℃ for 60 min, then denatured at 85℃ for 5 min. Using an ICycler (BioRad, Hercules, CA), cDNA was amplified in 50 µl reaction mixtures containing 1 U AmpliTaq DNA polymerase (Perkin Elmer, Shelton, CT), 50 mM Tris (pH 8.3), 0.25 g/L BSA, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM dNTPs, 1/50,000 dilution of SYBR green I (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) and 0.25 µM of the requisite PCR primers. Primer sequences were as follows: nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2 (NF-κB2) forward, 5'-TCCACCTTTAAGTTGCCCTG-3', reverse, 5'-TCTGCTCTCGTCATGTCACC-3'; phospholipase A2-activating protein (PLAA) forward, 5'-TTAAACACCCACCCACCAAG-3', reverse, 5'-CGAAAGCCTGGAGGTAAAGA-3'; signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) forward, 5'-TCAGACCCATCATCAAGCAA-3', reverse, 5'-ATGACAGGTAAATGGGCGAG-3'; TNFα forward, 5'-TGCACCACAGTTTAAACCCA-3', reverse, 5'-GACTCCTTCAGGTGCTCAGG-3'; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) forward, 5'-GTGGCTGCTATAATTTGCTGTG-3', reverse, 5'-GAAGGTGTCATCTGGATGGGT-3'; PPARγ forward, 5'-CAAGACTACCCTTTAAGTGAA-3', reverse, 5'-CTACTTTGATCGCACTTTGGT-3'; and β-actin forward, 5'-GGGTCAGAAGGACTCCTATG-3', reverse, 5'-GTAACAATGCCATGTTCAAT-3'. The following reaction conditions were used: one cycle of denaturing at 95℃ for 5 min, followed by 30 cycles of 95℃ for 30 s, 60℃ for 45 s and 72℃ for 1 min. Relative RNA levels were determined by analyzing the changes in SYBR green I fluorescence during amplification, according to the manufacturer's instructions. β-actin was amplified in parallel; the results were used for normalization. PCR product sizes were confirmed by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and staining with ethidium bromide. The purity of PCR products was determined by melting point analysis using the ICycler software (BioRad, Hercules, CA)
Promoter analysis
Promoter analysis was performed using oPOSSUM v1.3 (Ho Sui et al., 2005), a web-based tool for analyzing sets of co-expressed genes. It incorporates cross-species comparisons, PSSM-based promoter motif detection and statistical methods for identification of over-represented transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) using a pre-computed database. The database was constructed from an initial set of 14,083 orthologs from both human and mouse, which were obtained by selecting only 'one-to-one' human-mouse orthologs from Ensembl (Clamp et al., 2003). We analyzed 2,000 bp upstream and downstream of the transcription start site (TSS) for each differentially-expressed gene. The level of conservation with the aligned orthologous mouse sequence was set to level 1 (the top 10 percentile of non-coding conserved regions with an absolute minimum percent identity of 70%). Two measures of statistical over-representation were used: a Z-score and a one-tailed Fisher exact probability.
UVB irradiation and NF-κB (p65/RelB) assay
HaCaT cells and NHEKs pretreated with kaempferol or vehicle were washed with PBS, after which fresh PBS was added and the cells were exposed to UVB radiation (40 mJ/cm2) delivered through a bank of FS40 lamps (Westinghouse, Pittsburgh, PA) with a UVB emission maximum at 313 nm. UV wavelengths not normally present in natural incident solar radiation were blocked using a Kodacel cellulose filter (Eastman Kodak Co., Rochester, MN), as described previously (Katiyar et al., 2001). Following irradiation, the culture medium was reintroduced and cells were incubated for a further 6 h. Kaempferol treatment occurred 6 h prior to and following UVB irradiation. Following treatment of cells with kaempferol and/or UVB, nuclear extracts were prepared and assayed using a TransFactor extraction kit (BD Bioscience CLONTECH, San Jose, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Nuclear extracts were spun at 20,000 g for 5 min at 4℃, after which the supernatants were assayed for p65 or RelB content. Equal amounts of nuclear lysate were added to incubation wells pre-coated with the DNA-binding consensus sequence and the presence of translocated p65 or the RelB subunit was assayed.
Plasmids and reporter gene assays
The reporter plasmid PPRE-tk-Luc, which contains three PPAR response elements (PPREs), and the receptor expression plasmid pCMX-mPPAR, have been described previously (Kliewer et al., 1994; Lee and Kang 2000). A modified calcium phosphate precipitation procedure was used for transient transfection (Lee et al., 2002b). In brief, HaCaT cells (1 × 105/well) were seeded into a 12-well culture plate and transfected with DNA mixtures (1.3 µg/well) containing carrier DNA (pBluescript), reporter plasmid (0.1 µg), β-galactosidase (β-gal) expression vector (0.2 µg) and pCMX-mPPAR expression vector (10 ng), using LipofectaminePlus (GIBCO BRL, Grand Island, NY). The cells were treated for 24 h with test compounds, after which luciferase activity was determined using a luminometer, according to the manufacturer's instructions. Luciferase activity was normalized for transfection efficiency using the corresponding β-gal activity.
