Abstract
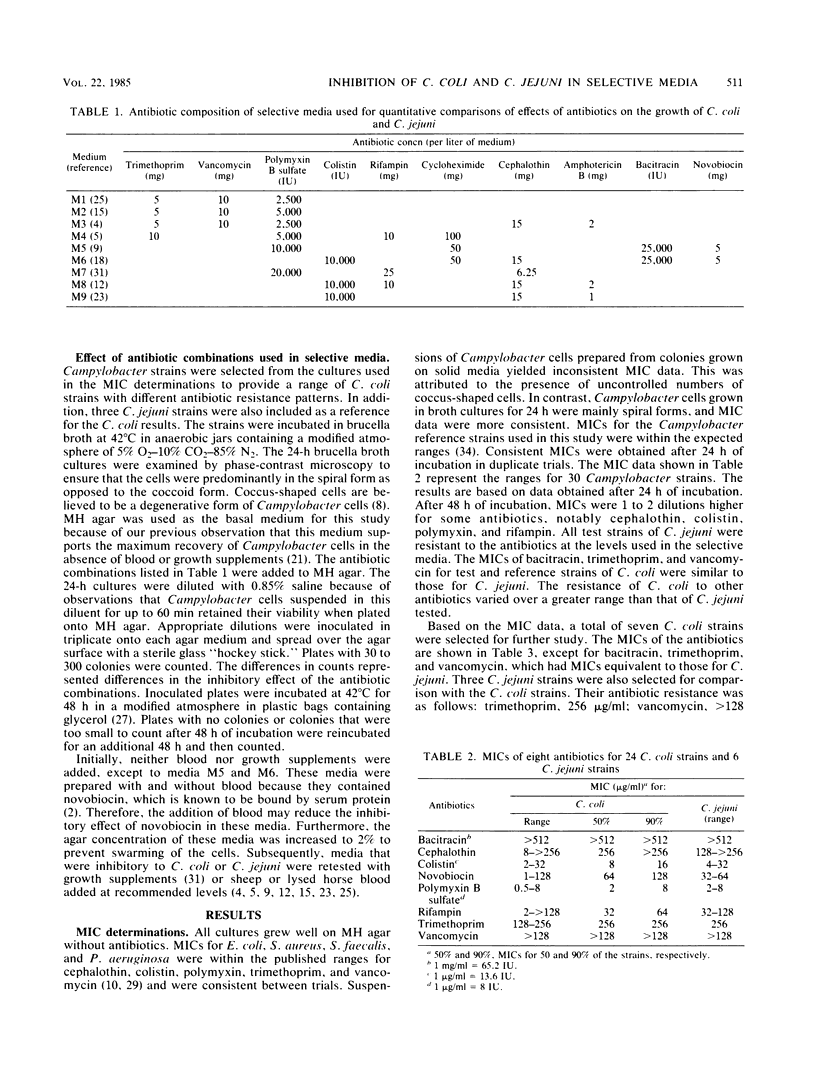
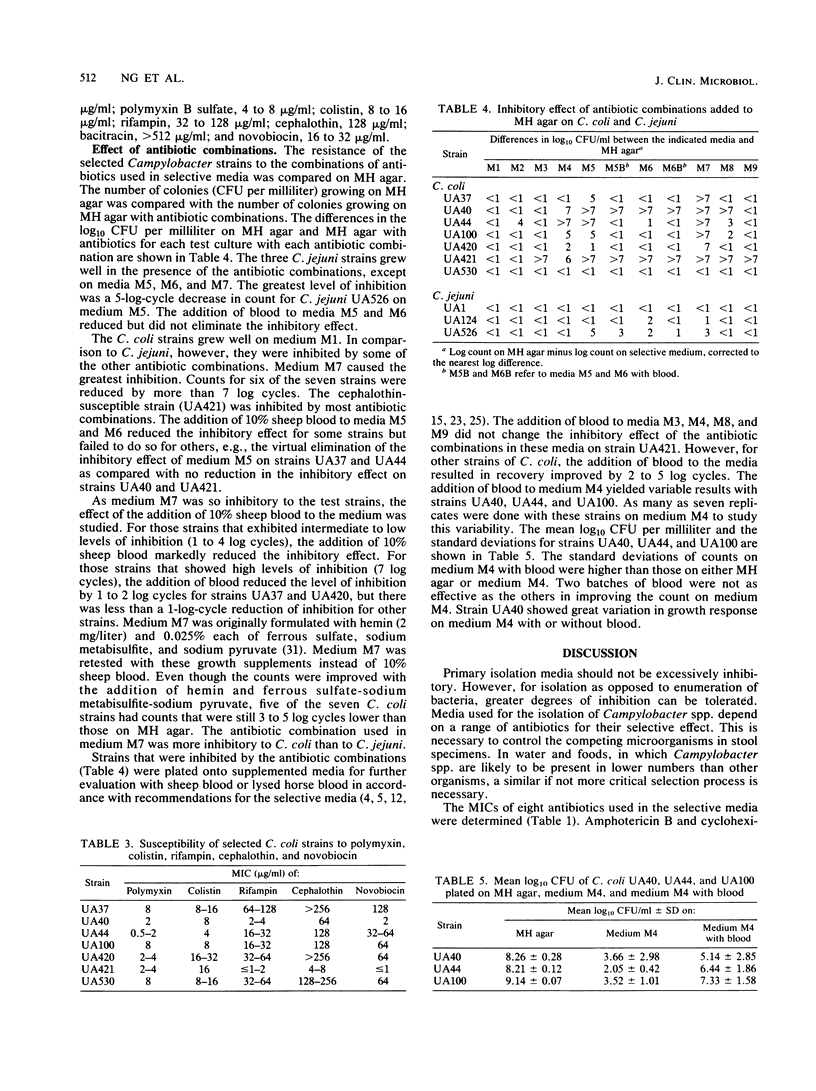
The ability of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni to grow in the presence of antibiotics used in selective growth media was compared. MIC data for C. coli indicated that some strains were more susceptible to the antibiotics than were the C. jejuni strains tested. A reduction of greater than 1 log cycle in the numbers of cells growing on plates containing antibiotics was considered to be a marked level of inhibition. Only one of nine of the antibiotic combinations studied did not markedly inhibit most of the C. coli strains tested. Although one C. coli strain was not inhibited by any of the antibiotic combinations, the other six strains were inhibited for up to 7 log cycles. The addition of blood or growth supplements reduced but did not eliminate the inhibitory effect. The inhibition of laboratory strains of C. coli on media developed for the isolation of Campylobacter spp. indicates that the incidence of C. coli may be underestimated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahonkhai V. I., Cherubin C. E., Sierra M. F., Bokkenheuser V. D., Shulman M. A., Mosenthal A. C. In vitro susceptibility of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni to N-formimidoyl thienamycin, rosaramicin, cefoperazone, and other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):850–851. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Robertson L. A selective medium for isolating Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Apr;35(4):462–467. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.4.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp C. A., Wells J. G., Barrett T. J. Trimethoprim activity in media selective for Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):808–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.808-812.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Dekeyser P., Detrain M., Dehaen F. Related vibrio in stools. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):493–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekeyser P., Gossuin-Detrain M., Butzler J. P., Sternon J. Acute enteritis due to related vibrio: first positive stool cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):390–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Ward G. E., Kurtz H. J. In vitro activities of 47 antimicrobial agents against three Campylobacter spp. from pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):55–59. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens H., De Boeck M., Butzler J. P. A new selective medium for the isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from human faeces. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;2(4):389–393. doi: 10.1007/BF02019476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., De Grandis S., Fleming P. