Abstract
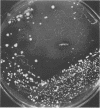
Two cases of unsuspected Strongyloides stercoralis infection were elucidated by the displacement of bacterial colonies on primary plating media. Observation of primary plates inoculated for the diagnosis of bacterial pneumonia or gastroenteritis revealed that normal flora colonies had been moved and were aligned in a pathway, or track. This unusual colony alignment prompted us to request a stool for the examination of parasites, and S. stercoralis was found. It was concluded that the parasite is capable of motility on agar surfaces, resulting in the displacement of bacterial colonies that make up the normal flora.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Harris R. A., Jr, Musher D. M., Fainstein V., Young E. J., Clarridge J. Disseminated strongyloidiasis. Diagnosis made by sputum examination. JAMA. 1980 Jul 4;244(1):65–66. doi: 10.1001/jama.244.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igra-Siegman Y., Kapila R., Sen P., Kaminski Z. C., Louria D. B. Syndrome of hyperinfection with Strongyloides stercoralis. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):397–407. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieterse A. S., Blumbergs P. Test and teach. Number forty-four. Diagnosis: strongyloidiasis. Pathology. 1983 Oct;15(4):366-7, 506-7. doi: 10.3109/00313028309085160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Meyers W. M., Connor D. H. Fatal strongyloidiasis in immunosuppressed patients. Am J Med. 1974 Apr;56(4):488–493. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter R. M., Burke A. M., MacGregor R. R. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection masquerading as cerebral vasculitis. Arch Neurol. 1984 Nov;41(11):1213–1216. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050220115030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]