Abstract
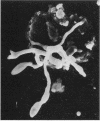
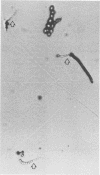
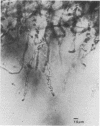
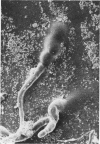
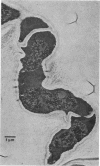
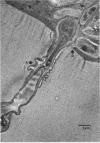
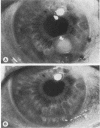
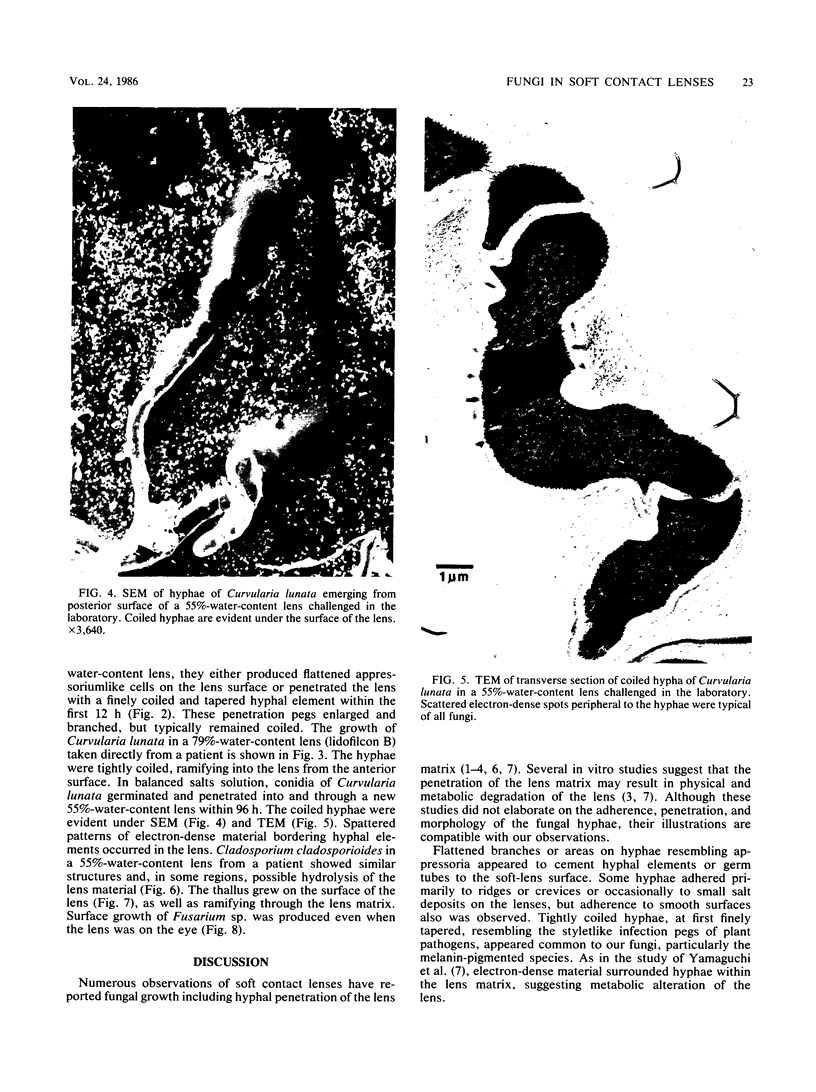
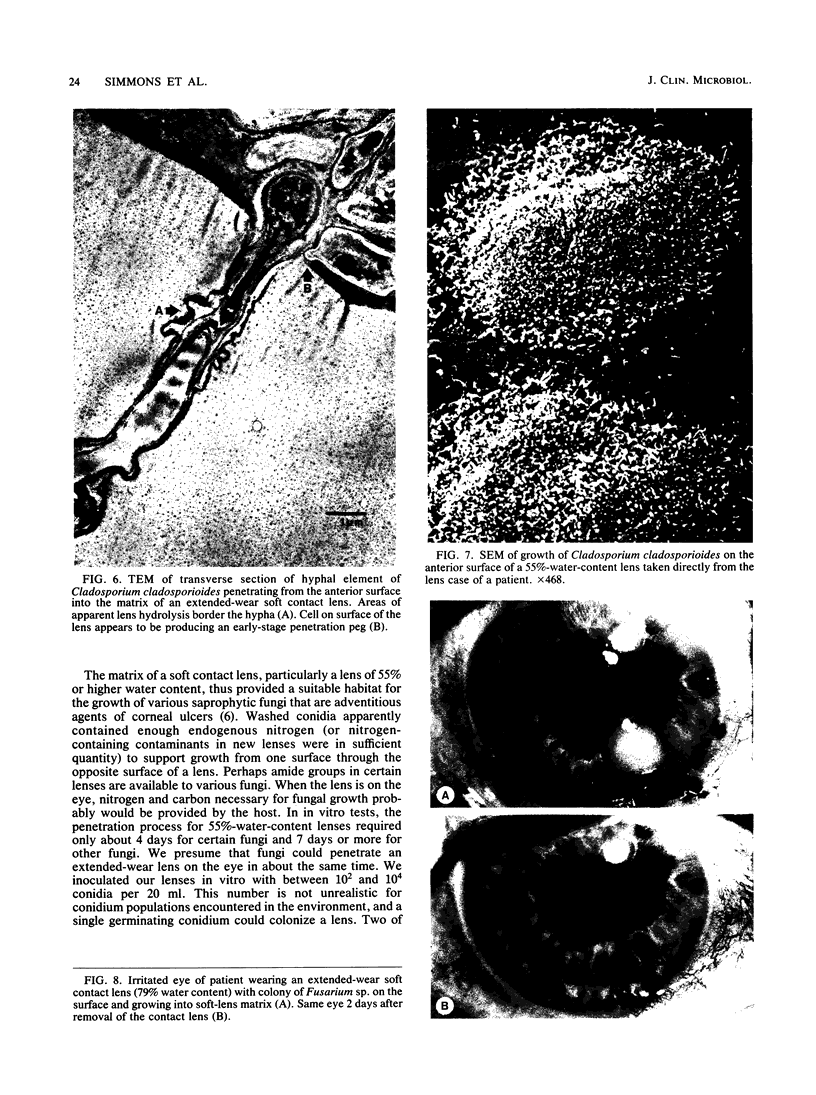
Filamentous fungi of the genera Acremonium, Aspergillus, Alternaria, Cladosporium, Curvularia, and Fusarium penetrated the matrix of soft contact lenses both during normal usage and in laboratory studies. Growth of the fungi within the lens matrix increased with increasing water content of the lens. Hyphae within the lens were coiled. Some species penetrated completely through the lens within 96 h. More frequent cleaning and disinfection of extended-wear soft contact lenses is recommended.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger R. O., Streeten B. W. Fungal growth in aphakic soft contact lenses. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981 May;91(5):630–633. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer V., Jensen O. A., Prause J. U. Morphological, histochemical and X-ray microanalytical examination of deposits on soft contact lenses in extended wearing. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1979 Oct;57(5):847–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1979.tb01852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filppi J. A., Pfister R. M., Hill R. M. Penetration of hydrophilic contact lenses by Aspergillus fumagatus. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom. 1973 Jul;50(7):553–557. doi: 10.1097/00006324-197307000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A., Ahearn D. G. Association of fungi with extended-wear soft contact lenses. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986 Apr 15;101(4):434–436. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(86)90642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi T., Hubbard A., Fukushima A., Kimura T., Kaufman H. E. Fungus growth on soft contact lenses with different water contents. CLAO J. 1984 Apr-Jun;10(2):166–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]