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus to eight cephalosporins with special reference to species differentiation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):948–951. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., De Grandis S., Fleming P. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni with special reference to resistance patterns of Canadian isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):593–597. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):527–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauwers S., De Boeck M., Butzler J. P. Campylobacter enteritis in Brussels. Lancet. 1978 Mar 18;1(8064):604–605. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J., Rogol M., Dickman D. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni to sixteen antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):796–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Stiles M. E., Taylor D. E. Comparison of basal media for culturing Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):226–230. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.226-230.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringertz S., Rockhill R. C., Ringertz O. Susceptibility of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni, isolated from patients in Jakarta, Indonesia to ten antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):333–336. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosef O., Gondrosen B., Kapperud G., Underdal B. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from domestic and wild mammals in Norway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):855–859. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.855-859.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saku K., Sugimoto K., Uchiyama Y. [MIC test of Campylobacter jejuni/coli]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1983 Oct;36(10):2757–2762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoof R., Vanderlinden M. P., Dierickx R., Lauwers S., Yourassowsky E., Butzler J. P. Susceptibility of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni to twenty-nine antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):553–556. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder M. Susceptibility of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni to twenty antimicrobiol agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jul;16(1):37–39. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesley R. D., Swaminathan B., Stadelman W. J. Isolation and enumeration of Campylobacter jejuni from poultry products by a selective enrichment method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1097–1102. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1097-1102.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiffen A. J. The Production, Assay, and Antibiotic Activity of Actidione, an Antiobiotic from Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1948 Sep;56(3):283–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


