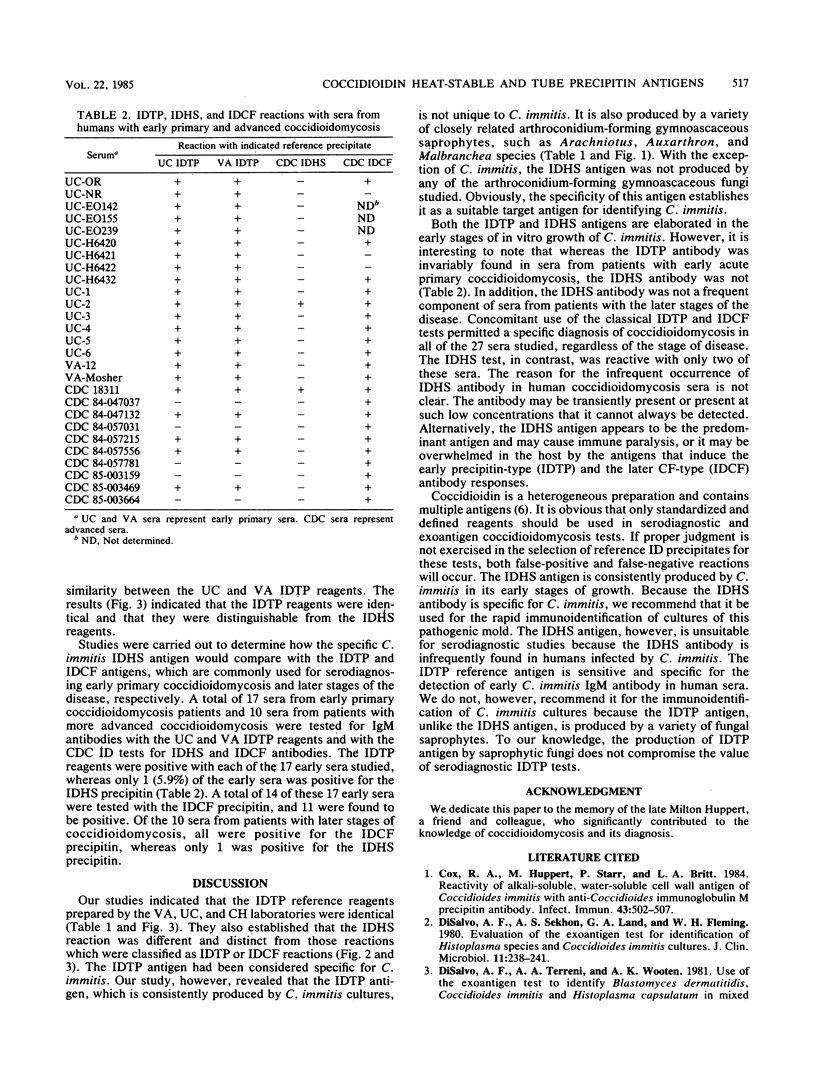
Abstract
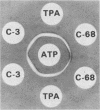
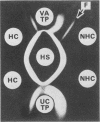
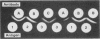
Coccidioides immitis produces two unrelated heat-stable antigens which are diagnostically useful in immunodiffusion tests. One, the tube precipitin antigen, is valuable for specifically detecting antibody and diagnosing early primary cases of coccidioidomycosis. The other heat-stable antigen, designated HS, is the most useful coccidioidin antigen for specifically immunoidentifying C. immitis cultures. Both of the antigens were compared and evaluated for their usefulness in exoantigen and serologic immunodiffusion tests. Our studies indicated that the detection of tube precipitin antigen is of limited value for immunoidentifying C. immitis isolates because the antigen is common to certain gymnoascaceous saprophytes, such as Arachniotus, Auxarthron, and Malbranchea species, that form alternate arthroconidia. Antibodies to HS antigens are infrequently found in human sera from patients with coccidioidomycosis and are thus of little serodiagnostic value.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox R. A., Huppert M., Starr P., Britt L. A. Reactivity of alkali-soluble, water-soluble cell wall antigen of Coccidioides immitis with anti-Coccidioides immunoglobulin M precipitin antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):502–507. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.502-507.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSalvo A. F., Sekhon A. S., Land G. A., Fleming W. H. Evaluation of the exoantigen test for identification of Histoplasma species and Coccidioides immitis cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.238-241.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. H., Harrell W. K., Gray S. B., Johnson J. E., Bolin R. C., Gross H., Malcolm G. B. H and M antigens of Histoplasma capsulatum: preparation of antisera and location of these antigens in yeast-phase cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):826–831. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.826-831.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Adler J. P., Rice E. H., Sun S. H. Common antigens among systemic disease fungi analyzed by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.479-485.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Sun S. H., Rice E. H. Specificity of exoantigens for identifying cultures of Coccidioides immitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):346–348. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.346-348.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. Improved version of the exoantigen test for identification of Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.42-45.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standard P. G., Kaufman L. Immunological procedure for the rapid and specific identification of Coccidioides immitis cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):149–153. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.149-153.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]