Abstract
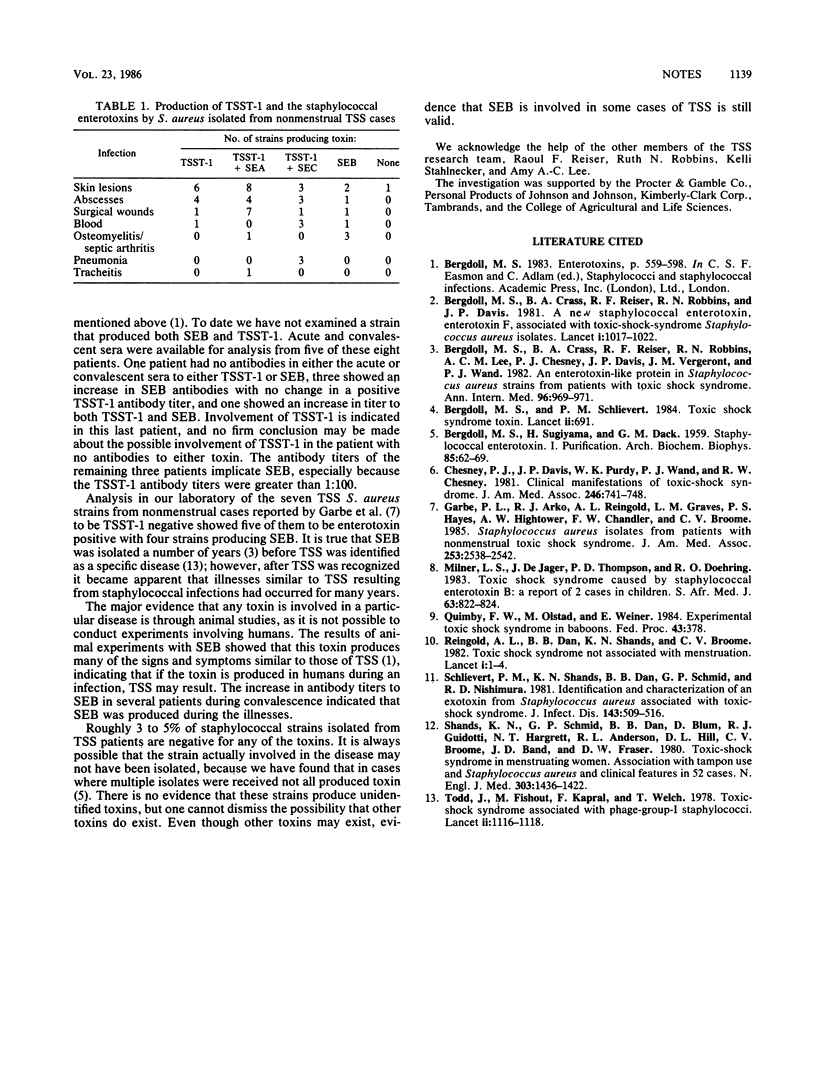
Adequate evidence is available to show that the major toxin responsible for toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is TSS toxin 1 (TSST-1). More than 90% of the staphylococcal strains isolated from TSS patients produce this toxin. However, approximately 60% of these strains produce one or more of the staphylococcal enterotoxins, with a number of them producing only enterotoxin, primarily enterotoxin B. Of 55 staphylococcal strains isolated from nonmenstrual cases, 46 produced TSST-1; 42 produced one of the enterotoxins, including 8 that produced only enterotoxin B. The fact that the enterotoxins can produce in monkeys many signs and symptoms similar to those observed in TSS in humans implicates them as the cause of some cases of TSS.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGDOLL M. S., SUGIYAMA H., DACK G. M. Staphylococcal enterotoxin. I. Purification. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Nov;85:62–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Lee A. C., Chesney P. J., Davis J. P., Vergeront J. M., Wand P. J. An enterotoxin-like protein in Staphylococcus aureus strains from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):969–971. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney P. J., Davis J. P., Purdy W. K., Wand P. J., Chesney R. W. Clinical manifestations of toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1981 Aug 14;246(7):741–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe P. L., Arko R. J., Reingold A. L., Graves L. M., Hayes P. S., Hightower A. W., Chandler F. W., Broome C. V. Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. Evidence for additional toxins. JAMA. 1985 May 3;253(17):2538–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner L. S., de Jager J., Thomson P. D., Doehring R. O. Toxic shock syndrome caused by staphylococcal enterotoxin B. A report of 2 cases in children. S Afr Med J. 1983 May 21;63(21):822–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Broome C. V. Toxic-shock syndrome not associated with menstruation. A review of 54 cases. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