Statistical analysis
ANOVA tests were performed using SigmaStat (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL); P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Identification of kaempferol-responsive genes
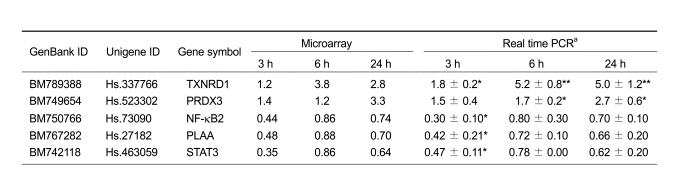
To identify genes regulated differentially by kaempferol, we compared the expression levels of ca. 10,000 genes from kaempferol- and vehicle-treated HaCaT cells. cDNA microarray analyses revealed a > 2-fold difference in the expression of 147 transcripts, at one or more time points (Supplementary Table 1). Of these, 18 and 129 were up- and down-regulated, respectively. Altered expression of the majority of down-regulated transcripts (117) occurred 3 h after kaempferol treatment. To provide independent validation of the microarray data, we performed real-time PCR analyses on expression of selected genes. In concordance with the results obtained from the microarray experiments, transcript levels for genes encoding NF-κB2, Plaa and Stat3 decreased following kaempferol treatment (Table 1).
Table 1.
Validation of microarray data by real-time PCR.
aHaCaT cells (1 × 105) were cultivated in medium containing 10% FBS for 24 h. Following subsequent 24 h serum starvation, kaempferol was added and incubation continued for the time periods indicated. Control cultures were maintained in medium supplemented with a 1 : 10,000 dilution of vehicle (DMSO). Total RNA was isolated and the relative mRNA expression levels of different genes were measured by real-time RT-PCR analysis with SYBR green. Data are expressed as fold changes (means ± SD) (n = 3), normalized to β-actin mRNA expression. The values for the control group were set at 1.00. Analyses were performed in triplicate for each group. *P < 0.05 compared with the control group. **P < 0.001 compared with the control group.
Functional categorization and hierarchical clustering of differentially-expressed genes
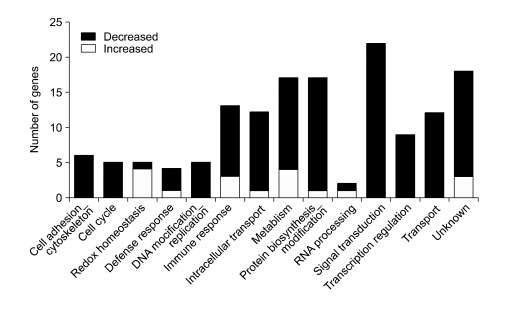
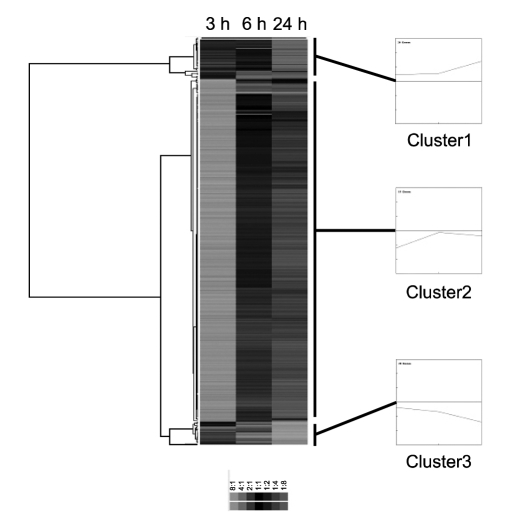
The 147 transcripts were classified into 12 categories, according to their functional roles. The majority of down-regulated genes were involved in cell adhesion/cytoskeleton, cell cycle, DNA modification/replication, signal transduction, transcription regulation and transport (Figure 1). In contrast, up-regulated genes were involved in cellular redox homeostasis (Figure 1). The 147 transcripts were clustered into 3 distinct expression patterns, following a hierarchical clustering of similarity (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
Global gene expression in functional categories. Black and white bars represent the numbers of genes with decreased and increased expression, respectively, following kaempferol treatment.
Figure 2.
