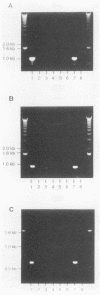
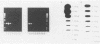
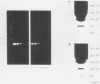
Abstract
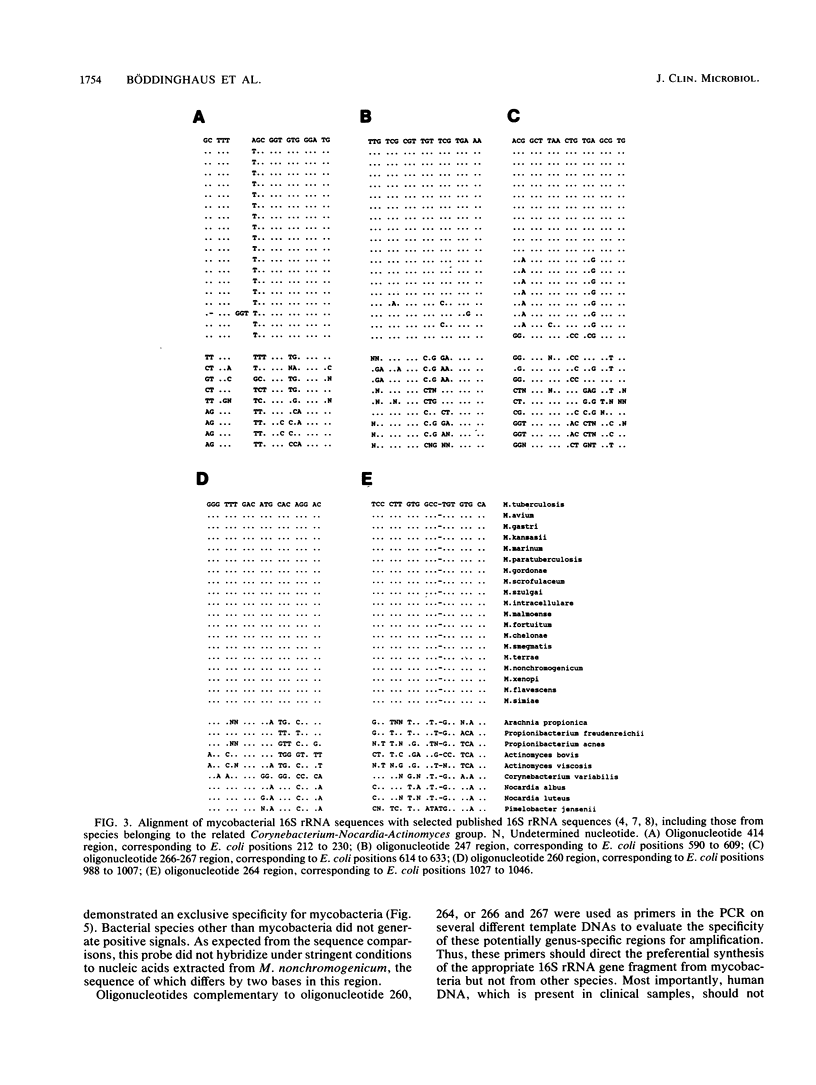
Oligonucleotides specific at a genus, group, or species level were defined by a systematic comparison of small-subunit rRNA sequences from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. africanum, M. bovis BCG, M. avium, M. kansasii, M. marinum, M. gastri, M. chelonae, M. smegmatis, M. terrae, M. nonchromogenicum, M. xenopi, M. malmoense, M. szulgai, M. scrofulaceum, M. fortuitum, M. gordonae, M. intracellulare, M. simiae, M. flavescens, M. paratuberculosis, M. sphagni, M. cookii, M. komossense, M. phlei, and M. farcinica. On the basis of the defined oligonucleotides, the polymerase chain reaction technique was explored to develop a sensitive taxon-specific detection system for mycobacteria. By using M. tuberculosis as a model system, fewer than 10 bacteria could be reliably detected by this kind of assay. These results suggest that amplification of rRNA sequences by the polymerase chain reaction may provide a highly sensitive and specific tool for the direct detection of microorganisms without the need for prior cultivation.
