Abstract
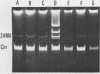
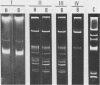
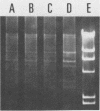
The transmission of pathogenic bacteria from animals to humans is widely studied because of its public health importance. In this study, we show the transmission of Salmonella typhimurium from cattle which had received no growth-promoting antibiotics to humans who had direct contact with the ill animals. On one cattle farm, the veterinarian attending the sick animals became ill, and two other individuals living on the farm later developed salmonellosis. The strains isolated from both humans and animals at one farm were identical as to antibiotic susceptibility and phage type, and they were specifically traced by the presence of a common 24-megadalton plasmid. Restriction enzyme digests of this plasmid from both human and animal strains were identical. At another farm, tetracycline-resistant S. typhimurium strains possessing a different profile (eight plasmids) were isolated from both animals and humans. The tetracycline-resistant clone was also isolated from animals at a third farm, but with animals and humans having no known contact with those of the other two farms.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezanson G. S., Khakhria R., Bollegraaf E. Nosocomial outbreak caused by antibiotic-resistant strain of Salmonella typhimurium acquired from dairy cattle. Can Med Assoc J. 1983 Feb 15;128(4):426–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. L. Applications and relevance of plasmid analysis in clinical microbiology laboratories. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jun;9(6):420–422. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.6.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hickman F. W., Sikes J. V. Automation of Salmonella typhi phage typing. Lancet. 1975 Oct 25;2(7939):787–790. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges M. C., Wachsmuth I. K., Birkness K. A., Moseley S. L., Georges A. J. Genetic probes for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from childhood diarrhea in the Central African Republic. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.199-202.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsen S., Breen O. Investigation of an outbreak of Salmonella oranienburg infections in Norway, caused by contaminated black pepper. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 May;119(5):806–812. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Davis B. R., Cohen M. L. High-molecular-weight plasmid correlates with Escherichia coli enteroinvasiveness. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1295–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1295-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Osterholm M. T., Senger K. A., Cohen M. L. Drug-resistant Salmonella from animals fed antimicrobials. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 6;311(10):617–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409063111001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Cohen M. L. Comparison of plasmid profile analysis, phage typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing in characterizing Salmonella typhimurium isolates from outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):100–104. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.100-104.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. W., Samples C. L., DeSilva H. N., Ross K. A., Julian E. M., Checko P. J. An epidemic of resistant Salmonella in a nursery. Animal-to-human spread. JAMA. 1980 Feb 8;243(6):546–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Shahid N., Huq M. I., Alim A. R., Cohen M. L. Usefulness of plasmid profiles for differentiation of Shigella isolates in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):300–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.300-301.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Bied J. M., Munro J. S., Feldman R. A. Salmonella dublin infections in the United States, 1979-1980. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):322–327. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Bopp C., Birkness K., Cohen M. L. An outbreak of salmonellosis associated with a fatality in a healthy child: a large dose and severe illness. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Jun;119(6):907–912. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Wachsmuth I. K., Shangkuan Y. H., Schmidt E. V., Barrett T. J., Schrader J. S., Scherach C. S., McGee H. B., Feldman R. A., Brenner D. J. Salmonellosis associated with marijuana: a multistate outbreak traced by plasmid fingerprinting. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 27;306(21):1249–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205273062101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]