Hierarchical clustering of genes that were significantly up- or down-regulated by kaempferol treatment. Differentially-expressed genes were clustered hierarchically based on similarities in their expression profiles. The expression pattern of each gene is displayed as a horizontal strip. The color scale is indicated below. Clusters 1-3 are defined according to their gene expression patterns, and the log ratio values of genes for each class are presented as line graphs.
Promoter analysis of differentially-expressed genes
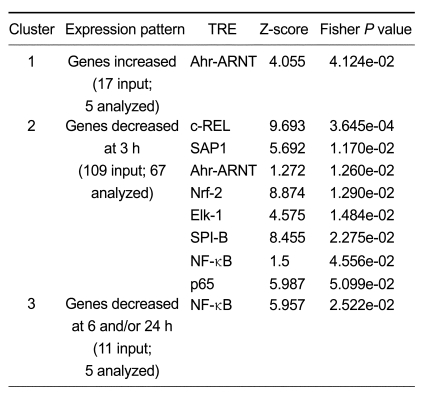
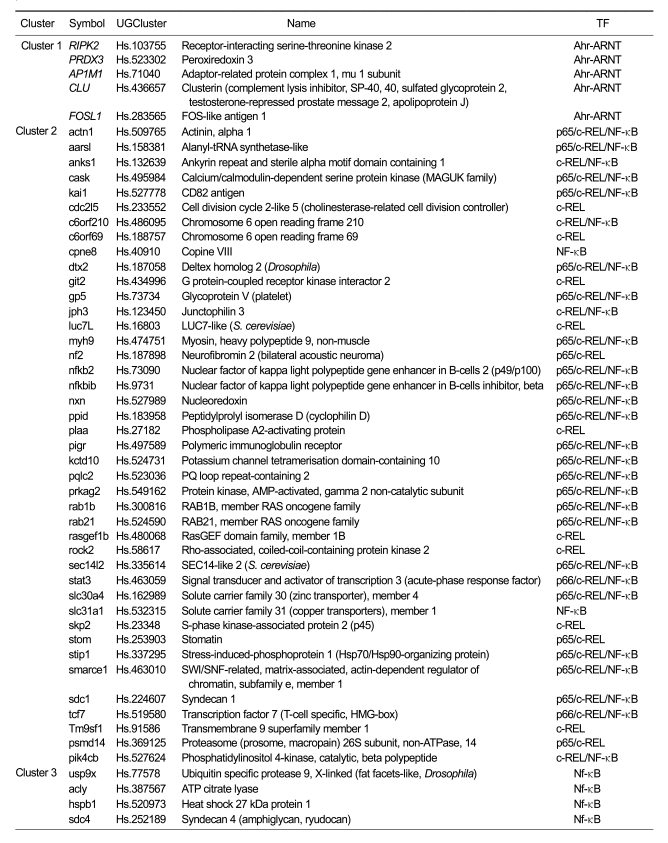
The nonredundant set of 147 differentially-expressed genes (based on GenBank accession number) was mapped computationally to 137 unique UniGene clusters. In order to identify biologically relevant transcription factor binding sites (referred to here as transcription regulatory elements or TREs), we performed promoter analyses on the regulatory regions of these genes (2,000 bp up- and downstream of the TSS) using oPOSSUM v1.3 (Ho Sui et al., 2005). The number of genes submitted to oPOSSUM, as well as the genes mapped to mouse orthologs and used for subsequent analyses, are presented in Table 2. We used a Fisher P value cutoff of 0.05 to identify over-represented TREs. Over represented TREs for genes exhibiting altered expression following kaempferol treatment were as follows: increased expression, Ahr-ARNT; decreased expression, c-REL, SAP-1, Ahr-ARNT, Nrf-2, Elk-1, SPI-B, NF-κB and p65. The c-REL, p65 and NF-κB are all members of the NF-κB family of TFs, and these ranked first, seventh and eighth using Fisher P values (Table 2). The differentially expressed genes following kaempferol treatment with overrepresented Ahr-ARNT, p65, c-REL and NF-κB in their promoters are listed in Table 3.
Table 2.
Over-represented TREs in the promoters of differentially-expressed genes following treatment with Kaempferol.
Promoter analysis was performed using oPOSSUM v1.3 (Ho Sui et al., 2005), a web-based promoter motif detection and statistical methods for identification of over-represented transcription response elements (TREs) in the promoters of gene set. 2,000 bp upstream and 500 bp downstream of the transcription start site (TSS) for each differentially-expressed gene were analyzed. The level of conservation with the aligned orthologous mouse sequence was set to level 1 (the top 10 percentile of non-coding conserved regions with an absolute minimum percent identity of 70%). Two measures of statistical over-representation were used: a Z-score and a one-tailed Fisher exact probability. TREs with the mostly highly ranked Z-scores or with Fisher P-value < 0.05 were listed. See (Ho Sui et al., 2005) for how the Z-score and Fisher P-values were calculated.