Full text
PDF



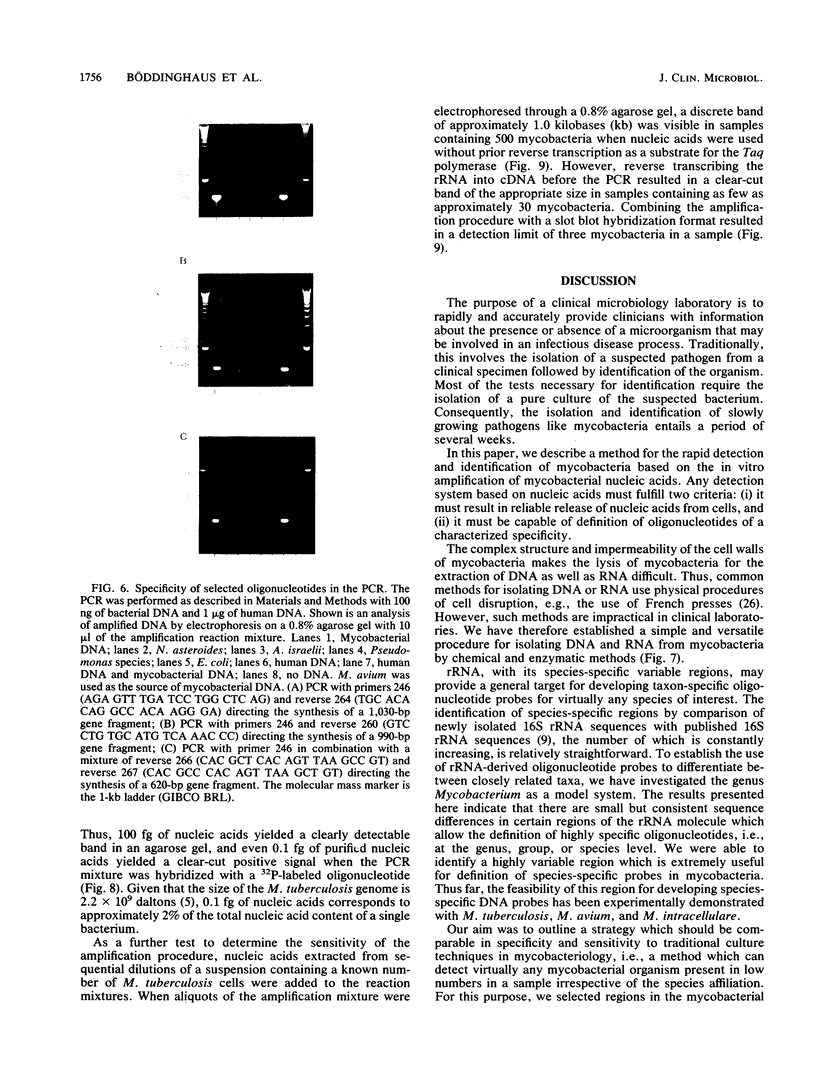
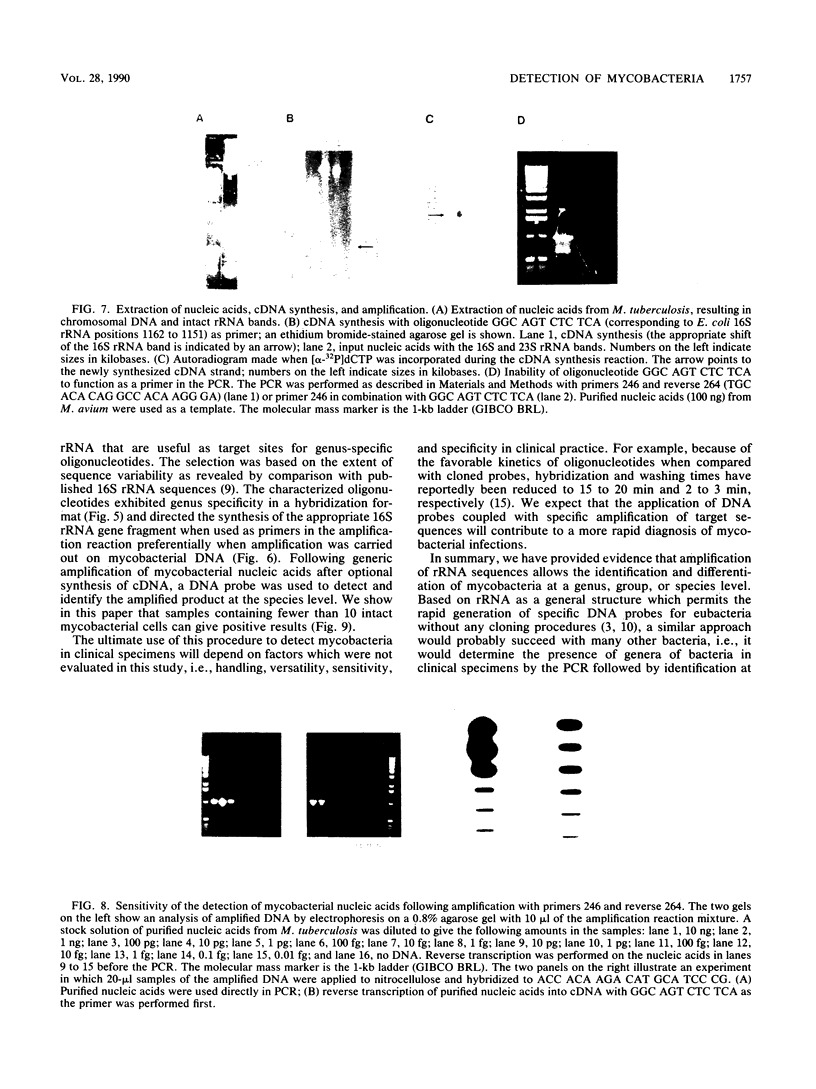


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates J. H. Diagnosis of tuberculosis. Chest. 1979 Dec;76(6 Suppl):757–763. doi: 10.1378/chest.76.6_supplement.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C. Rapid determination of bacterial ribosomal RNA sequences by direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. AIDS-related mycobacterial disease. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1988;10(4):375–391. doi: 10.1007/BF02053847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dams E., Hendriks L., Van de Peer Y., Neefs J. M., Smits G., Vandenbempt I., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r87–173. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards U., Rogall T., Blöcker H., Emde M., Böttger E. C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7843–7853. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göbel U. B., Geiser A., Stanbridge E. J. Oligonucleotide probes complementary to variable regions of ribosomal RNA discriminate between Mycoplasma species. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1969–1974. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Grandchamp B., Lévy-Frébault V., Lecossier D., Rauzier J., Bocart D., Gicquel B. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of mycobacterial DNA. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):843–849. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartskeerl R. A., de Wit M. Y., Klatser P. R. Polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Mycobacterium leprae. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2357–2364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini B., Svartengren G., Hoffner S. E., Unge G., Widström O. Tenosynovitis of the hand caused by Mycobacterium terrae. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;8(8):722–724. doi: 10.1007/BF01963759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossau R., Vanmechelen E., De Ley J., Van Heuverswijn H. Specific Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA-probes derived from ribosomal RNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1735–1745. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura H. H., Graham D. Y. Nucleic acid hybridization studies of mycobactin-dependent mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1309–1312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1309-1312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]