Abstract
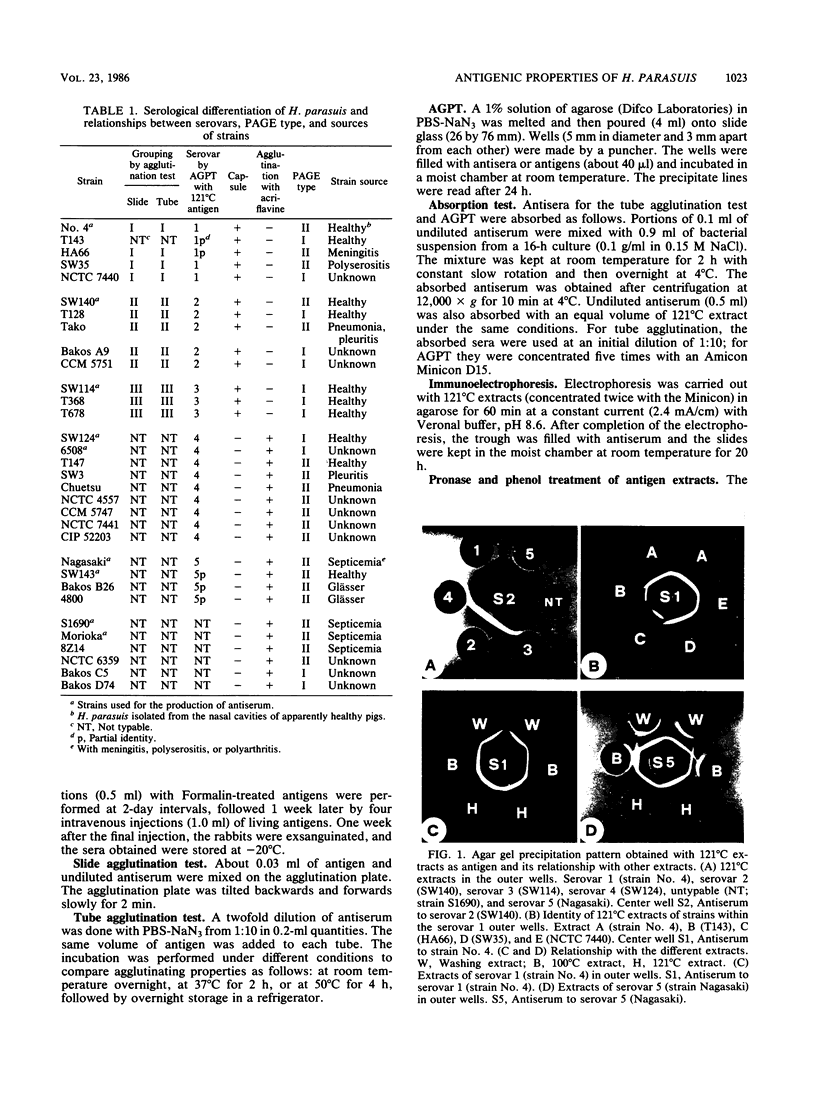
We propose a serological classification of Haemophilus parasuis into at least five serovars, using an agar-gel-precipitation test with extracts from autoclaved cells. Thirty-two strains were examined, and it was possible to classify 26 of them. The specific antigens were thermostable and soluble and were not affected by pronase treatment but could be extracted by phenol, suggesting a polysaccharide. This polysaccharide seemed to be identical with the capsular substance of serovars 1, 2, and 3. In the presumably uncapsulated strains of serovars 4 and 5, the specific antigen was probably located in the outer membrane. The diversity of the specific substance within the different serotypes was shown by the differences in their electrophoretic migration patterns. Other extraction procedures showed that the washing supernatant and extracts at 60 and 100 degrees C were identical with the 121 degrees C extracts for serovars 1, 2, and 3. In serovars 4 and 5, washing antigens, if present, were different from 100 and 121 degrees C extracts. Other common antigens, presumably proteinaceous antigens, were detected after extraction at 60 and 100 degrees C. The slide and tube agglutination tests allowed classification only for the capsulated strains of serovars 1, 2, and 3. The specific agglutinogens were very sensitive to incubation temperature, and the absorption test showed them to be identical with the 121 degrees C precipitinogens.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biberstein E. L., White D. C. A proposal for the establishment of two new Haemophilus species. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Feb;2(1):75–78. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler C. A., Fothergill L. D., Dingle J. H. The Pattern of Dissociation in Hemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1939 Apr;37(4):415–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.37.4.415-427.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi T., Hiramune T., Kobayashi K. Glässer's disease in piglets produced by intraperitoneal inoculation with Haemophilus parasuis. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1981 Fall;21(3):121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi T., Nicolet J. Morphological variations of Haemophilus parasuis strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):138–142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.138-142.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J. Sur l'hémophilose du pore. 3. Différenciation sérologique de Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(4):487–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]