Table 3.
Genes increased or decreased following kaempferol treatment, with overrepresented Ahr-ARNT, p65, c-REL and NF-κB in their promoters.
Effect of kaempferol on NF-κB activity
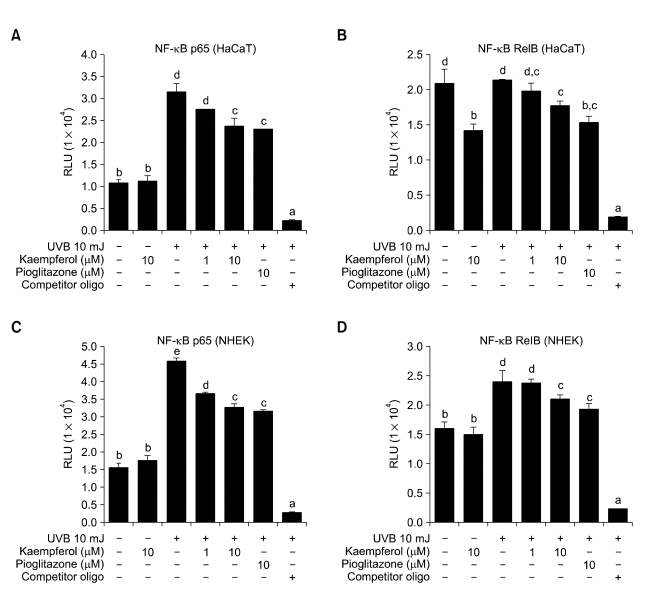
To verify the bioinformatic analyses, we used an ELISA-based transcription factor assay to examine the effect of 10 µM kaempferol on activation of NF-κB p65 and RelB in HaCaT cells and NHEKs irradiated with UVB (Figure 3). Although kaempferol treatment significantly inhibited activation of NF-κB p65 elicited by UVB irradiation, it had no effect on basal activity in HaCaT cells (Figure 3A). In contrast to NF-κB p65, RelB was not activated by UVB irradiation in HaCaT cells and kaempferol treatment decreased RelB basal activity, as well as RelB activity in UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells (Figure 3B). Although UVB-induced NF-κB activation was shown in both HaCaT cells and NHEKs, HaCaT cells were found to contain a constitutive aberrant NF-κB activity that is not found in NHEKs (Lewis et al., 2006). Therefore, we examine the effect of kaempferol on activation of NF-κB in NHEKs. Similar to HaCaT cells, kaempferol treatment significantly inhibited activation of NF-κB p65 elicited by UVB irradiation in NHEKs (Figure 3C). However, RelB showed a different response following UVB irradiation in NHEKs. RelB was activated by UVB irradiation and UVB-induced RelB activation was inhibited by kaempferol treatment in NHEKs (Figure 3D).
Figure 3.
Effects of kaempferol on NF-κB activity in HaCaT cells and NHEKs. Following treatment with kaempferol for 6 h, HaCaT cells and NHEKs were exposed to UVB irradiation ( 40 mJ cm-2) then cultured in media with kaempferol for a further 6 h. Nuclear extracts of HaCaT cells were prepared and the presence of translocated p65 (A) or RelB subunit (B) was assessed using ELISA. With nuclear extracts of NHEKs, the presence of translocated p65 (C) or RelB subunit (D) was assessed. Values represent means ± SD of 3 or 4 independent experiments. Means with differently-lettered superscripts differ at P < 0.05.
Effect of kaempferol on the transcriptional activity of PPARs
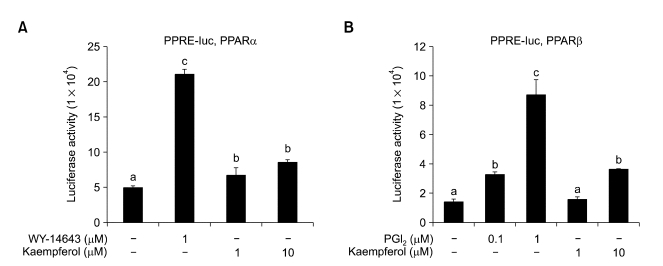
PPAR activation is one of several mechanisms that could account for decreased NF-κB activities (Yamamoto et al., 2003). As PPAR activators have been reported to antagonize the NF-κB signaling pathway directly (Blanquart et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2003), we tested whether or not kaempferol could activate the transcriptional activity of PPARs in HaCaT cells. We performed transient transfection experiments using the PPRE-tk-Luc reporter gene (Kliewer et al., 1994; Lee and Kang, 2000). When PPRE-tk-Luc was co-transfected with the PPARα, PPARβ/δ and PPARγ expression vectors, treatment with 10 µM kaempferol increased reporter activity by a factor of approximately 2.0, 2.6 and 3.0, respectively (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Effect of kaempferol on transcriptional activity of PPARs. HaCaT cells containing PPRE-tk-Luc were transiently transfected with 10 ng pCMX-mPPAR, then treated with WY14643, prostacyclin (PGI2), troglitazone (TGZ) or kaempferol. After 24 h, cells were assayed for luciferase activity, which was normalized to the corresponding β-gal activity. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 or 4 independent experiments. Means with differently-lettered superscripts differ at P < 0.05.
