Abstract
A panel of 15 monoclonal antibodies was prepared that could distinguish among the 15 serovars of Chlamydia trachomatis. Twelve of these antibodies were specific for a single serovar (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, K, L1, and L2) and three were specific for two serovars (B/Ba, C/J, and C/L3). Ten of the serovar-specific and two of the bispecific antibodies were shown by immunoblotting to recognize epitopes on the major outer membrane protein. These data provide evidence that such epitopes are closely correlated with and may be partly responsible for the antigenic variations detected by microimmunofluorescence that distinguish the currently recognized serovars. When used in a radioimmunoassay, these antibodies correctly identified the serovar of 17 strains that had been serotyped by the microimmunofluorescence test. In addition, we found that the chlamydial antigen derived from 1.0 cm2 of an infected HeLa cell monolayer was sufficient to allow serotyping with these antibodies. Thus, these monoclonal antibodies may provide a rapid and reliable alternative to mouse immunization and microimmunofluorescence for serotyping of clinical isolates.
Full text
PDF

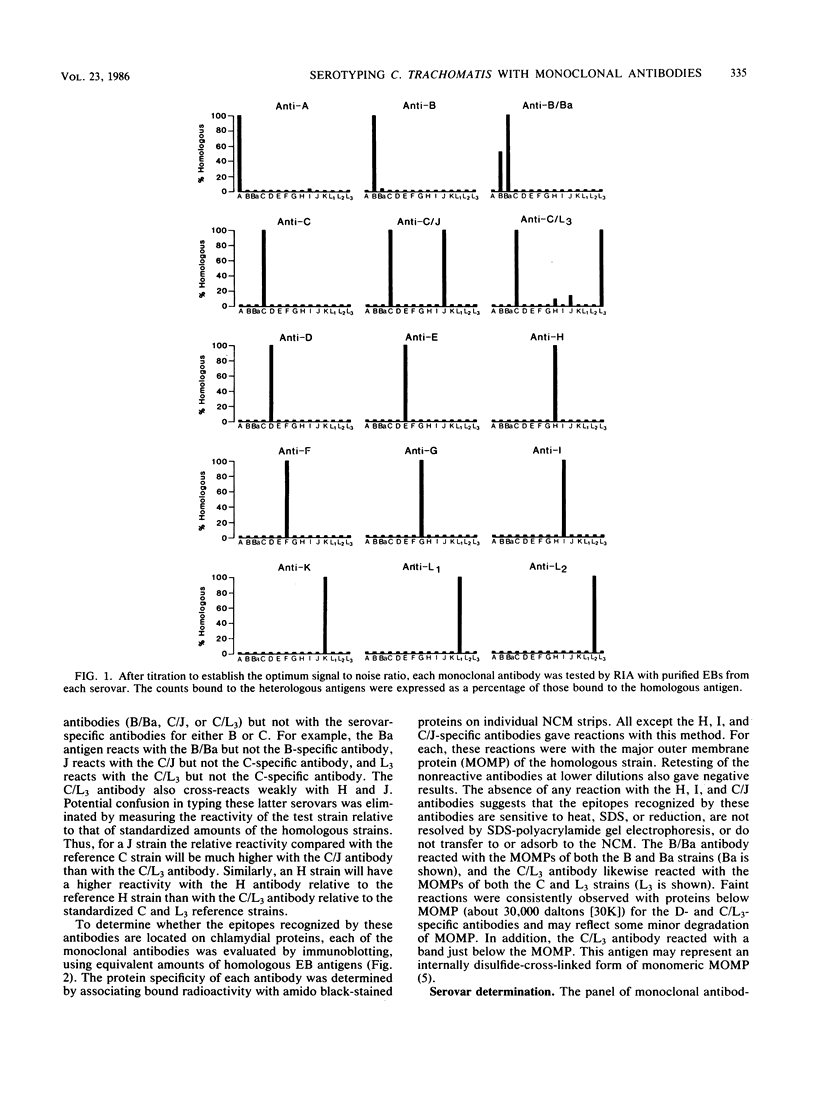

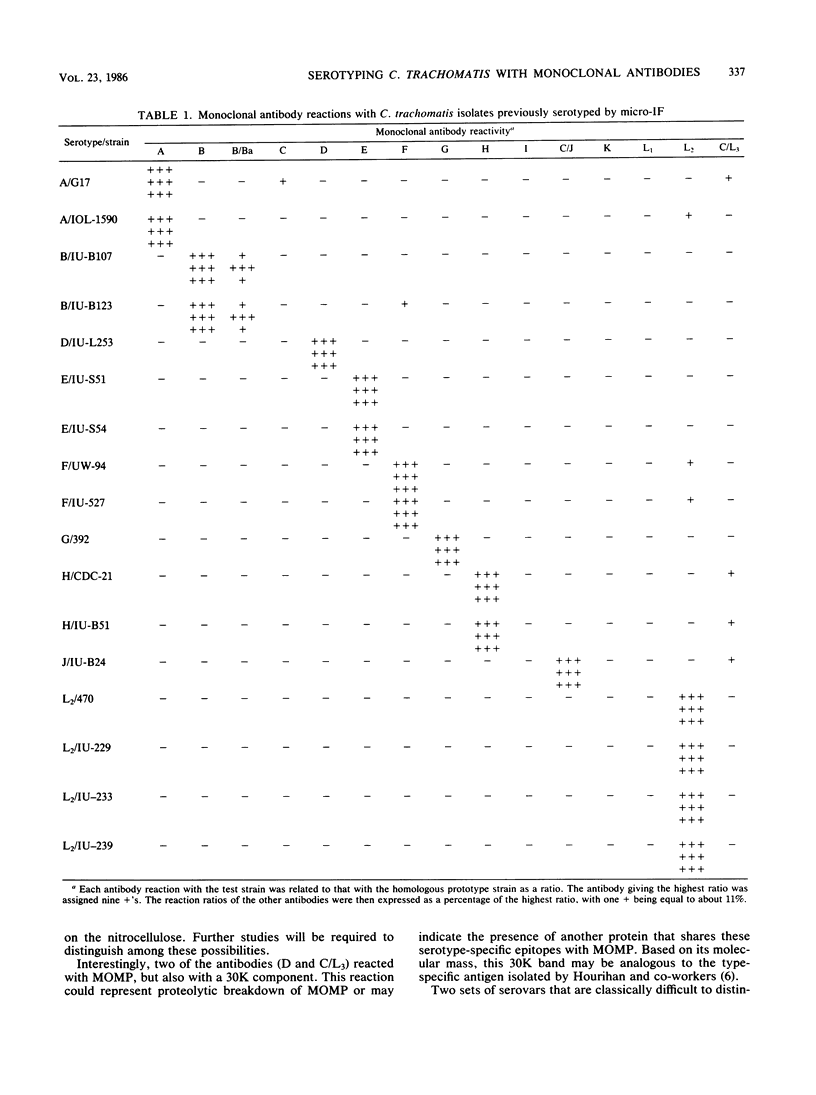

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson J. R., Hare P. E. O-phthalaldehyde: fluorogenic detection of primary amines in the picomole range. Comparison with fluorescamine and ninhydrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):619–622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Schachter J. Antigenic analysis of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia spp. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1024-1031.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Nachamkin I., Schatzki P. F., Dalton H. P. Localization of distinct surface antigens on Chlamydia trachomatis HAR-13 by immune electron microscopy with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1273–1278. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1273-1278.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Todd W. J., Caldwell H. D. Disulfide-mediated interactions of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein: role in the differentiation of chlamydiae? J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.25-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourihan J. T., Rota T. R., MacDonald A. B. Isolation and purification of a type-specific antigen from Chlamydia trachomatis propagated in cell culture utilizing molecular shift chromatography. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2399–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Holmes K. K., Grayston J. T. Immunotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis isolates in Seattle, Washington. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.865-868.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matikainen M. T., Terho P. Immunochemical analysis of antigenic determinants of Chlamydia trachomatis by monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2343–2350. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Batteiger B., Jones R. B. Analysis of the human serological response to proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1181-1189.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Kuo C. C., Newport G., Agabian N. Molecular cloning and expression of Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):713–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.713-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Tam M. R., Kuo C. C., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis: antibody specificities and antigen characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. A simplified method for immunological typing of trachoma-inclusion conjunctivitis-lymphogranuloma venereum organisms. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):356–360. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.356-360.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



