Abstract
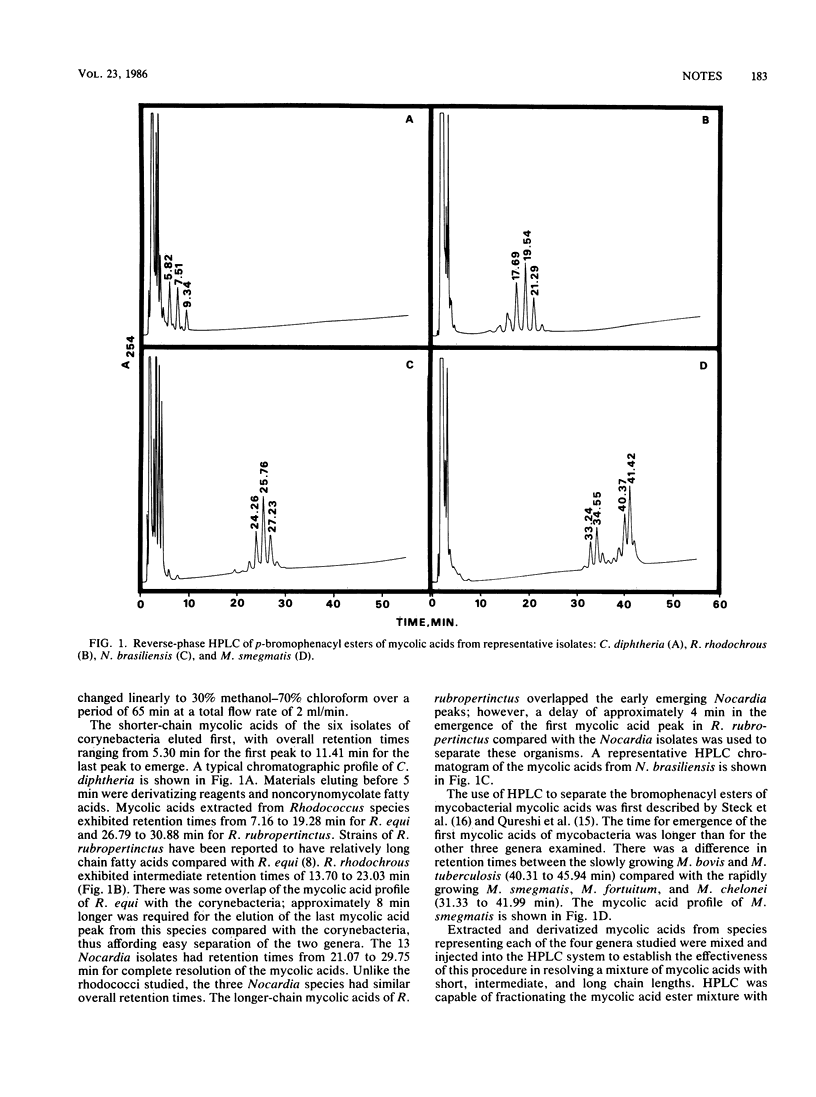
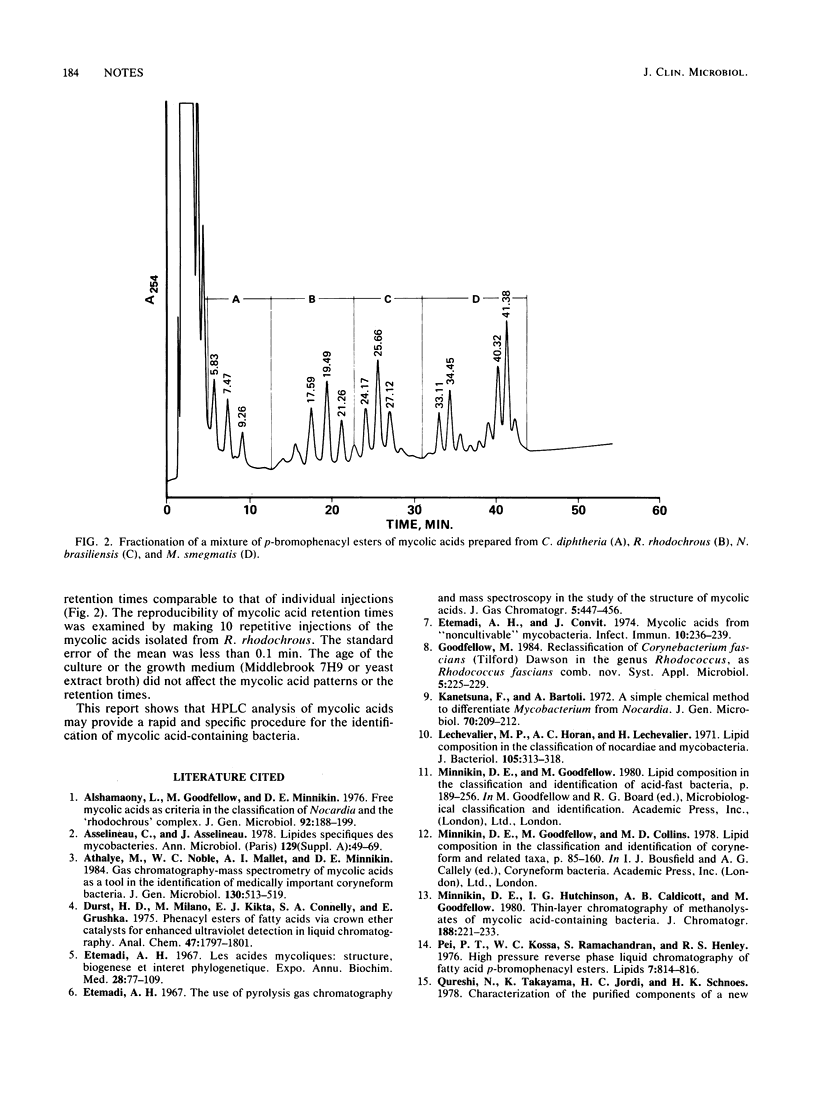
High-performance liquid chromatography of bromophenacyl esters of mycolic acid was used as an aid to assign a particular organism to one of four mycolic acid-containing genera. A gradient elution system, with methanol and chloroform, was used to distinguish representative mycolic acid patterns for the genera Corynebacterium, Rhodococcus, Nocardia, and Mycobacterium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alashamaony L., Goodfellow M., Minnikin D. E. Free mycolic acids as criteria in the classification of Nocardia and the 'rhodochrous' complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jan;92(1):188–199. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselineau C., Asselineau J. Lipids spécifiques des mycobactéries. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Jan;129(1):49–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athalye M., Noble W. C., Mallet A. I., Minnikin D. E. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of mycolic acids as a tool in the identification of medically important coryneform bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Mar;130(3):513–519. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durst H. D., Milano M., Kikta E. J., Jr, Connelly S. A., Grushka E. Phenacyl esters of fatty acids via crown ether catalysts for enhanced ultraviolet detection in liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1975 Sep;47(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1021/ac60361a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etemadi A. H., Convit J. Mycolic acids from "noncultivable" mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):236–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.236-239.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etémadi A. H. Les acides mycoliques structure, biogenèse et intérêt phylogénétique. Expos Annu Biochim Med. 1967;28:77–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanetsuna F., Bartoli A. A simple chemical method to differentiate Mycobacterium from Nocardia. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):209–212. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier M. P., Horan A. C., Lechevalier H. Lipid composition in the classification of nocardiae and mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.313-318.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnikin D. E., Goodfellow M. Lipid composition in the classification and identification of acid-fast bacteria. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1980;8:189–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei P. T., Kossa W. C., Ramachandran S., Henly R. S. High pressure reverse phase liquid chromatography of fatty acid p-bromophenacyl esters. Lipids. 1976 Nov;11(11):814–816. doi: 10.1007/BF02533409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Takayama K., Jordi H. C., Schnoes H. K. Characterization of the purified components of a new homologous series of alpha-mycolic acids from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5411–5417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck P. A., Schwartz B. A., Rosendahl M. S., Gray G. R. Mycolic acids. A reinvestigation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5625–5629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdall P. A., Roberts G. D., Anhalt J. P. Identification of clinical isolates of mycobacteria with gas-liquid chromatography alone. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):506–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.506-514.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