Discussion
The beneficial effects of kaempferol have been demonstrated in cell-free systems and a variety of cell types (Noroozi et al., 1998; Wang et al., 1999; Selloum et al., 2001; Murota et al., 2002; Dobrzynska et al., 2004; Samhan-Arias et al., 2004). However, its effects on gene expression in the skin have rarely been studied. Therefore, we used cDNA microarray analysis to examine its effects on epidermal keratinocytes. We assessed the levels of ca. 10,000 transcripts in kaempferol-treated HaCaT cells and observed marked alterations in the expression of 147 genes. These genes are involved in cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, redox homeostasis, immune and defense responses, metabolism, protein biosynthesis and modification, DNA modification and replication, regulation of transcription, signal transduction and transport in a wide range of biological systems, including human skin cells (Ashburner et al., 2000; The Gene Ontology, http://www. geneontology.org).
Following kaempferol treatment of HaCaT cells, we observed a > 2-fold upregulation of genes involved in redox homeostasis, such as an endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin superfamily member (18 kDa), peroxiredoxin 3 and thioredoxin reductase 1. Tea-associated compounds are known to exhibit potent antioxidant activity and have been implicated in the alleviation of cancer-associated oxidative stresses (Ahmad and Mukhtar, 1999, 2001; Park and Dong, 2003). In relation to such activities, flavonoids isolated from green tea leaves have been shown to regulate several genes differentially (Ahmad and Mukhtar, 1999). However, the regulatory effects of kaempferol on genes involved in cellular redox homeostasis in the skin have not yet been studied intensively. Our microarray data provide a starting point for unraveling the molecular mechanisms underlying the antioxidative action of kaempferol in skin cells.
We observed decreased expression patterns in genes encoding proteins involved in inflammatory and immune responses, such as CD68 antigen, interferon (α, β, and ω) receptor 1, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2 (p49/p100), nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor β, interferon α-inducible protein (clone IFI-15K), interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3, Toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acutephase response factor). Several in vitro studies have investigated the inhibitory activity of flavonoids on NO and cytokine production in macrophage cell lines such as RAW264.7 (Kim et al., 1999, 2004; Xagorari et al., 2001; Blonska et al., 2003; Jung et al., 2007) and J774.1 (Blonska et al., 2004). Kaempferol was shown to have an inhibitory effect on M-CSF-induced proliferation of macrophages obtained from bone marrow cultures (Comalada et al., 2006). In the primary macrophage cultures, it downregulated iNOS expression and inhibited LPS-induced TNFα secretion (Comalada et al., 2006). In osteoblasts, it downregulated TNFα-induced production of the osteoclastogenic cytokines IL-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) (Pang et al., 2006). It has been suggested that the antioxidative/radical scavenging properties of flavonoids are related in part to their anti-inflammatory activities and specifically to inhibition of the NF-κB pathway (Comalada et al., 2006). These aspects should be considered in relation to the gene expression profiles revealed in our study.
The regulatory regions of promoters from differentially-expressed genes have the potential to provide insight into coordinated regulation. Therefore, promoter analysis was performed using oPOSSUM v1.3 (Ho Sui et al., 2005). Two measures of statistical over-representation were used: a Z-score and a one-tailed Fisher exact probability. The Z-score compares the rate of occurrence of a TRE in the set of co-expressed genes to the expected rate estimated from the pre-computed background set (Ho Sui et al., 2005). Thus, Z-score indicates a significant difference in the rate of existence of sites, and is particularly useful for detecting increased prevalence of common sites. The Fisher exact test compares the proportion of co-expressed genes containing a particular TRE to the proportion of the non-target group that contains the site to determine the probability of a non-random association between the target group and the TRE of interest (Ho Sui et al., 2005). A significant value for the Fisher exact probability indicates that there are a significant proportion of genes that contain the site, and is particularly good for rare TREs (Ho Sui et al., 2005). oPOSSUM analysis identified binding sites for transcription factors that play important roles in cell proliferation, differentiation and developmental processes. The Ahr-ARNT TRE was over-represented among both genes increased and decreased following kaempferol treatment. Several TFs have been shown to have transactivatory and suppressive properties simultaneously in the same type of cell under the same condition, depending on interacting partners and target genes. For example, a positive role for AP-1 in the estrogen-mediated induction of target genes is well established, but a role for AP-1 in gene repression is also elucidated in estrogen-treated cells. In that case, AP-1 interacts with estrogen receptor and corepressor NRIP1 (Carroll et al., 2006). Similarly, it might be possible that Ahr-ARNT TRE can have roles in the kaempferol-mediated induction and repression of target genes simultaneously.
