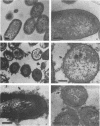
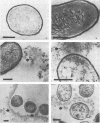
Abstract
We tested nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from cystic fibrosis (CF) patients for the expression of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) serotype antigens, serum sensitivity, and production of mucoid exopolysaccharide (MEP). When all nonmucoid isolates were compared with a set of random mucoid isolates, 20 of 52 (38%) nonmucoid isolates were typable and serum resistant, compared with 13 of 51 (24%) mucoid isolates (P = 0.16 by chi-square analysis). However, nonmucoid strains from CF patients colonized only with nonmucoid strains were more frequently typable and serum resistant (67%) than were nonmucoid isolates from patients cocolonized with mucoid strains (31%) (P = 0.012, Fisher exact test). An inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay done with bacterial extracts, a direct-whole-cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay done with affinity-purified antibody to MEP, and immune electron microscopy all demonstrated production of MEP by all nonmucoid P. aeruginosa isolates tested, including nonmucoid revertants of mucoid strains. No other bacterial species tested positive in these assays. These findings suggest that MEP is produced by all P. aeruginosa isolates obtained from CF patients, that the initial colonizing nonmucoid strains produce a smooth LPS, and that once LPS-rough, mucoid strains appear in the sputum, the predominant LPS phenotype is rough regardless of colony morphology.
Full text
PDF


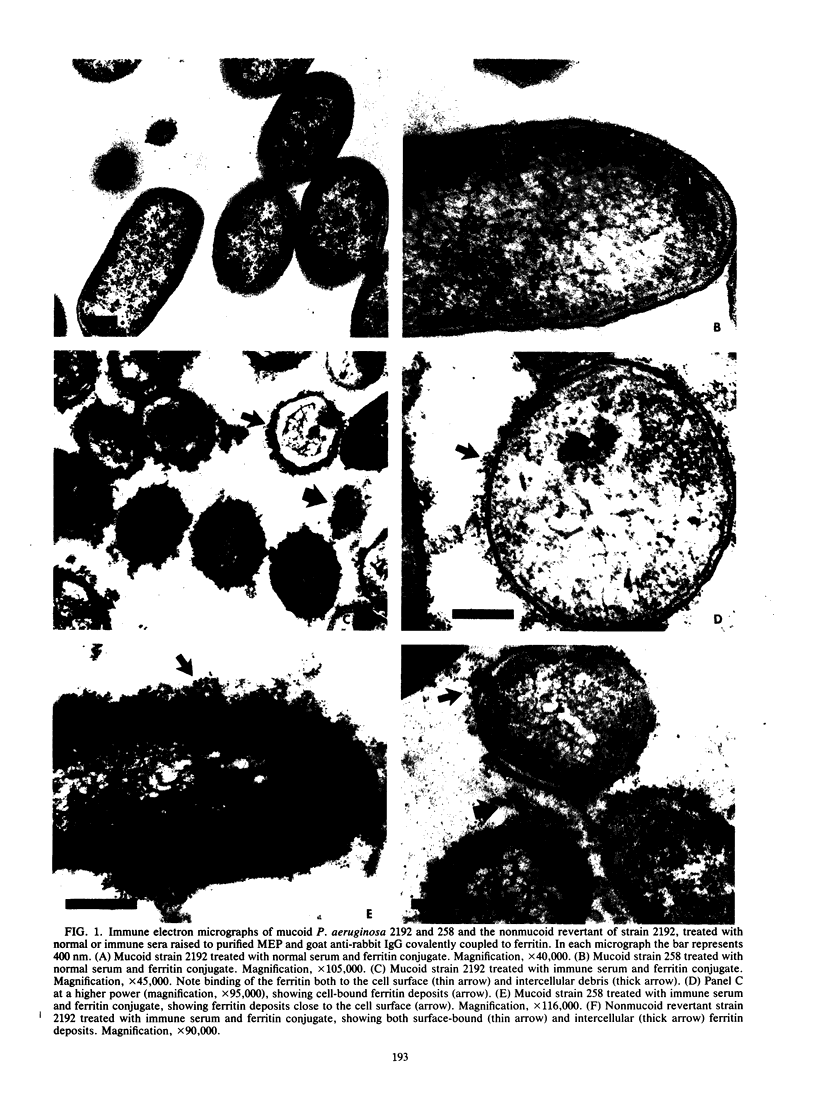



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames P., DesJardins D., Pier G. B. Opsonophagocytic killing activity of rabbit antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):281–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.281-285.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergan T., Hoiby N. Epidemiological markers for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 6. Relationship between concomitant non-mucoid and mucoid strains from the respiratory tract in cystic fibrosis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1975 Dec;83(6):553–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski R. S., Stock L. M., Schiller N. L. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for studying Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell surface antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):736–741. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.736-741.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kureishi A., Rabin H. R. Detection of antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate extracellular polysaccharide in animals and cystic fibrosis patients by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):276–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.276-282.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. B., di Sant'Agnese P. A. Diagnosis and treatment of cystic fibrosis. An update. Chest. 1984 Jun;85(6):802–809. doi: 10.1016/s0012-3692(16)62421-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Wheeler R., Montie T. C. Flagellar preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: animal protection studies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):276–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.276-280.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Rosendal K. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients treated at a cystic fibrosis centre. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson C. A., Jeanes A. A new modification of the carbazole analysis: application to heteropolysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1968 Sep;24(3):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford D. T., Hiller J. Prospective, controlled study of a polyvalent pseudomonas vaccine in cystic fibrosis--three year results. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Dec;59(12):1131–1134. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.12.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., McVeigh T., Owen P. Immunochemical and biochemical analysis of the polyvalent Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine PEV. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):675–686. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.675-686.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Sastry P. A., Drake D., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B. Pseudomonas pili. Studies on antigenic determinants and mammalian cell receptors. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A., Pitt T., Roberts D., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. The relationship of phenotype changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the clinical condition of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):605–608. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Hickey W. F., Blackwood L. L., Arnaut M. A. Active immunization with lipopolysaccharide Pseudomonas antigen for chronic Pseudomonas bronchopneumonia in guinea pigs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1140–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI110358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Matthews W. J., Jr, Eardley D. D. Immunochemical characterization of the mucoid exopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):494–503. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa surface polysaccharide vaccines. New therapeutic approaches from basic research. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Thomas D. M. Lipopolysaccharide and high-molecular-weight polysaccharide serotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):217–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Sadoff J. C., Pyle M., Silipigni J. D. Role of pili in the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to injured tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.38-40.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Kazmierowski J. A., Newball H. H. Specificity of opsonic antibodies to enhance phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):376–385. doi: 10.1172/JCI108102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale T. W., Thirkill H., Tarpay M., Flux M., Rennert O. M. Serotypes and antibiotic susceptibilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from single sputa of cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.72-78.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Bryan L. E. Studies on the ability of alginate to act as a protective immunogen against infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in animals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):581–588. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Sant'agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Cystic fibrosis in adults. 75 cases and a review of 232 cases in the literature. Am J Med. 1979 Jan;66(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90491-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]