Abstract
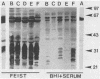
The production of protective antigen in modified serum-free nutrient broth (H. Feist, K.-D. Flossmann, and W. Erler, Arch. Exp. Veterinaermed. 30:49-57, 1976) and in brain heart infusion broth supplemented with 10% horse serum (BHIS) was evaluated for six strains of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae serotypes 1a, 2, 2b, 4, and N. All six strains grew to higher cell densities in modified Feist medium than in BHIS and produced larger amounts of 64,000- to 66,000- and 39,000- to 40,000-molecular-weight antigens involved in immunity to erysipelas. A vaccine produced in Feist medium from E. rhusiopathiae SE-9 (serotype 2) was highly effective in a mouse protection test. We therefore suggest that modified Feist medium is an excellent, if not superior, alternative to BHIS for production of erysipelas vaccine.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durner K., Güttner H., Kamieth R., Rothe F., Schmidt P., Winkler H., Kludas K. H. Supplemente als Bestandteil von Nährmedien für Bakterien- und Zellkulturen. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1972;26(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eamens G. J., Turner M. J., Catt R. E. Serotypes of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in Australian pigs, small ruminants, poultry, and captive wild birds and animals. Aust Vet J. 1988 Aug;65(8):249–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1988.tb14311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erler W. Serologische, chemische und immunchemische Untersuchungen an Rotlaufbakterien. 13. Das immunisierende Antigen. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1973;27(2):321–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feist H., Flossmann K. D., Erler W. Einige Untersuchungen zum Nährstoffbedarf der Rotlaufbakterien. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1976 Jan 1;30(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Timoney J. F. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a protective antigen of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3116–3121. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3116-3121.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kludas K. H., Meese M. The significance of various supplements in nutrient media for the appearance of the immunizing antigen Erysipelothrix insidiosa. 1. Characterization of effective serum components. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1968;13(6):515–517. doi: 10.1007/BF02874224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'leary W. M. THE FATTY ACIDS OF BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Dec;26(4):421–447. doi: 10.1128/br.26.4.421-447.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. R., Verwey W. F. Isolation and Characterization of a Protective Antigen-Containing Particle from Culture Supernatant Fluids of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):380–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.380-386.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. L., Harrington R., Jr Serotypes of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolated from swine and from soil and manure of swine pens in the United States. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Nov;39(11):1833–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. L. Swine erysipelas--a review of prevalence and research. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Apr 15;184(8):944–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]