The c-REL, SAP-1, Nrf-2, Elk-1, SPI-B, NF-κB and p65 binding sites were over-represented in genes with decreased expression. The Fisher P values of TREs for members of the NF-κB family, such as c-REL, p65 and NF-κB, ranked highly. These bioinformatic analyses were consistent with the ELISA-based transcription factor assay, which indicated decreased NF-κB p65 and RelB activity in kaempferol-treated HaCaT cells and NHEKs. Therefore, the downregulation of genes in Clusters 2 and 3 may be attributed in part to reduced activity of members of the NF-κB-family. In addition, our observations are consistent with previous reports, which demonstrated that kaempferol blocked TNFα-induced translocation of the NF-κB subunit p65 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in mouse primary calvarial osteoblasts (Pang et al., 2006) and downregulate iNOS and TNFα expression via NF-κB inactivation in aged rat gingival tissues (Kim et al., 2007). Kim et al. (2007) showed the inhibitory effects of kaempferol against the aging process such as inflammation in gingival tissues and demonstrated the underlying molecular mechanisms. We predicted the NF-κB family signal as one putative regulatory network from the epidermal genes regulated differentially by kaempferol using bioinformatic methods and confirmed the prediction with the ELISA-based transcription factor assay. Our result was consistent with Kim et al.'s result. Contrary to their hypothesis-driven approach, however, our unbiased approach gave comprehensive information about wide ranges of effects of kaempferol. Besides NF-κB family members, many transcription factors have to be validated.
Kaempferol was shown to bind to the PPAR γ in a competition binding assay using Gst-PPARγ LBD fusion protein and kaempferol-induced stimulation of PPAR transactivation activity was detected in transient transfection experiments employing the mouse macrophage cell line RAW264.7 (Liang et al., 2001). In addition, PPAR activators have been reported to antagonize the NF-κB signaling pathway directly (Blanquart et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2003). Therefore, among the mechanisms that can account for decreased NF-κB activity, we examined activation of PPARs. Kaempferol stimulated PPAR transcriptional activity in HaCaT cells transiently transfected with the PPRE-tk-Luc reporter gene, suggesting that, at least in part, its mode of action may be mediated by PPAR pathways.
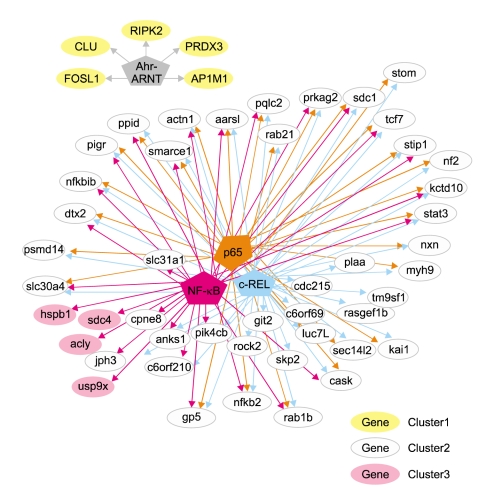
In summary, we investigated kaempferol-induced alterations in the transcriptional profiles of immortalized human keratinocytes and analyzed the promoters of differentially regulated genes using bioinformatics. We identified altered gene expression profiles in response to kaempferol, and this information will be useful for establishing its regulatory network (Figure 5), as well as determining gene-nutrient interactions. Further studies of promoter occupancy and transcription factor perturbation are now required to provide a functional validation of the TREs identified in this study, as well as the TFs that bind to them.
Figure 5.
A network showing relations between the over-represented TREs (P value < 0.05) and differentially-expressed genes following treatment with kaempferol. The pentagonal boxes represent the TREs and ellipses represent the genes.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Jae Sung Hwang's research was supported in part by a grant from the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A050432).
