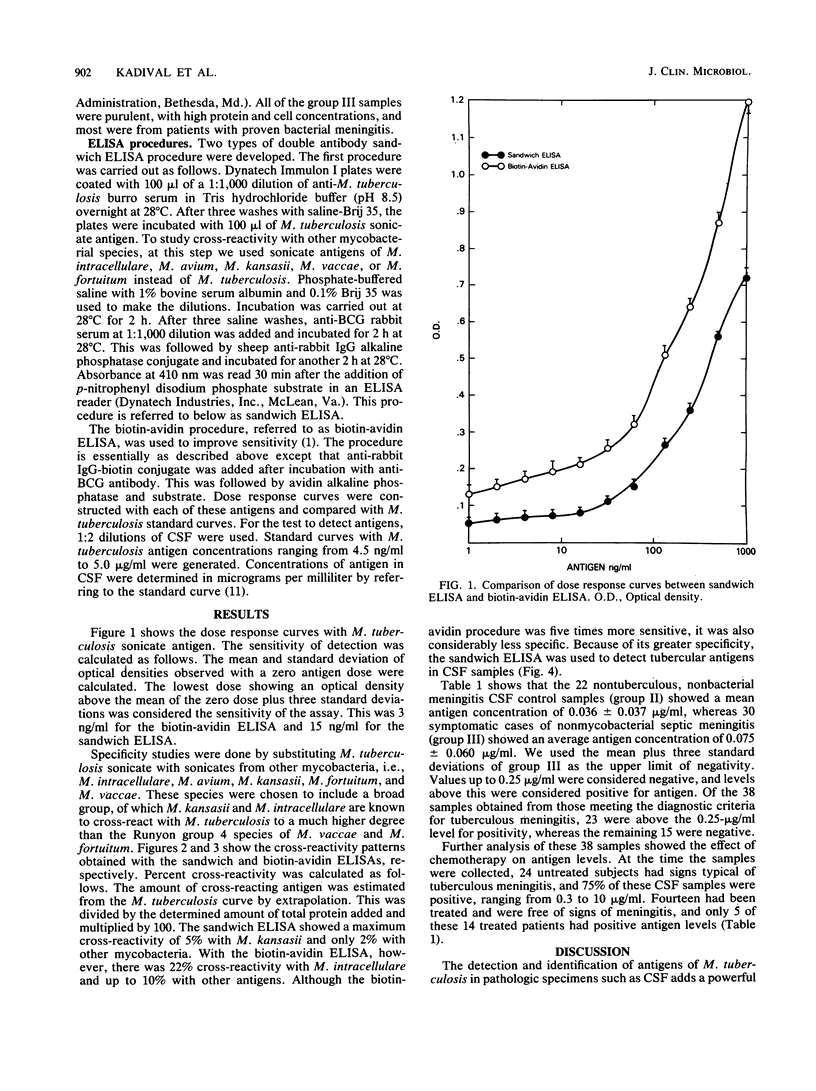
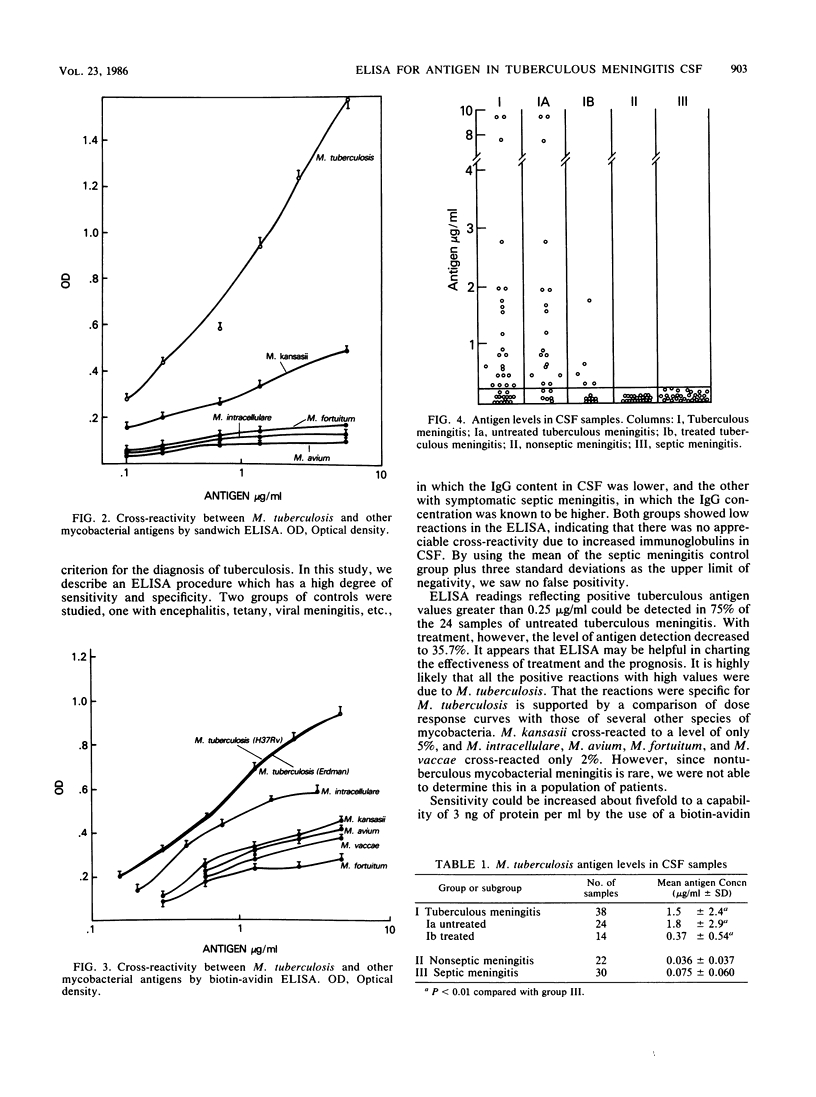
Abstract
A sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed for its potential utility in the detection of antigen in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tuberculous meningitis. Cerebrospinal fluids examined included those from untreated (group Ia) and treated (group Ib) Mycobacterium tuberculosis meningitis, nonseptic central nervous conditions (group II) such as epilepsy, viral meningitis, and tetany, and nonmycobacterial septic meningitis (group III). The average levels of antigens determined and percent positive specimens, respectively, for each group were (group): Ia, 1.8 micrograms/ml and 75% positive; Ib, 0.37 microgram/ml and 36% positive; II, 0.036 microgram/ml and 100% negative; and III, 0.075 microgram/ml and 100% negative. The system developed employed hyperimmune polyclonal antibody raised against M. tuberculosis and Mycobacterium bovis BCG in burros and rabbits. Cross-reactivity by other mycobacterial species was very low; e.g., 5% for M. kansasii and less than 2% for M. intracellulare, M. avium, M. vaccae, and M. fortuitum. The test shows promise as a specific adjunct for the early diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaparas S. D., Brown T. M., Hyman I. S. Antigenic relationships of various mycobacterial species with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jun;117(6):1091–1097. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.6.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel A. M., Kadival G. V., Ashtekar M. D., Ganatra R. D. Evaluation of tubercular antigen & antitubercular antibodies in pleural & ascitic effusions. Indian J Med Res. 1984 Nov;80:563–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel A. M., Kadival G. V., Irani S., Pandya S. K., Ganatra R. D. A sensitive and specific method for diagnosis of tubercular meningitis. Indian J Med Res. 1983 May;77:752–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


