Abstract
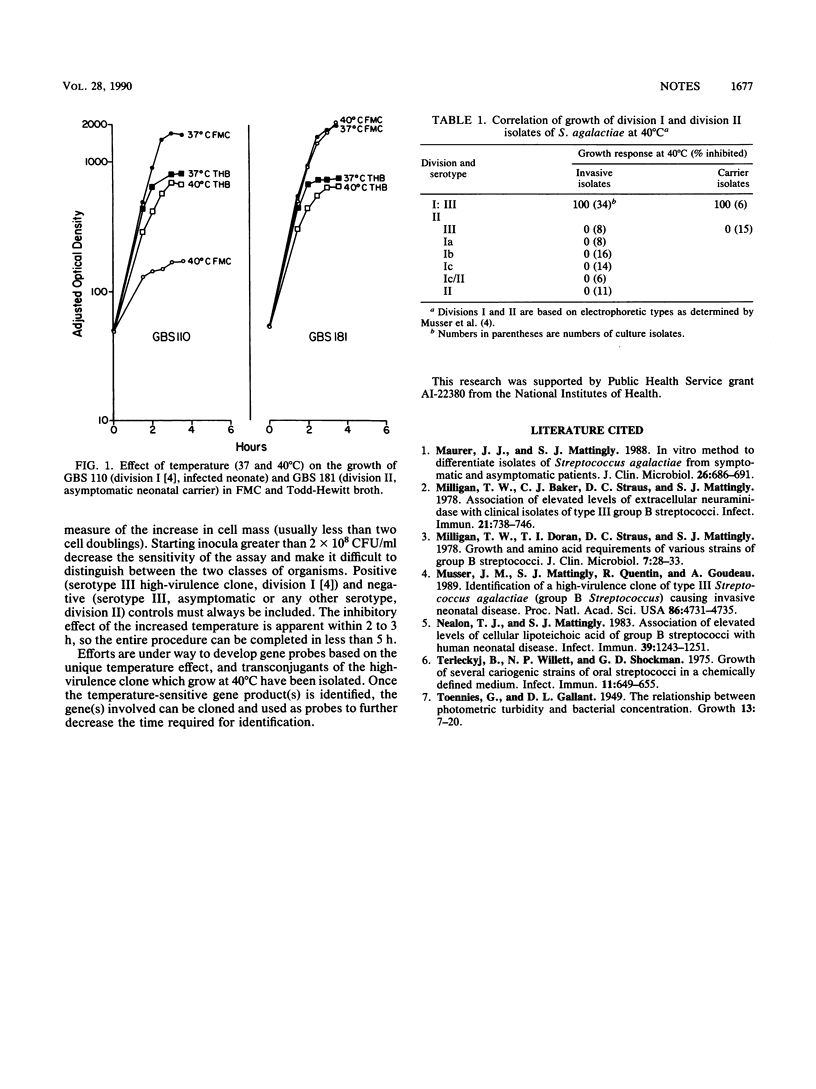
A high-virulence clone of serotype III Streptococcus agalactiae causing invasive neonatal disease was previously identified by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. A simple procedure involving growth at 40 degrees C distinguished all isolates classified in this high-virulence clone from other serotype III isolates, which are more frequently associated with asymptomatically colonized infants, as well as the other serotypes of group B streptococci. The high-virulence clone failed to grow at 40 degrees C in FMC, a chemically defined medium, in contrast to the other organisms, which grew readily.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Maurer J. J., Mattingly S. J. In vitro method to differentiate isolates of type III Streptococcus agalactiae from symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.686-691.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Baker C. J., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Association of elevated levels of extracellular neuraminidase with clinical isolates of type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):738–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.738-746.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Doran T. I., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Growth and amino acid requirements of various strains of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):28–33. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.28-33.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Mattingly S. J., Quentin R., Goudeau A., Selander R. K. Identification of a high-virulence clone of type III Streptococcus agalactiae (group B Streptococcus) causing invasive neonatal disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4731–4735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealon T. J., Mattingly S. J. Association of elevated levels of cellular lipoteichoic acids of group B streptococci with human neonatal disease. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1243–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1243-1251.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