Abbreviations
- NF-κB
nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells
- PLAA
phospholipase A2-activating protein
- PPAR
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- STAT3
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TF
transcription factor
- TFBS
transcription factor binding site
- TRE
transcription regulatory element
- TSS
transcriptional start site
Supplementary Material
Supplemental Data
References
- 1.Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Green tea polyphenols and cancer: Biologic mechanisms and practical implications. Nutr Rev. 1999;57:78–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1999.tb06927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Cutaneous photochemoprotection by green tea: A brief review. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2001;14:69–76. doi: 10.1159/000056336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ahn JI, Lee KH, Shin DM, Shim JW, Lee JS, Chang SY, Lee YS, Brownstein MJ, Lee SH, Lee YS. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of differentiation of embryonic stem cells into midbrain and hindbrain neurons. Dev Bio. 2004;265:491–501. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.09.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, Powell JI, Yang L, Marti GE, Moore T, Hudson J, Jr, Lu L, Lewis DB, Tibshirani R, Sherlock G, Chan WC, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Armitage JO, Warnke R, Levy R, Wilson W, Grever MR, Byrd JC, Botstein D, Brown PO, Staudt LM. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell-lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. doi: 10.1038/35000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blanquart C, Barbier O, Fruchart JC, Staels B, Glineur C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: regulation of transcriptional activities and roles in inflammation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;85:267–273. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Blonska M, Czuba ZP, Krol W. Effect of flavone derivatives on interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) mRNA expression and IL-1beta protein synthesis in stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 2003;57:162–166. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2003.01213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Blonska M, Bronikowska J, Pietsz G, Czuba ZP, Scheller S, Krol W. Effects of ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) and its flavones on inducible gene expression in J774A.1 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;91:25–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2003.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1998;106:761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brown PO, Botstein D. Exploring the new world of the genome with DNA microarrays. Nat Genet. 1999;21:33–37. doi: 10.1038/4462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Carroll JS, Meyer CA, Song J, Li W, Geistlinger TR, Eeckhoute J, Brodsky AS, Keeton EK, Fertuck KC, Hall GF, Wang Q, Bekiranov S, Sementchenko V, Fox EA, Silver PA, Gingeras TR, Liu XS, Brown M. Genome-wide analysis of estrogen receptor binding sites. Nat Genet. 2006;11:1289–1297. doi: 10.1038/ng1901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen F, Wang M, O'Connor JP, He M, Tripathi T, Harrison LE. Phosphorylation of PPARgamma via active ERK1/2 leads to its physical association with p65 and inhibition of NF-κB. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:732–744. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Clamp M, Andrews D, Barker D, Bevan P, Cameron G, Chen Y, Clark L, Cox T, Cuff J, Curwen V, Down T, Durbin R, Eyras E, Gilbert J, Hammond M, Hubbard T, Kasprzyk A, Keefe D, Lehvaslaiho H, Iyer V, Melsopp C, Mongin E, Pettett R, Potter S, Rust A, Schmidt E, Searle S, Slater G, Smith J, Spooner W, Stabenau A, Stalker J, Stupka E, Ureta-Vidal A, Vastrik I, Birney E. Ensembl 2002: accommodating comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:38–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Comalada M, Ballester I, Bailon E, Sierra S, Xaus J, Galvez J, de Medina FS, Zarzuelo A. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory markers in primary bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by naturally occurring flavonoids: analysis of the structure-activity relationship. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:1010–1021. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.de Vries JH, Janssen PL, Hollman PC, van Staveren WA, Katan MB. Consumption of quercetin and kaempferol in free-living subjects eating a variety of diets. Cancer Lett. 1997;114:141–144. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(97)04645-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dobrzynska MM, Baumgartner A, Anderson D. Antioxidants modulate thyroid hormone- and noradrenaline-induced DNA damage in human sperm. Mutagenesis. 2004;19:325–330. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geh037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D. Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14863–14868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.25.14863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gibson DFC, Ratnam AV, Bikle DD. Evidence for separate control mechanisms in the message, protein, and enzyme activation levels for transglutaminase during calciuminduced differentiation of normal and transformed human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1996;106:154–161. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12329856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ho Sui SJ, Mortimer JR, Arenillas DJ, Brumm J, Walsh CJ, Kennedy BP, Wasserman WW. oPOSSUM: identification of over-represented transcription factor binding sites in coexpressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:3154–3164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hsu S. Green tea and the skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52:1049–1059. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2004.12.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jung CH, Kim JH, Hong MH, Seog HM, Oh SH, Lee PJ, Kim GJ, Kim HM, Um JY, Ko SG. Phenolic-rich fraction from Rhus verniciflua Stokes (RVS) suppress inflammatory response via NF-kappaB and JNK pathway in lipopolysaccharideinduced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;110:490–497. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Katiyar SK, Afaq F, Azizuddin K, Mukhtar H. Inhibition of UVB-induced oxidative stress-mediated phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in cultured human epidermal keratinocytes by green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001;176:110–117. doi: 10.1006/taap.2001.9276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim HK, Cheon BS, Kim YH, Kim SY, Kim HP. Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure-activity relationships. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58:759–765. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(99)00160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kim HK, Park HR, Lee JS, Chung TS, Chung HY, Chung J. Down-regulation of iNOS and TNF-α expression by kaempferol via NF-κB inactivation in aged rat gingival tissues. Biogerontology. 2007;8:399–408. doi: 10.1007/s10522-007-9083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim JH, Kim HY, Lee YS. A novel method using edge detection for signal extraction from cDNA microarray image analysis. Exp Mol Med. 2001;33:83–88. doi: 10.1038/emm.2001.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim SJ, Park H, Kim HP. Inhibition of nitric oxide production from lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 cells by synthetic flavones: structure-activity relationship and action mechanism. Arch Pharm Res. 2004;27:937–943. doi: 10.1007/BF02975847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kliewer SA, Forman BM, Blumberg B, Ong ES, Borgmeyer U, Mangelsdorf DJ, Umesono K, Evans RM. Differential expression and activation of a family of murine peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:7355–7359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee KH, Chang MY, Ahn JI, Yu DH, Jung SS, Choi JH, Noh YH, Lee YS, Ahn MJ. Differential gene expression in retinoic acid-induced differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells, NB4 and HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002a;296:1125–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee MO, Kang HJ. Role of coactivators and corepressors in the induction of the RARbeta gene in human colon cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2000;25:1298–1302. doi: 10.1248/bpb.25.1298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee MO, Kang HJ, Kim Y, Oum JH, Park J. Repression of FasL Expression by Retinoic acid Involves a Novel Mechanism of Inhibition of Transactivation Function of the Nuclear Factors of Activated T-cells. Eur J Biochem. 2002b;269:1162–1170. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lewis DA, Hengeltraub SF, Gao FC, Leivant MA, Spandau DF. Aberrant NF-kappaB activity in HaCaT cells alters their response to UVB signaling. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:1885–1892. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liang YC, Tsai SH, Tsai DC, Lin-Shiau SY, Lin JK. Suppression of inducible cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase through activation of peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor-gamma by flavonoids in mouse macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2001;496:12–18. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02393-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Murota K, Shimizu S, Miyamoto S, Izumi T, Obata A, Kikuchi M, Terao J. Unique uptake and transport of isoflavone aglycones by human intestinal caco-2 cells: comparison of isoflavonoids and flavonoids. J Nutr. 2002;132:1956–1961. doi: 10.1093/jn/132.7.1956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Noroozi M, Angerson WJ, Lean ME. Effects of flavonoids and vitamin C on oxidative DNA damage to human lymphocytes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998;67:1210–1218. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/67.6.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pang JL, Ricupero DA, Huang S, Fatma N, Singh DP, Romero JR, Chattopadhyay N. Differential activity of kaempferol and quercetin in attenuating tumor necrosis factor receptor family signaling in bone cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;71:818–826. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.12.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Park AM, Dong Z. Signal transduction pathways: targets for green and black tea polyphenols. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;36:66–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Park JS, Rho HS, Kim DH, Chang IS. Enzymatic preparation of kaempferol from green tea seed and its antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:2951–2956. doi: 10.1021/jf052900a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Samhan-Arias AK, Martin-Romero FJ, Gutierrez-Merino C. Kaempferol blocks oxidative stress in cerebellar granule cells and reveals a key role for reactive oxygen species production at the plasma membrane in the commitment to apoptosis. Free Radical Biol Med. 2004;37:48–61. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sekine T, Arita J, Yamaguchi A, Saito K, Okonogi S, Morisaki N, Iwasaki S, Murakoshi I. Two flavonol glycosides from seeds of camellia sinensis. Phytochemistry. 1991;30:991–995. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(91)85293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Selloum L, Reichl S, Muller M, Sebihi L, Arnhold J. Effects of flavonols on the generation of superoxide anion radicals by xanthine oxidase and stimulated neutrophils. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001;395:49–56. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2001.2562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. [last accessed May 8, 2006];The Gene Ontology. Available from: http://www.geneontology.org.
- 42.Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:5116–5121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091062498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang IK, Lin-Shiau SY, Lin JK. Induction of apoptosis by apigenin and related flavonoids through cytochrome c release and activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 in leukaemia HL-60 cells. Eur J Cancer. 1999;35:1517–1525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xagorari A, Papapetropoulos A, Mauromatis A, Economou M, Fotsis T, Roussos C. Luteolin inhibits an endotoxinstimulated phosphorylation cascade and proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophages. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;296:181–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yamamoto Y, Verma UN, Gaynor RB. Tools to interfere with NF-κB activation. In: Beyaert R, editor. Nuclear Factor κB: regulation and role in disease. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer academic publishers; 2003. pp. 199–219. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental Data